2020年ACCA考试公司法与商法专业词汇汇编(1)
发布时间:2020-10-14
今日51题库考试学习网为大家带来“2020年ACCA考试公司法与商法专业词汇汇编(1)”的相关知识点,各位辛勤备考的小伙伴一起来看看吧。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Financial
Accounting
【English Terms】
Financial Accounting
【中文翻译】
财务会计
【详情解释/例子】
公司通过定期对外发表财务报表,向公众通报公司的财务状况及表现。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Financial
Engineering
【English Terms】
Financial Engineering
【中文翻译】
金融资产重整
【详情解释/例子】
通过创新的设计或重整现有的金融工具创造新的、更好的金融产品。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Financial
Asset
【English Terms】
Financial Asset
【中文翻译】
金融资产
【详情解释/例子】
价值来自有合约性索偿权的资产,例如股票、债券及银行存款。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Financial
Accounting Standards Board -(FASB)
【English Terms】
Financial Accounting Standards Board
-(FASB)
【中文翻译】
财务会计标准委员会
【详情解释/例子】
制定财务会计及报告标准的指定机构。制定的标准控制财务报告的编制方法,并且获得美国证监会的承认。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Financial
Intermediary
【English Terms】
Financial Intermediary
【中文翻译】
金融中介机构
【详情解释/例子】
担任投资者与融资机构中间人的机构,也称为金融机构。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:FIFO
【English Terms】
"First In, First Out(FIFO)
【中文翻译】
先进先出
【详情解释/例子】
库存管理及估值方法,要点在于先出售最早买入的产品。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Firm
commitment
【English Terms】
Firm commitment
【中文翻译】
坚定承诺
【详情解释/例子】
1. 贷款公司承诺在特定时期内与特定实体签署贷款协议。
2. 承诺承担所有库存风险及直接向发行人以向公众售股价格买入。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Financial
Performance
【English Terms】
Financial Performance
【中文翻译】
财务表现
【详情解释/例子】
公司在特定时期内通过日常运作产生新资源的能力。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Financial
Supermarket
【English Terms】
Financial Supermarket
【中文翻译】
金融超级市场
【详情解释/例子】
向客户提供范围广泛服务的金融公司。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Financial
Planner
【English Terms】
Financial Planner
【中文翻译】
财务规划
【详情解释/例子】
协助客户编制财务计划及协调不同财务活动的投资专业人员。
ACCA财经词汇汇编:Fiscal
Agent
【English Terms】
Fiscal Agent
【中文翻译】
财务代理
【详情解释/例子】
承担无关联方财政责任的机构,例如银行或信托公司等。
以上就是51题库考试学习网带给大家的全部内容,相信小伙伴们都了解清楚。预祝12月份ACCA考试取得满意的成绩,如果想要了解更多关于ACCA考试的资讯,敬请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
1 Stuart is a self-employed business consultant aged 58. He is married to Rebecca, aged 55. They have one child,
Sam, who is aged 24 and single.
In November 2005 Stuart sold a house in Plymouth for £422,100. Stuart had inherited the house on the death of
his mother on 1 May 1994 when it had a probate value of £185,000. The subsequent pattern of occupation was as
follows:
1 May 1994 to 28 February 1995 occupied by Stuart and Rebecca as main residence
1 March 1995 to 31 December 1998 unoccupied
1 January 1999 to 31 March 2001 let out (unfurnished)
1 April 2001 to 30 November 2001 occupied by Stuart and Rebecca
1 December 2001 to 30 November 2005 used occasionally as second home
Both Stuart and Rebecca had lived in London from March 1995 onwards. On 1 March 2001 Stuart and Rebecca
bought a house in London in their joint names. On 1 January 2002 they elected for their London house to be their
principal private residence with effect from that date, up until that point the Plymouth property had been their principal
private residence.
No other capital disposals were made by Stuart in the tax year 2005/06. He has £29,500 of capital losses brought
forward from previous years.
Stuart intends to invest the gross sale proceeds from the sale of the Plymouth house, and is considering two
investment options, both of which he believes will provide equal risk and returns. These are as follows:
(1) acquiring shares in Omikron plc; or
(2) acquiring further shares in Omega plc.
Notes:
1. Omikron plc is a listed UK trading company, with 50,250,000 shares in issue. Its shares currently trade at 42p
per share.
2. Stuart and Rebecca helped start up the company, which was then Omega Ltd. The company was formed on
1 June 1990, when they each bought 24,000 shares for £1 per share. The company became listed on 1 May
1997. On this date their holding was subdivided, with each of them receiving 100 shares in Omega plc for each
share held in Omega Ltd. The issued share capital of Omega plc is currently 10,000,000 shares. The share price
is quoted at 208p – 216p with marked bargains at 207p, 211p, and 215p.
Stuart and Rebecca’s assets (following the sale of the Plymouth house but before any investment of the proceeds) are
as follows:
Assets Stuart Rebecca
£ £
Family house in London 450,000 450,000
Cash from property sale 422,100 –
Cash deposits 165,000 165,000
Portfolio of quoted investments – 250,000
Shares in Omega plc see above see above
Life insurance policy note 1 note 1
Note:
1. The life insurance policy will pay out a sum of £200,000 on the death of the first spouse to die.
Stuart has recently been diagnosed with a serious illness. He is expected to live for another two or three years only.
He is concerned about the possible inheritance tax that will arise on his death. Both he and Rebecca have wills whose
terms transfer all assets to the surviving spouse. Rebecca is in good health.
Neither Stuart nor Rebecca has made any previous chargeable lifetime transfers for the purposes of inheritance tax.
Required:
(a) Calculate the taxable capital gain on the sale of the Plymouth house in November 2005 (9 marks)
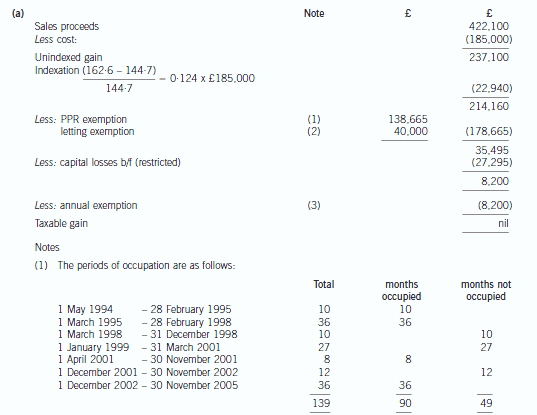
Note that the last 36 months count as deemed occupation, as the house was Stuart’s principal private residence (PPR)
at some point during his period of ownership.
The first 36 months of the period from 1 March 1995 to 31 March 2001 qualifies as a deemed occupation period as
Stuart and Rebecca returned to occupy the property on 1 April 2001. The remainder of the period will be treated as a
period of absence, although letting relief is available for part of the period (see below).
The exempt element of the gain is the proportion during which the property was occupied, real or deemed. This is
£138,665 (90/139 x £214,160).
(2) The chargeable gain is restricted for the period that the property was let out. This is restricted to the lowest of the
following:
(i) the gain attributable to the letting period (27/139 x 214,160) = £41,599
(ii) £40,000
(iii) the total exempt PPR gain = £138,665
i.e. £40,000.
(3) The taper relief is effectively wasted, having restricted losses b/f to preserve the annual exemption.
(b) Using the information contained in Appendix 1.1, discuss the financial performance of HLP and MAS,
incorporating details of the following in your discussion:
(i) Overall client fees (total and per consultation)
(ii) Advisory protection scheme consultation ‘utilisation levels’ for both property and commercial clients
(iii) Cost/expense levels. (10 marks)
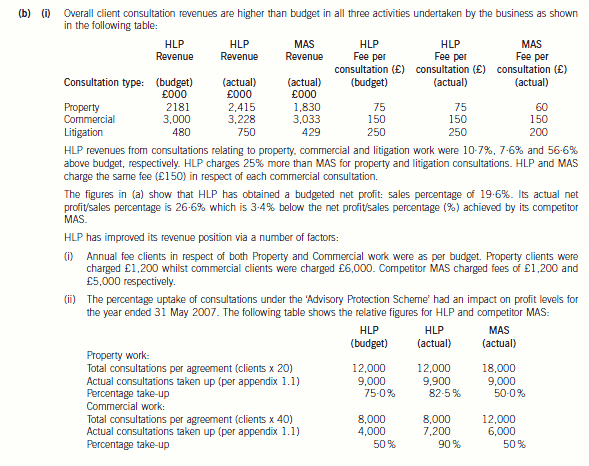
(ii) As far as annual agreements relating to property work are concerned, HLP had a take up rate of 82·5% whereas MAS
had a take up rate of only 50%. Therefore, HLP has ‘lost out’ to competitor MAS in relative financial terms as regards
the ‘take-up’ of consultations relating to property work. This is because both HLP and MAS received an annual fee from
each property client irrespective of the number of consultations given. MAS should therefore have had a better profit
margin from this area of business than HLP. However, the extent to which HLP has ‘lost out’ cannot be quantified since
we would need to know the variable costs per consultation and this detail is not available. What we do know is that
HLP earned actual revenue per effective consultation amounting to £90·90 whereas the budgeted revenue per
consultation amounted to £100. MAS earned £120 per effective consultation.
The same picture emerges from annual agreements relating to commercial work. HLP had a budgeted take up rate of
50%, however the actual take up rate during the period was 90%. MAS had an actual take up rate of 50%. The actual
revenue per effective consultation earned by HLP amounted to £167 whereas the budgeted revenue per consultation
amounted to £300. MAS earned £250 per effective consultation.
There could possibly be an upside to this situation for HLP in that it might be the case that the uptake of 90% of
consultations without further charge by clients holding annual agreements in respect of commercial work might be
indicative of a high level of customer satisfaction. It could on the other hand be indicative of a mindset which says ‘I
have already paid for these consultations therefore I am going to request them’.
(iii) Budgeted and actual salaries in HLP were £50,000 per annum, per advisor. Two additional advisors were employed
during the year in order to provide consultations in respect of commercial work. MAS paid a salary of £60,000 to each
advisor which is 20% higher than the salary of £50,000 paid to each advisor by HLP. Perhaps this is indicative that
the advisors employed by MAS are more experienced and/or better qualified than those employed by HLP.
HLP paid indemnity insurance of £250,000 which is £150,000 (150%) more than the amount of £100,000 paid by
MAS. This excess cost may well have arisen as a consequence of successful claims against HLP for negligence in
undertaking commercial work. It would be interesting to know whether HLP had been the subject of any successful
claims for negligent work during recent years as premiums invariably reflect the claims history of a business. Rather
worrying is the fact that HLP was subject to three such claims during the year ended 31 May 2007.
Significant subcontract costs were incurred by HLP during the year probably in an attempt to satisfy demand and retain
the goodwill of its clients. HLP incurred subcontract costs in respect of commercial properties which totalled £144,000.
These consultations earned revenue amounting to (320 x £150) = £48,000, hence a loss of £96,000 was incurred
in this area of the business.
HLP also paid £300,000 for 600 subcontract consultations in respect of litigation work. These consultations earned
revenue amounting to (600 x £250) = £150,000, hence a loss of £150,000 was incurred in this area of the business.
In contrast, MAS paid £7,000 for 20 subcontract consultations in respect of commercial work and an identical amount
for 20 subcontract consultations in respect of litigation work. These consultations earned revenue amounting to
20 x (£150 + £200) =£7,000. Therefore, a loss of only £7,000 was incurred in respect of subcontract consultations
by MAS.
Other operating expenses were budgeted at 53·0% of sales revenue. The actual level incurred was 40·7% of sales
revenue. The fixed/variable split of such costs is not given but it may well be the case that the fall in this percentage is
due to good cost control by HLP. However, it might simply be the case that the original budget was flawed. Competitor
MAS would appear to have a slightly superior cost structure to that of HLP since its other operating expenses amounted
to 38·4% of sales revenue. Further information is required in order to draw firmer conclusions regarding cost control
within both businesses.
5 Which of the following events after the balance sheet date would normally qualify as adjusting events according
to IAS 10 Events after the balance sheet date?
1 The bankruptcy of a credit customer with a balance outstanding at the balance sheet date.
2 A decline in the market value of investments.
3 The declaration of an ordinary dividend.
4 The determination of the cost of assets purchased before the balance sheet date.
A 1, 3, and 4
B 1 and 2 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 1 and 4 only
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-04-04
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2021-04-02
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2021-04-02
- 2020-10-14
- 2021-04-02
- 2020-10-14
- 2021-04-02
- 2021-04-04
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2021-04-02
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2021-04-02
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14
- 2020-10-14