考取注册税务师收入有前景吗
发布时间:2021-11-30
考取注册税务师收入有前景吗
最佳答案
税务师行业是非常有前景的行业。注册税务师目前市场需求量很大,很多事务所都会大量招聘相关人才,一般来说在大的税务师事务所,一线城市,年薪在12-15万之间是比较正常,职位高的另当别论。二线城市应该在8-10万左右,就业前景还是比较乐观的!
中国注册税务师协会理事、陕西宏泰税务师事务所所长杨俊岑表示,税务师行业是永不消亡的行业。人的一生有两件大事不可避免,第一件是死亡;第二件就是税收。每个人的工作生活都要牵涉到税收问题。如果你把税务师作为一种事业,作为自己永久性的规划,一辈子你都干不完学不完,你不存在跳槽的问题,也不存在被工作所淘汰的问题,税务师行业的人才缺口相当大。各位大学生、在职人员一定要珍惜现在的黄金年龄,做好自己的人生规划,积极报考税务师。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) Identify the points that must be confirmed and any action necessary in order for capital treatment to
apply to the transaction. (4 marks)
(ii) Ensuring capital treatment
For the capital treatment to apply, a number of conditions need to be satisfied such that the following points need to be
confirmed.
– The business of Acrux Ltd consists wholly or mainly of the carrying on of a trade as opposed to the making of
investments.
– Spica is UK resident and ordinarily resident despite living in both the UK and Solaris.
– The transaction is being carried out for the purpose of the company’s trade and is not part of a scheme intended
to avoid tax. This is likely to be the case as HMRC accept that a management disagreement over the running of
the company has an adverse effect on the running of the business.
In addition, Spica must have owned the shares for at least five years so the transaction must not take place until
1 October 2008.
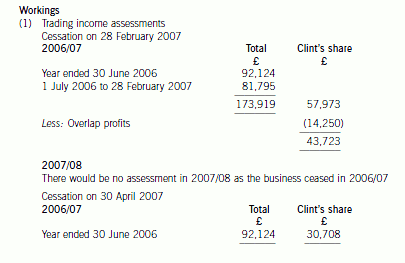
(ii) Analyse the effect of delaying the sale of the business of the Stiletto Partnership to Razor Ltd until
30 April 2007 on Clint’s income tax and national insurance position.
You are not required to prepare detailed calculations of his income tax or national insurance liabilities.
(4 marks)
(ii) The implications of delaying the sale of the business
The implications of delaying the sale of the business until 30 April would have been as follows:
– Clint would have received an additional two months of profits amounting to £6,920 (£20,760 x 1/3).
– Clint’s trading income in 2006/07 would have been reduced by £13,015 (£43,723 – £30,708), much of which
would have been subject to income tax at 40%. His additional trading income in 2007/08 of £19,935 would all
have been taxed at 10% and 22%.
– Clint is entitled to the personal age allowance of £7,280 in both years. However, it is abated by £1 for every £2
by which his total income exceeds £20,100. Once Clint’s total income exceeds £24,590 (£20,100 + ((£7,280
– £5,035) x 2)), his personal allowance will be reduced to the standard amount of £5,035. Accordingly, the
increased personal allowance would not be available in 2006/07 regardless of the year in which the business was
sold. It is available in 2007/08 (although part of it is wasted) but would not have been if the sale of the business
had been delayed.
– Clint’s class 4 national insurance contributions in 2006/07 would have been reduced due to the fall in the level
of his trading income. However, much of the saving would be at 1% only. Clint is not liable to class 4 national
insurance contributions in 2007/08 as he is 65 at the start of the year.
– Changing the date on which the business was sold would have had no effect on Clint’s class 2 liability as he is
not required to make class 2 contributions once he is 65 years old.
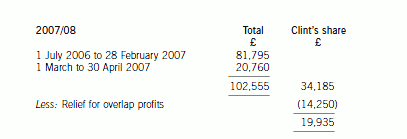
(ii) Discuss whether gains and losses that have been reported initially in one section of the performance
statement should be ‘recycled’ in a later period in another section and whether only ‘realised’ gains and
losses should be included in such a statement. (9 marks)
(ii) Recycling is an issue for both the current performance statements and the single statement. Recycling occurs where an
item of financial performance is reported in more than one accounting period because the nature of the item has in some
way changed. It raises the question as to whether gains and losses originally reported in one section of the statement
should be reported in another section at a later date. An example would be gains/losses on the retranslation of the net
investment in an overseas subsidiary. These gains could be reported annually on the retranslation of the subsidiary and
then again when the subsidiary was sold.
The main arguments for recycling to take place are as follows:
1. when unrealised items become realised they should be shown again
2. when uncertain measurements become certain they should be reported again
3. all items should be shown in operating or financing activities at some point in time as all items of performance are
ultimately part of operating or financing activities of an entity.
There is no conceptual justification for recycling. Once an item has been recognised in a statement of financial
performance it should not be recognised again in a future period in a different part of that statement. Once an item is
recognised in the statement there is an assumption that it can be reliably measured and therefore it should be recognised
in the appropriate section of the statement with no reason to show it again.
Gains and losses should not be based on the notion of realisation. Realisation may have been a critical event historically
but given the current financial exposures of many entities, such a principle has limited value. A realised gain reflects the
same economic gain as an unrealised gain. Items should be classified in the performance statement on the basis of
characteristics which are more useful than realisation. The effect of realisation is explained better in the cash flow
statement. Realisation means different things in different countries. In Europe and Asia it refers to the amount of
distributable profits but in the USA it refers to capital maintenance. The amount of distributable profits is not an
accounting but a legal issue, and therefore realisation should not be the overriding determinant of the reporting of gains
and losses.
An alternative view could be that an unrealised gain is more subjective than a realised gain. In many countries, realised
gains are recognised for distribution purposes because of their certainty because this gives more economic stability to
the payment of dividends.
(b) Examine how adopting a Six Sigma approach would help address the quality problems at UPC.
(10 marks)
(b) In many ways Six Sigma started out as a quality control methodology. It focused on measurement and the minimisation of
faults through pursuing Six Sigma as a statistical measure of some aspects of organisational performance. However, Six Sigma
has developed into something much more than a process control technique. It includes a problem-solving process called
DMAIC and a comprehensive toolkit ranging from brainstorming to balanced scorecards and process dashboards. It also has
defined team roles for managers and employees, often with martial arts names such as Black Belt, Green Belt and Master
Black Belt.
Six Sigma was first used in organisations in the early 1990s. However, it was its adoption and promotion by Jack Welch, the
CEO of GE that brought Six Sigma wider publicity. He announced that ‘Six Sigma is the most important initiative GE has ever
undertaken’. As Paul Harmon comments, ‘Welch’s popularity with the business press, and his dynamic style, guaranteed that
Six Sigma would become one of the hot management techniques of the late 1990s’.
Six Sigma uses an approach called DMAIC in its problem solving process. This stands for Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve
and Control. Three aspects of this are considered below in the context of how they would address the problems at UPC.
Defining the problem
Part of defining the problem is the identification of the customer. It is important to understand what customers really want
and value and one of the main themes of Six Sigma is its focus on the customer. Six Sigma explicitly recognises the ‘voice of
the customer’ (VOC) in its approach. In the UPC situation quality requirements are currently defined by the physical condition
of the goods and by the alignment of the image. However, this may be a limiting view of quality because there is no evidence
of any systematic investigation of the requirements of the customer. Solving these problems may not lead to any significant
long-term gain; they may be quickly replaced by other ‘quality issues’. Furthermore, the customer is also perceived in a limited
way. These quality requirements are in the eye of the gift shop owner who is interested in saleable products. The end customer
– the consumer – who buys and uses the product may have other requirements which can also be addressed at this time.
By considering the VOC the problem and scope of the project becomes re-defined and the solution of the problems potentially
more valuable.
Measurement
Measurement is fundamental to Six Sigma. This includes the gathering of data to validate and quantify the problem. The
creation of the inspection team was based on initial evidence about an increase in breakages. This needs to be quantified.
The inaccurate printing of the image had been quantified as 500 units per month, out of the 250,000 shipped out of the
company. This equates to a failure rate of 0·2%, so that 99·8% of items are shipped with a correctly aligned image. This
sounds quite reasonable but it still raises issues and complaints that have to be dealt with, as well as creating wastage costs
of $10,000 per month. The problem is that even a relatively low percentage of defects can lead to a lot of unhappy customers.
Aiming for Six Sigma would reduce defects down to about one faulty item per month, reducing the wastage cost to $20.
Analysis
Analysis is concerned with understanding the process to find the root cause. Six Sigma focuses on processes and their
analysis. Analysis concerns methods, machines, materials, measures, Mother Nature and people. The alignment problem
needs investigation to find out what causes the imaging machine to irregularly produce misaligned images. Management
currently appear to blame the machine but it may be due to the way that certain people load the machine. The analysis of
the breakages is particularly important. It is unclear at present where these breakages occur (for example, are some of the
items broken before they leave UPC’s despatch facility) or are they all broken in transit? Neither is it understood why the
breakages occur. Management appear to blame the packers for packing incorrectly and not following the correct method.
However, it may be that the material is just not strong enough to withstand heavy handling by couriers who are outside the
control of UPC. Additionally, the breakages may be due to some manufacturing problem or raw material imperfection in the
items that break. Six Sigma stresses understanding the problem before solving it.
Although DMAIC has been selected as the framework for the sample answer, focusing on other aspects of Six Sigma would
be acceptable – as long as they are presented in the context of the UPC scenario.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-06-11
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-02-11
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-12-27
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-04-22
- 2021-06-05
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-05-13
- 2021-05-25
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-01-03
- 2021-04-14
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-04-16
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-01-04
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-10
- 2021-03-23
- 2021-03-12
- 2021-05-08
- 2021-05-09
- 2021-01-01
- 2021-03-11
- 2021-03-12