关于ACCA每次考试最多报考几门,一起来看看本篇文章!
发布时间:2019-12-31
ACCA是财经领域有非常多科目的考试之一,截止到2020年新的ACCA考试政策,学科依然高达15门,其中必考的有13门。ACCA考试一共需要通过13门考试,那我们一次最多能报考几门考试呢?今天就跟随51题库考试学习网一起看看以下内容吧。
根据ACCA官方的规定,每个考季最多能够报考4门考试,毕竟每个考季仅间隔3个月的时间,最大限度的去复习4门考试,时间相当紧张,备考效率要非常的高。很多同学会根据自己的时间情况安排选择2-3门考试,非常有把握的一刷而过。当然,有些同学抱着试一试的心态,希望能够临阵磨枪冲一把说不定低分飘过,这样也是一种考试策略,可根据考生自己的情况来定夺。
如果每个考季报考4门全通过,那么不到1年是不是就全科通过ACCA了?
理想很美好,现实很骨感,虽然ACCA官方规定,每季可以报考4门考试,但是一年内最多只能报考8门,虽然考季增多,但是总的ACCA考试科目限制并没有随之变化。当然,也是存在一年内拿下ACCA考试的大神的,这样的大神一般是获得ACCA官方认可的部分科目免考的。例如CPA持证者可以免考九门ACCA考试,再考四科即可拿到ACCA证书。这样的情况下,我们是完完全全可以在一年内拿下全部考试的。
不过,虽然每个学员都想更快通过ACCA考试,但是很多学员由于自制力比较薄弱,容易越久越学不下去的懈怠之中。
提醒大家,ACCA应用阶段没有考试通过期限(FIA同样如此),但战略阶段的考试通过期限为7年。所以开始考ACCA P阶段课程的同学既要做好打持久战的准备,也要提高效率,抓紧时间。
为什么那么多人报考ACCA,来这里看看答案。
备受国际认可
ACCA会员资格备受国际广泛认可,尤其是得到欧盟立法以及许多国家公司法的承认,所以说,拥有ACCA会员资格,就等于拥有了在世界各地就业的“通行证”。
就业前景广阔
ACCA考试的课程是根据当前社会对财会人员实际要求进行开发、设计的,致力于培养学员的分析能力和决策、判断能力,让学员成为具有全面管理素质的高级财务管理专家。成为ACCA会员,无论是在国企、四大事务所、金融机构或者是财政、税务机构,都可以任职。甚至很多ACCA会员在世界各大公司大人高级管理职位,如:CEO、CFO等。
薪资水平比较高
根据ACCA调查显示,ACCA会员的年薪主要在10万至80万之间,远高于一般市场上的财务人员的收入。国际证书会员中26岁-30岁的会员中主要薪资范围集中在10万-30万,部分会员收入高达200万元。由此可见,ACCA会员薪资水平还是比较高的。但并不是考下ACCA便可以享受高薪职位,ACCA是起着锦上添花的作用,更多的还是要靠个人的能力水平,在不断的实践经验中,不断完善自己,实现高薪就业。
以上就是51题库考试学习网为大家分享的关于ACCA考试的相关信息,请考生们注意查收。如有疑问,欢迎到51题库考试学习网咨询,我们会及时回复你的信息。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Distinguish between strategic and operational risks, and explain why the secrecy option would be a source
of strategic risk. (10 marks)
(b) Strategic and operational risks
Strategic risks
These arise from the overall strategic positioning of the company in its environment. Some strategic positions give rise to
greater risk exposures than others. Because strategic issues typically affect the whole of an organisation and not just one or
more of its parts, strategic risks can potentially concern very high stakes – they can have very high hazards and high returns.
Because of this, they are managed at board level in an organisation and form. a key part of strategic management.
Operational risks
Operational risks refer to potential losses arising from the normal business operations. Accordingly, they affect the day-to-day
running of operations and business systems in contrast to strategic risks that arise from the organisation’s strategic positioning.
Operational risks are managed at risk management level (not necessarily board level) and can be managed and mitigated by
internal control systems.
The secrecy option would be a strategic risk for the following reasons.
It would radically change the environment that SHC is in by reducing competition. This would radically change SHC’s strategic
fit with its competitive environment. In particular, it would change its ‘five forces’ positioning which would change its risk
profile.
It would involve the largest investment programme in the company’s history with new debt substantially changing the
company’s financial structure and making it more vulnerable to short term liquidity problems and monetary pressure (interest
rates).
It would change the way that stakeholders view SHC, for better or worse. It is a ‘crisis issue’, certain to polarise opinion either
way.
It will change the economics of the industry thereby radically affecting future cost, revenue and profit forecasts.
There may be retaliatory behaviour by SHC’s close competitor on 25% of the market.
[Tutorial note: similar reasons if relevant and well argued will attract marks]
(c) (i) Identify and describe FOUR quality control procedures that are applicable to the individual audit
engagement; and (8 marks)
(c) (i) ISQC 1 Quality Control for Firms That Perform. Audits and Reviews of Historical Financial Information and Other
Assurance and Related Services Engagements provides guidance on the overall quality control systems that should be
implemented by an audit firm. ISA 220 Quality Control for Audits of Historical Financial Information specifies the quality
control procedures that should be applied by the engagement team in individual audit assignments.
Procedures include the following:
Client acceptance procedures
There should be full documentation, and conclusion on, ethical and client acceptance issues in each audit assignment.
The engagement partner should consider whether members of the audit team have complied with ethical requirements,
for example, whether all members of the team are independent of the client. Additionally, the engagement partner should
conclude whether all acceptance procedures have been followed, for example, that the audit firm has considered the
integrity of the principal owners and key management of the client. Other procedures on client acceptance should
include:
– Obtaining professional clearance from previous auditors
– Consideration of any conflict of interest
– Money laundering (client identification) procedures.
Engagement team
Procedures should be followed to ensure that the engagement team collectively has the skills, competence and time to
perform. the audit engagement. The engagement partner should assess that the audit team, for example:
– Has the appropriate level of technical knowledge
– Has experience of audit engagements of a similar nature and complexity
– Has the ability to apply professional judgement
– Understands professional standards, and regulatory and legal requirements.
Direction
The engagement team should be directed by the engagement partner. Procedures such as an engagement planning
meeting should be undertaken to ensure that the team understands:
– Their responsibilities
– The objectives of the work they are to perform
– The nature of the client’s business
– Risk related issues
– How to deal with any problems that may arise; and
– The detailed approach to the performance of the audit.
The planning meeting should be led by the partner and should include all people involved with the audit. There should
be a discussion of the key issues identified at the planning stage.
Supervision
Supervision should be continuous during the engagement. Any problems that arise during the audit should be rectified
as soon as possible. Attention should be focused on ensuring that members of the audit team are carrying out their work
in accordance with the planned approach to the engagement. Significant matters should be brought to the attention of
senior members of the audit team. Documentation should be made of key decisions made during the audit engagement.
Review
The review process is one of the key quality control procedures. All work performed must be reviewed by a more senior
member of the audit team. Reviewers should consider for example whether:
– Work has been performed in accordance with professional standards
– The objectives of the procedures performed have been achieved
– Work supports conclusions drawn and is appropriately documented.
The review process itself must be evidenced.
Consultation
Finally the engagement partner should arrange consultation on difficult or contentious matters. This is a procedure
whereby the matter is discussed with a professional outside the engagement team, and sometimes outside the audit
firm. Consultations must be documented to show:
– The issue on which the consultation was sought; and
– The results of the consultation.
15 A trader who fixes her prices by adding 50% to cost actually achieved a mark-up of 45%.
Which of the following factors could account for the shortfall?
1 Sales were lower than expected.
2 The opening inventories had been overstated.
3 The closing inventories of the business were higher than the opening inventories.
4 Goods taken from inventories by the proprietor were recorded by debiting drawings and crediting purchases with
the cost of the goods.
A All four factors
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 2 only
D 3 and 4 only
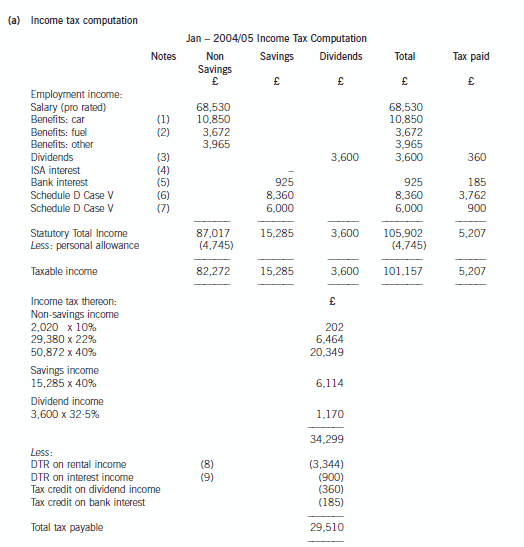
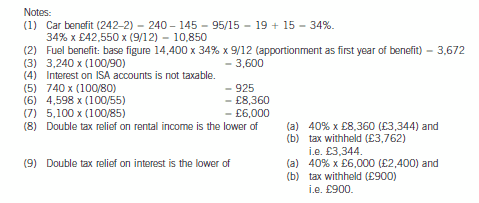
2 Assume that today’s date is 1 July 2005.
Jan is aged 45 and single. He is of Danish domicile but has been working in the United Kingdom since 1 May 2004
and intends to remain in the UK for the medium to long term. Although Jan worked briefly in the UK in 1986, he
has forgotten how UK taxation works and needs some assistance before preparing his UK income tax return.
Jan’s salary from 1 May 2004 was £74,760 per annum. Jan also has a company car – a Jaguar XJ8 with a list price
of £42,550 including extras, and CO2 emissions of 242g/km. The car was available to him from 1 July 2004. Free
petrol is provided by the company. Jan has other taxable benefits amounting to £3,965.
Jan’s other 2004/05 income comprises:
£
Dividend income from UK companies (cash received) 3,240
Interest received on an ISA account 230
Interest received on a UK bank account 740
Interest remitted from an offshore account (net of 15% withholding tax) 5,100
Income remitted from a villa in Portugal (net of 45% withholding tax) 4,598
The total interest arising on the offshore account was £9,000 (gross). In addition, Jan has not remitted other
Portuguese rental income arising in the year, totalling a further £1,500 (gross).
Jan informs you that his employer is thinking of providing him with rented accommodation while he looks for a house
to buy. The accommodation would be a two bedroom flat, valued at £155,000 with an annual value of £6,000. It
would be made available from 6 August 2005. The company will pay the rent of £600 per month for the first six
months. All other bills will be paid by Jan.
Jan also informs you that he has 25,000 ordinary shares in Gilet Ltd (‘Gilet’), an unquoted UK trading company. He
has held these shares since August 1986 when he bought 2,500 shares at £4.07 per share. In January 1994, a
bonus issue gave each shareholder nine shares for each ordinary share held. In the last week all Gilet’s shareholders
have received an offer from Jumper plc (‘Jumper’) who wishes to acquire the shares. Jumper has offered the following:
– 3 shares in Jumper (currently trading at £3.55 per share) for every 5 shares in Gilet, and
– 25p cash per share
Required:
(a) Calculate Jan’s 2004/05 income tax (IT) payable. (11 marks)
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-12
- 2021-05-14
- 2019-03-30
- 2020-10-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-05-02
- 2020-02-19
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-12
- 2020-03-19
- 2021-06-25
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-05-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-03-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-17