号外!号外!青海省2020年ACCA考试准考证可以打印啦!这些打印流程你知道吗?
发布时间:2020-01-08
2020年已经过去了一个多周了,除去周末节假日和春节假日,留给大家备考ACCA考试的时间也不多了,相信现在有很多ACCAer们已经开始埋头苦读、认真备考了,但是51题库考试学习网在这里提醒大家:认真备考的同时千万不要忘了一个最最最重要的事情:打印准考证!“新手”ACCAer不知道打印的流程也不用担心,51题库考试学习网会把大家想要知道的咨询都分享给大家:
ACCA考试准考证打印是什么时候?
首先,ACCAer们需要注意的第一件事情就是:ACCA各科目的准考证必须学员自行通过ACCA全球官网下载,原则上不允许从第三方网站上下载相关准考证。2020年3月ACCA考试准考证目前尚未开放下载,请大家等待,ACCA考试准考证一般来说会在考试前2-3周时间开放,请各位ACCAer们注意时间,以免错过打印的时间。打印的步骤如下所示:
1、在ACCA官网主页http://www.accaglobal.com/en.html点击MYACCA,进入登录页面:
2、进入MYACCA账户后点击左侧的EXAM
ENTRY:
3、进入个人页面后点击左侧的“DOCKET”;
4、点击下方红色的“Access your
docket”进入准考证界面;
5、点击“Access your
docket” ,在随后出现的页面中选择学习方式及培训机构,培训机构选择“Beijing Champion Hi-Tech Co. Ltd.Dist...”(2019年3月考季起,ACCA全球统考准考证将不会再有个人照片!)
6、 在弹出的页面或者提示栏中选择“保存”(或是“下载”) ,准考证会以 pdf 格式显示。(一个考季内,第一次进入准考证界面时会出现以下“调查”,按实际情况填写并保存即可。)
7.下载好以后,打开文件,仔细核对准考证上的个人信息及考试信息,准考证共2页。(建议:以正反面的形式,打印在一张纸上)准考证会以 pdf 格式显示,打印完成后,考试时带上您的准考证、身份证/护照参加考试即可。
准考证打印相关注意事项有哪些?
参加笔试的考生,记得要带黑色圆珠笔。
不能用水笔的,一定是黑色圆珠笔。准考证打印好后一定要与其他考试物品(如:黑色圆珠笔,计算器等)放在一起。考试那天,把这些一并带上,另外,不要忘了带身份证(或护照)!
准考证是每位ACCA学员参加考试时必须的进场证明,所以我们要注意的准考证数量要与我们参加的考试科数相同,此外,还要仔细核对报考科目和考试地点有无错误。
需要注意的是:准考证打印没有要求彩色的,所以可以选择黑白也可选择彩色的打印。同时,准考证的要求双面打印的,这两点要尤其重视一下,提前做好准备,预防出现不必要的麻烦。
看完以上的这些信息之后,ACCAer们是不是顿时觉得打印准考证不是很难呀?51题库考试学习网在这里由衷地告诉大家:“只有一条路不能选择——那就是放弃的路;只有一条路不能拒绝——那就是成长的路。”加油~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
1 Stuart is a self-employed business consultant aged 58. He is married to Rebecca, aged 55. They have one child,
Sam, who is aged 24 and single.
In November 2005 Stuart sold a house in Plymouth for £422,100. Stuart had inherited the house on the death of
his mother on 1 May 1994 when it had a probate value of £185,000. The subsequent pattern of occupation was as
follows:
1 May 1994 to 28 February 1995 occupied by Stuart and Rebecca as main residence
1 March 1995 to 31 December 1998 unoccupied
1 January 1999 to 31 March 2001 let out (unfurnished)
1 April 2001 to 30 November 2001 occupied by Stuart and Rebecca
1 December 2001 to 30 November 2005 used occasionally as second home
Both Stuart and Rebecca had lived in London from March 1995 onwards. On 1 March 2001 Stuart and Rebecca
bought a house in London in their joint names. On 1 January 2002 they elected for their London house to be their
principal private residence with effect from that date, up until that point the Plymouth property had been their principal
private residence.
No other capital disposals were made by Stuart in the tax year 2005/06. He has £29,500 of capital losses brought
forward from previous years.
Stuart intends to invest the gross sale proceeds from the sale of the Plymouth house, and is considering two
investment options, both of which he believes will provide equal risk and returns. These are as follows:
(1) acquiring shares in Omikron plc; or
(2) acquiring further shares in Omega plc.
Notes:
1. Omikron plc is a listed UK trading company, with 50,250,000 shares in issue. Its shares currently trade at 42p
per share.
2. Stuart and Rebecca helped start up the company, which was then Omega Ltd. The company was formed on
1 June 1990, when they each bought 24,000 shares for £1 per share. The company became listed on 1 May
1997. On this date their holding was subdivided, with each of them receiving 100 shares in Omega plc for each
share held in Omega Ltd. The issued share capital of Omega plc is currently 10,000,000 shares. The share price
is quoted at 208p – 216p with marked bargains at 207p, 211p, and 215p.
Stuart and Rebecca’s assets (following the sale of the Plymouth house but before any investment of the proceeds) are
as follows:
Assets Stuart Rebecca
£ £
Family house in London 450,000 450,000
Cash from property sale 422,100 –
Cash deposits 165,000 165,000
Portfolio of quoted investments – 250,000
Shares in Omega plc see above see above
Life insurance policy note 1 note 1
Note:
1. The life insurance policy will pay out a sum of £200,000 on the death of the first spouse to die.
Stuart has recently been diagnosed with a serious illness. He is expected to live for another two or three years only.
He is concerned about the possible inheritance tax that will arise on his death. Both he and Rebecca have wills whose
terms transfer all assets to the surviving spouse. Rebecca is in good health.
Neither Stuart nor Rebecca has made any previous chargeable lifetime transfers for the purposes of inheritance tax.
Required:
(a) Calculate the taxable capital gain on the sale of the Plymouth house in November 2005 (9 marks)
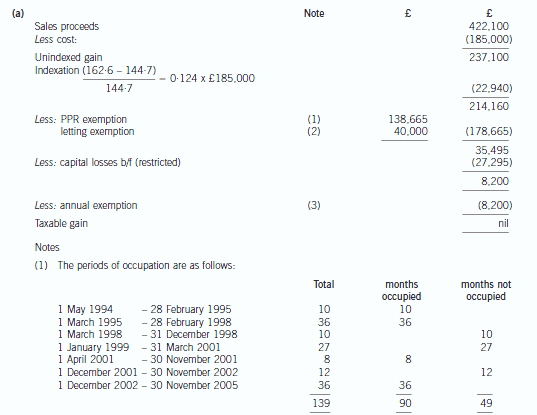
Note that the last 36 months count as deemed occupation, as the house was Stuart’s principal private residence (PPR)
at some point during his period of ownership.
The first 36 months of the period from 1 March 1995 to 31 March 2001 qualifies as a deemed occupation period as
Stuart and Rebecca returned to occupy the property on 1 April 2001. The remainder of the period will be treated as a
period of absence, although letting relief is available for part of the period (see below).
The exempt element of the gain is the proportion during which the property was occupied, real or deemed. This is
£138,665 (90/139 x £214,160).
(2) The chargeable gain is restricted for the period that the property was let out. This is restricted to the lowest of the
following:
(i) the gain attributable to the letting period (27/139 x 214,160) = £41,599
(ii) £40,000
(iii) the total exempt PPR gain = £138,665
i.e. £40,000.
(3) The taper relief is effectively wasted, having restricted losses b/f to preserve the annual exemption.
The following information is available for a manufacturing company which produces multiple products:
(i) The product mix ratio
(ii) Contribution to sales ratio for each product
(iii) General fixed costs
(iv) Method of apportioning general fixed costs
Which of the above are required in order to calculate the break-even sales revenue for the company?
A.All of the above
B.(i), (ii) and (iii) only
C.(i), (iii) and (iv) only
D.(ii) and (iii) only
The method of apportioning general fixed costs is not required to calculate the break-even sales revenue.
In relation to the courts’ powers to interpret legislation, explain and differentiate between:
(a) the literal approach, including the golden rule; and (5 marks)
(b) the purposive approach, including the mischief rule. (5 marks)
Tutorial note:
In order to apply any piece of legislation, judges have to determine its meaning. In other words they are required to interpret the
statute before them in order to give it meaning. The diffi culty, however, is that the words in statutes do not speak for themselves and
interpretation is an active process, and at least potentially a subjective one depending on the situation of the person who is doing
the interpreting.
Judges have considerable power in deciding the actual meaning of statutes, especially when they are able to deploy a number of
competing, not to say contradictory, mechanisms for deciding the meaning of the statute before them. There are, essentially, two
contrasting views as to how judges should go about determining the meaning of a statute – the restrictive, literal approach and the
more permissive, purposive approach.
(a) The literal approach
The literal approach is dominant in the English legal system, although it is not without critics, and devices do exist for
circumventing it when it is seen as too restrictive. This view of judicial interpretation holds that the judge should look primarily
to the words of the legislation in order to construe its meaning and, except in the very limited circumstances considered below,
should not look outside of, or behind, the legislation in an attempt to fi nd its meaning.
Within the context of the literal approach there are two distinct rules:
(i) The literal rule
Under this rule, the judge is required to consider what the legislation actually says rather than considering what it might
mean. In order to achieve this end, the judge should give words in legislation their literal meaning, that is, their plain,
ordinary, everyday meaning, even if the effect of this is to produce what might be considered an otherwise unjust or
undesirable outcome (Fisher v Bell (1961)) in which the court chose to follow the contract law literal interpretation of
the meaning of offer in the Act in question and declined to consider the usual non-legal literal interpretation of the word
(offer).
(ii) The golden rule
This rule is applied in circumstances where the application of the literal rule is likely to result in what appears to the court
to be an obviously absurd result. It should be emphasised, however, that the court is not at liberty to ignore, or replace,
legislative provisions simply on the basis that it considers them absurd; it must fi nd genuine diffi culties before it declines
to use the literal rule in favour of the golden one. As examples, there may be two apparently contradictory meanings to a
particular word used in the statute, or the provision may simply be ambiguous in its effect. In such situations, the golden
rule operates to ensure that preference is given to the meaning that does not result in the provision being an absurdity.
Thus in Adler v George (1964) the defendant was found guilty, under the Offi cial Secrets Act 1920, with obstruction
‘in the vicinity’ of a prohibited area, although she had actually carried out the obstruction ‘inside’ the area.
(b) The purposive approach
The purposive approach rejects the limitation of the judges’ search for meaning to a literal construction of the words of
legislation itself. It suggests that the interpretative role of the judge should include, where necessary, the power to look beyond
the words of statute in pursuit of the reason for its enactment, and that meaning should be construed in the light of that purpose
and so as to give it effect. This purposive approach is typical of civil law systems. In these jurisdictions, legislation tends to set
out general principles and leaves the fi ne details to be fi lled in later by the judges who are expected to make decisions in the
furtherance of those general principles.
European Community (EC) legislation tends to be drafted in the continental manner. Its detailed effect, therefore, can only be
determined on the basis of a purposive approach to its interpretation. This requirement, however, runs counter to the literal
approach that is the dominant approach in the English system. The need to interpret such legislation, however, has forced
a change in that approach in relation to Community legislation and even with respect to domestic legislation designed to
implement Community legislation. Thus, in Pickstone v Freemans plc (1988), the House of Lords held that it was permissible,
and indeed necessary, for the court to read words into inadequate domestic legislation in order to give effect to Community
law in relation to provisions relating to equal pay for work of equal value. (For a similar approach, see also the House of Lords’
decision in Litster v Forth Dry Dock (1989) and the decision in Three Rivers DC v Bank of England (No 2) (1996).) However,
it has to recognise that the purposive rule is not particularly modern and has its precursor in a long established rule of statutory
interpretation, namely the mischief rule.
The mischief rule
This rule permits the court to go behind the actual wording of a statute in order to consider the problem that the statute is
supposed to remedy.
In its traditional expression it is limited by being restricted to using previous common law rules in order to decide the operation
of contemporary legislation. Thus in Heydon’s case (1584) it was stated that in making use of the mischief rule the court
should consider what the mischief in the law was which the common law did not adequately deal with and which statute law
had intervened to remedy. Use of the mischief rule may be seen in Corkery v Carpenter (1950), in which a man was found
guilty of being drunk in charge of a carriage although he was in fact only in charge of a bicycle.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-08-15
- 2021-01-01
- 2020-12-24
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-08-14
- 2020-08-15
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-01-01
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-12-24
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-09-04
- 2021-01-03
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-01-03
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10