北京市考生注意:最新ACCA考试新增题型和题型分析
发布时间:2020-01-10
随着国家相关政策的发布和改革,备受大家关注的ACCA考试也在近些年悄悄地发生着变化,尤其是考试题型的部分,这一部分51题库考试学习网建议各位备考ACCA的同学们提前了解一下,以此来有目的性地复习各科考试科目。那到底发生了怎么样的变化呢?且随51题库考试学习网一起了解了解:
首先就是在ACCA F阶段的一些新题型:
|
ACCA考试科目 |
考试题型 |
|
F5 F7 F9 |
15 x 2 mark 客观题 3 x 10 mark 案例客观题 2 x 20 mark 主观题 |
|
F6 (UK) |
15 x 2 mark 客观题 3 x 10 mark 案例客观题 1 x 10 mark 主观题 2 x 15 mark 主观题 |
|
F8 |
3 x 10 mark 案例客观题
1 x 30 mark 主观题 |
ACCA 机考题型介绍(主要是F阶段)
(一)客观题(Objective test questions/ OT questions)客观题是指这些单一的,题干较短的,并且自动判分的题目。每道客观题的分值为2分,考生必须回答的完全正确才可以得分,即使回答正确一部分,也不能得到分数。所以,考生要认真仔细的看问题,不要马虎大意
(二)案例客观题 (OT case questions)
案例客观题是ACCA引入的新题型,每道案例客观题都是由一组与一个案例相关的客观题组成的,因此要求考生从多个角度来思考一个案例。这种题型能很好的反映出考生将如何在实践中完成这些任务。
(三) 主观题 (Constructed response questions/ CR qustions)考生将使用电子表格程序和文字处理程序去完成主观题的回答。就像笔试中的主观题一样,答案最终将由专家判分。
以上就是ACCA考试F阶段的关于考试题型的介绍,如果你已经通过了F阶段的所有考试科目,那么下面对P阶段的题型分析建议你可以好好浏览~和F阶段相比,P阶段需要你付出的更多,需要更加加倍的努力才可以通过,因此备考的各位千万不要松懈~
ACCA P阶段题型分析
P1考试题型构成
Section A: 1 compulsory case study * 50 Marks;
Section B: Choice of 2 from 3 questions * (25 marks each)
Section A will be a compulsory case study question with typically four or five sub-requirements relating to the same scenario information. The question will usually assess and link a range of subject areas acrossthe syllabus. It will require students to demonstrate high-level capabilities to understand the complexities of the case and evaluate, relate and apply the information in the case study to the requirements.
Section B questions are more likely to assess a range of discrete subject areas from the main syllabus section headings. They may require evaluation and synthesis of information contained within short scenarios and application of this information to the question requirements.
ACCA P2考试题型构成
Section A will consist of one scenario based question worth 50 marks. It will deal with the preparation of consolidated financial statements including group statements of cash flows and with issues in financial reporting. A written part normally covering a particular accounting treatment and ethical and social issues in financial reporting.
Students will be required to answer two out of three questions in Section B, which will normally comprise two questions which will be scenario or case-study based and one essay question which may have some computational element. Section B could deal with any aspects of the syllabus. New accounting standards will feature prominently in this section on initial introduction.
ACCA P3考试题型构成
Section A: 1 compulsory case study * 50 Marks;
Section B: Choice of 2 from 3 questions * (25 marks each)
Section A will be a compulsory case study question with several requirements relating to the same scenario information. The question will usually assess and link several subject areas from across the syllabus, and will require you to demonstrate high-level capabilities to evaluate, relate and apply the information in the scenario to the question requirements. There will always be some financial or numerical data in the scenario and marks will be available for numerical analysis which supports your written argument.
Section B questions are more likely to examine discrete subject areas. They will be based on short scenarios, and you will be expected to apply information from the scenarios to the question requirements.
ACCA P4考试题型构成
Section A contains ONE compulsory question of 50 marks.
Section B is a choice of TWO from three questions, each carrying 25 marks. There are 3 hours for the exam, plus 15 minutes of reading time.
ACCA P5考试题型构成
Part A One compulsory question 50 marks.
Part B Two from three questions each of 25 marks
ACCA P7考试题型构成
The first 2 questions in the exam are compulsory and will be worth anywhere between 50% and 70%. The remaining 30% – 50% are divided between 2 from 3 other questions
辛勤奋战在学海,汗水扬起成功帆。无烟战场今日起,气定神闲退万军。心态良好细审题,才思敏捷答考卷。自信人生二百年,收获人生好前程。
最后51题库考试学习网提前预祝小伙伴们成功上岸!!加油!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
5 Your manager has heard of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory and how it has some relevance to motivational techniques.
Required:
(a) Explain Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory. (10 marks)
5 The way in which managers’ duties are undertaken can significantly influence the satisfaction that employees derive from their work. Abraham Maslow suggested that individuals have a hierarchy of personal needs which are identifiable, universally applicable and can be satisfied in the workplace. Understanding this concept provides guidance to management as to the appropriateness of
motivational techniques.
(a) Maslow’s theory of motivation is a content theory. Its basic idea is that each individual has a set of needs which have to be
satisfied in a set order of priority.
Maslow suggested that individuals have five needs:
Self-actualisation
(or self fulfilment)
Esteem needs
(or ego)
Social needs
Safety needs
Physiological needs
These needs are arranged in a hierarchy of importance and movement is upwards, from physiological needs to selfactualisation.Any individual will always want more; each need must be satisfied before the next is sought. However – andcritically so far as motivation in the workplace is concerned – a satisfied need is no longer a motivator.
The theory is usually presented in the shape of a triangle, with physiological needs at its base and self-actualisation at itsapex. The triangle shape has a clear significance. As an individual moves up toward the apex, the needs thin out, that isphysiological needs are far greater than self-actualisation needs. For many individuals, reaching social needs is often thehighest need to be satisfied. The theory is sometimes presented as a staircase; again with self-actualisation at the top. Thissecond diagrammatic form. reflects the application of the theory to more modern situations, where it can reasonably beassumed that those within the organisation have already achieved physiological and safety needs. For such individuals, socialand esteem needs may well be greater.
Physiological needs are the basic survival needs which, although part of the theory, probably have less relevance today. Theseneeds are usually seen as food, shelter (which is sometimes noted as a safety need), warmth and clothing.
Safety needs are the desire for security, order, certainty and predictability in life and freedom from threat. The above two so-called ‘lower order needs’ dominate until satisfied.
Social needs are the gregarious needs of mankind, the need for friendship, relationships and affection. This is often seen as the desire to be part of a family.
Esteem needs are the desire for recognition and respect, often associated with status, especially in the modern world.
Self-actualisation (self fulfilment) is the ultimate goal. Once this state is achieved the individual has fulfilled personal potential.
However, later work by Maslow has suggested that there are two additional needs; freedom of enquiry (free speech and justice) and knowledge (the need to explore and learn). These additional needs are a further development of social needs and recognise the changing nature of modern life.
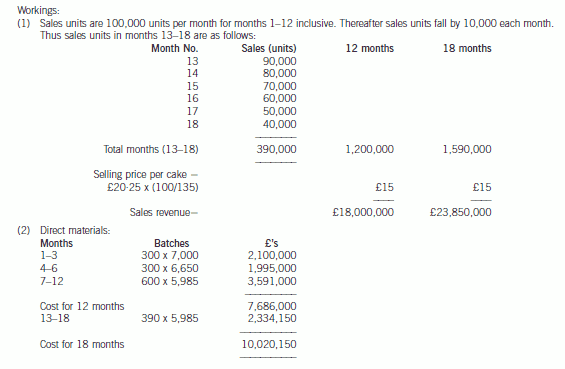
1 The Great Western Cake Company (GWCC) is a well-established manufacturer of specialist flour confectionery
products, including cakes. GWCC sells its products to national supermarket chains. The company’s success during
recent years is largely attributable to its ability to develop innovative products which appeal to the food selectors within
national supermarket chains.
The marketing department of Superstores plc, a national supermarket chain has asked GWCC to manufacture a cake
known as the ‘Mighty Ben’. Mighty Ben is a character who has recently appeared in a film which was broadcast
around the world. The cake is expected to have a minimum market life of one year although the marketing department
consider that this might extend to eighteen months.
The management accountant of GWCC has collated the following estimated information in respect of the Mighty Ben
cake:
(1) Superstores plc has decided on a launch price of £20·25 for the Mighty Ben cake and it is expected that this
price will be maintained for the duration of the product’s life. Superstores plc will apply a 35% mark-up on the
purchase price of each cake from GWCC.
(2) Sales of the Mighty Ben cake are expected to be 100,000 units per month during the first twelve months.
Thereafter sales of the Mighty Ben cake are expected to decrease by 10,000 units in each subsequent month.
(3) Due to the relatively short shelf-life of the Mighty Ben cake, management has decided to manufacture the cakes
on a ‘just-in-time’ basis for delivery in accordance with agreed schedules. The cakes will be manufactured in
batches of 1,000. Direct materials input into the baking process will cost £7,000 per batch for each of the first
three months’ production. The material cost of the next three months’ production is expected to be 95% of the
cost of the first three months’ production. All batches manufactured thereafter will cost 90% of the cost of the
second three months’ production.
(4) Packaging costs will amount to £0·75 per cake. The original costs of the artwork and design of the packaging
will amount to £24,000. Superstores plc will reimburse GWCC £8,000 in the event that the product is
withdrawn from sale after twelve months.
(5) The design of the Mighty Ben cake is such that it is required to be hand-finished. A 75% learning curve will
apply to the total labour time requirement until the end of month five. Thereafter a steady state will apply with
labour time required per batch stabilising at that of the final batch in month five. The labour requirement for the
first batch of Mighty Ben cakes to be manufactured is expected to be 6,000 hours at £10 per hour.
(6) A royalty of 5% of sales revenue (subject to a maximum royalty of £1·1 million) will be payable by GWCC to the
owners of the Mighty Ben copyright.
(7) Variable overheads are estimated at £3·50 per direct labour hour.
(8) The manufacture of the Mighty Ben cake will increase fixed overheads by £75,000 per month.
(9) In order to provide a production facility dedicated to the Mighty Ben cake, an investment of £1,900,000 will be
required and this will be fully depreciated over twelve months.
(10) The directors of GWCC require an average annual return of 35% on their investment over 12 months and
18 months.
(11) Ignore taxation and the present value of cash flows.
Note: Learning curve formula:
y = axb
where y = average cost per batch
a = the cost of the initial batch
x = the total number of batches
b = learning index (= –0·415 for 75% learning rate)
Required:
(a) Prepare detailed calculations to show whether the manufacture of Mighty Ben cakes will provide the required
rate of return for GWCC over periods of twelve months and eighteen months. (20 marks)


(c) The Shirtmaster division and Corporate Clothing division, though being part of the same group, operate largely
independently of one another.
Assess the costs and benefits of the two divisions continuing to operate independently of one another.
(15 marks)
(c) The Shirtmaster Group has decided to structure itself using two divisions who are dealing with very different markets,
customers and buying behaviours. In so doing the intention is to provide more value to the customer through a better
understanding of their needs. The existence of the two divisions also reflects the origins of the two family businesses.
Mintzberg in his work on organisation design and structure sees divisional configurations as being appropriate in relatively
simple and static environments where significant strategic power is delegated from the ‘strategic apex’ to the ‘middle line‘
general managers with responsibility for the performance of the division. Indeed one of the benefits cited for divisionalised
companies is their ability to provide a good training ground in strategic decision making for general managers who can then
progress to senior positions at company headquarters. Tony Masters’s reluctance to delegate real strategic decision making
power to the senior managers in the Shirtmaster division may be preventing those managers developing key managerial skills.
Using the Boston Box model one could classify the Shirtmaster division as a ‘dog’ with low market share in a market exhibiting
change but little growth. The Corporate Clothing division, by contrast, can be regarded as a ‘problem child’ having a small
share but of a growing market. Porter’s ‘better-off test’ needs to be met – are the two divisions better off being in the same
Group? As it stands there seems little synergy between the two divisions – there seems to be little evidence of the two divisions
sharing resources or transferring skills or learning between the two divisions. Their two value chains and systems are both
separate and different though on the face of it there are many activities that are similar. Operating independently may
encourage healthy competition between the two divisions and consequently better performance through better motivated staff.
Specialised competences such as Corporate Clothing division’s on-line response to customer orders and design changes are
more easily developed within a divisionalised structure. Performance can be clearly identified and controlled and resources
channelled to those areas showing potential. However, this may be at the expense of costly duplication of resources and an
inability to get the necessary scale to compete in either of their separate markets. Certainly, the lack of co-operation betweenthe divisions in areas such as information systems may lead to higher costs and poorer performance.
(ii) Service quality; and (7 marks)
(ii) Quality of service is the totality of features and characteristics of the service package that bear upon its ability to satisfy
client needs. To some extent the number of complaints and the need to provide non-chargeable consultations associated
with the remedying of those complaints is indicative of a service quality problem that must be addressed. Hence this
problem needs to be investigated at the earliest opportunity. Assuming consultants could have otherwise undertaken
chargeable work, the revenue foregone as a consequence of the remedial consultations relating to commercial work
amounted to (180 x £1500) = £27,000. Client complaints received by HLP during the year amounted to 1·24% of
consultations undertaken by commercial advisors whereas none were budgeted. In contrast, competitor MAS received
135 complaints which coincided with the number of non-chargeable consultations undertaken by them. This may
indicate that MAS operate a policy of a remedial consultation in respect of all complaints received from clients.
With regard to the number of on-time consultations, HLP only achieved an on-time consultation percentage of 94·4%
which is far inferior to that of 99% achieved by competitor MAS. Also, HLP re-scheduled the appointment times of
1,620 (3%) of its total consultations whereas competitor MAS only re-scheduled 0·5% of its consultation times. The
percentage number of successful consultations provided by HLP and MAS was 85% and 95% respectively which
indicates that competitor MAS possesses a superior skills-base to that of HLP.
The most alarming statistic lies in the fact that HLP was subject to three successful legal actions for negligence. This
may not only account for the 150% increase in the cost of professional indemnity insurance premiums but may also
result in a loss of client confidence and precipitate a considerable fall in future levels of business should the claims
become much publicised.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-01-31
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-06
- 2020-04-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-25
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-08-16
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-15
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-22