ACCA所有科目都考完了,还需要缴纳年费吗?
发布时间:2020-03-29
在ACCA考试政策当中,我们报考ACCA需要缴纳的费用总共有以下几种:首次注册费/年费/考试报名费及教材费。有小伙伴问,ACCA都考完了还需要交年费吗?我们先看看下面的内容吧!
ACCA资格是现下大学校园中比较流行的一大选择,很多高校都逐渐开始了ACCA方向班,以培养学生的实践工作能力和未来的职业竞争力。不过,让很多人头疼的一大问题就是考试成本高。那么,考完ACCA大概需要花费多少钱呢?我们一起来了解一下吧!
首次注册费:根据ACCA官方公布的最新收费标准来看,ACCA学员的首次注册费为79英镑,缴费的具体数字会随着汇率的变化而变化,一般情况下约为700元人民币。
年费:ACCA年费是自学员报考ACCA证书的当年起就要缴纳的费用,每一自然年要缴纳一次。ACCA学员的年费为112英镑,且是全球统一的收费标准。ACCA年费折合成人民币,大约1000多元。
各科考试费:ACCA各科考试费,也采用了统一的标准,但是会根据不同的考试阶段而所有不同。按照提前报名时段计算的情况下,学员需要承担的考试费用约为:114*5+188+247*3=1199+,这样下来,所缴纳的ACCA各科考试费大约需要人民币一万五千元。
教材费:ACCA各科目都有对应的教材和练习册,平均下来每本约为300元人民币,13科目下来约为4000元。
随着ACCA在国际上的地位越来越高,就业前景越来越好,大多数的财务人事、金融行业的人员都是对ACCA充满了较大的兴趣,越来越多的人选择了学习ACCA,考取这个被人民日报称作高新证书的ACCA。虽然考试成本高昂,不过它所带来的就业优势却是远高于此的。
原则上来说,从你成为ACCA学员的那一刻起每年就要缴纳,而且考完以后成为准会员和以后申请成为会员所要交的年费比ACCA学员交的要更多。需要提醒大家的是即便成为ACCA会员也要终身缴纳,除非你退出ACCA协会。在这里建议大家还是继续交纳年费比较好。首先,如果不交年费,ACCA学员/准会员/会员的头衔就会被取消,可能有些同学会觉得,反正我ACCA学完了,本事都学到了,ACCA头衔对我来说可有可无,有这种想法是不对的。因为ACCA头衔带给大家的并不仅仅只是表面上的一张证书,ACCA官方会定期组织各种活动,能够获得与财会界许多同行一起交流的机会,这也是财会人拓宽自己视野和交际比较好的机会。在成为ACCA会员 5年以后还可以申请成为ACCA资深会员,即FCCA,为了年费失去这样的机会真的是得不偿失。
好了,看了上面的内容,相信大家对报考ACCA的年费的相关内容有了一定的了解。即便ACCA所有科目都考完了,年费还是要交的,不然会影响ACCA会员的头衔。如果还想了解更多信息,欢迎来51题库考试学习网留言哦!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
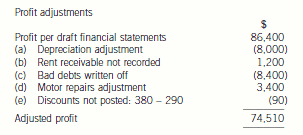
2 The draft financial statements of Choctaw, a limited liability company, for the year ended 31 December 2004 showed
a profit of $86,400. The trial balance did not balance, and a suspense account with a credit balance of $3,310 was
included in the balance sheet.
In subsequent checking the following errors were found:
(a) Depreciation of motor vehicles at 25 per cent was calculated for the year ended 31 December 2004 on the
reducing balance basis, and should have been calculated on the straight-line basis at 25 per cent.
Relevant figures:
Cost of motor vehicles $120,000, net book value at 1 January 2004, $88,000
(b) Rent received from subletting part of the office accommodation $1,200 had been put into the petty cash box.
No receivable balance had been recognised when the rent fell due and no entries had been made in the petty
cash book or elsewhere for it. The petty cash float in the trial balance is the amount according to the records,
which is $1,200 less than the actual balance in the box.
(c) Bad debts totalling $8,400 are to be written off.
(d) The opening accrual on the motor repairs account of $3,400, representing repair bills due but not paid at
31 December 2003, had not been brought down at 1 January 2004.
(e) The cash discount totals for December 2004 had not been posted to the discount accounts in the nominal ledger.
The figures were:
$
Discount allowed 380
Discount received 290
After the necessary entries, the suspense account balanced.
Required:
Prepare journal entries, with narratives, to correct the errors found, and prepare a statement showing the
necessary adjustments to the profit.
(10 marks)

5 GE Railways plc (GER) operates a passenger train service in Holtland. The directors have always focused solely on
the use of traditional financial measures in order to assess the performance of GER since it commenced operations
in 1992. The Managing Director of GER has asked you, as a management accountant, for assistance with regard to
the adoption of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement within GER.
Required:
(a) Prepare a memorandum explaining the potential benefits and limitations that may arise from the adoption of
a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement within GER. (8 marks)
(a) To: Board of directors
From: Management Accountant
Date: 8 June 2007
The potential benefits of the adoption of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement within GER are as
follows:
A broader business perspective
Financial measures invariably have an inward-looking perspective. The balanced scorecard is wider in its scope and
application. It has an external focus and looks at comparisons with competitors in order to establish what constitutes best
practice and ensures that required changes are made in order to achieve it. The use of the balanced scorecard requires a
balance of both financial and non-financial measures and goals.
A greater strategic focus
The use of the balanced scorecard focuses to a much greater extent on the longer term. There is a far greater emphasis on
strategic considerations. It attempts to identify the needs and wants of customers and the new products and markets. Hence
it requires a balance between short term and long term performance measures.
A greater focus on qualitative aspects
The use of the balanced scorecard attempts to overcome the over-emphasis of traditional measures on the quantifiable aspects
of the internal operations of an organisation expressed in purely financial terms. Its use requires a balance between
quantitative and qualitative performance measures. For example, customer satisfaction is a qualitative performance measure
which is given prominence under the balanced scorecard approach.
A greater focus on longer term performance
The use of traditional financial measures is often dominated by financial accounting requirements, for example, the need to
show fixed assets at their historic cost. Also, they are primarily focused on short-term profitability and return on capital
employed in order to gain stakeholder approval of short term financial reports, the longer term or whole life cycle often being
ignored.
The limitations of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement may be viewed as follows:
The balanced scorecard attempts to identify the chain of cause and effect relationships which will provide the stimulus for
the future success of an organisation.
Advocates of a balanced scorecard approach to performance measurement suggest that it can constitute a vital component
of the strategic management process.
However, Robert Kaplan and David Norton, the authors of the balanced scorecard concept concede that it may not be suitable
for all firms. Norton suggests that it is most suitable for firms which have a long lead time between management action and
financial benefit and that it will be less suitable for firms with a short-term focus. However, other flaws can be detected in
the balanced scorecard.
The balanced scorecard promises to outline the theory of the firm by clearly linking the driver/outcome measures in a cause
and effect chain, but this will be difficult if not impossible to achieve.
The precise cause and effect relationships between measures for each of the perspectives on the balanced scorecard will be
complex because the driver and outcome measures for the various perspectives are interlinked. For example, customer
satisfaction may be seen to be a function of several drivers, such as employee satisfaction, manufacturing cycle time and
quality. However, employee satisfaction may in turn be partially driven by customer satisfaction and employee satisfaction
may partially drive manufacturing cycle time. A consequence of this non-linearity of the cause and effect chain (i.e., there is
non-linear relationship between an individual driver and a single outcome measure), is that there must be a question mark
as to the accuracy of any calculated correlations between driver and outcome measures. Allied to this point, any calculated
correlations will be historic. This implies that it will only be possible to determine the accuracy of cause and effect linkages
after the event, which could make the use of the balanced scorecard in dynamic industries questionable. If the market is
undergoing rapid evolution, for example, how meaningful are current measures of customer satisfaction or market share?
These criticisms do not necessarily undermine the usefulness of the balanced scorecard in presenting a more comprehensive
picture of organisational performance but they do raise doubts concerning claims that a balanced scorecard can be
constructed which will outline a clear cause and effect chain between driver and outcome measures and the firm’s financial
objectives.
18 How should interest charged on partners’ drawings appear in partnership financial statements?
A As income in the income statement
B Added to net profit and charged to partners in the division of profit
C Deducted from net profit and charged to partners in the division of profit
D Deducted from net profit in the division of profit and credited to partners
(c) Increasing the revaluation reserve to $300,000 by revaluing goodwill from $800,000 to $1,000,000.
(1 mark)
(c) IFRS 3 Business combinations does not allow goodwill to be revalued upwards.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-05-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-03-08
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-04-25
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-01-05
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-03-06
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-03-04
- 2021-06-19
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-01-10