黑龙江考生:ACCA考试成绩有效期是多久?
发布时间:2020-01-10
当人生面对许多选择的时候,我们需要谨慎;当我们没有选择的时候,就把压力当挑战,给自己一个信心,近日,参加ACCA考试的小伙伴来咨询我一些关于ACCA考试成绩有效期的问题,接下来51题库考试学习网将一一为其解答,建议大家收藏起来哟~
ACCA F阶段(AB-FM)课程考试已正式取消考试期限,换句话说,已经考完的各F阶段科目的考试成绩永久有效,不必重新考试。
不过,对于ACCA核心课程(P阶段)的考试成绩还是设置了7年的有效期。每位学员必须在通过第一科战略课程之日起,7年内完成所有的P阶段科目考试。(超出规定年限就只能重新考试)
ACCA考完一般都需要多久?
ACCA每年有4次考季,每次最多可以报考4门,每年最多报考8门,而ACCA考试全科共需要通过13门考试,所以,全部都能一次通过考试的情况下,考完ACCA最快也要近两年的时间。
ACCA一般都能考多久呢?
以ACCA近年的考试通过率来看,在无免考的情况下,从F1-P阶段完成考试的时间大致是2年-3年的时间。当然,如果你有相应的免考机会,比如拥有CPA、MPAcc等证书的话则可以免除部分科目的考试。如此一来,就能大大缩短你通过考试的时间了。
ACCA免考政策如下:
教育部认可高校毕业生
1)会计学专业 - 获得学士或硕士学位(金融/财务管理/审计专业也享受等同会计学专业的免试政策,下同) 免试5门课程;(即是本科或者研究生毕业)
2)会计学 - 辅修专业 免试3门课程;(双学位的,且第二专业是会计的)
3)法律专业 免试1门课程;
4)商务及管理专业 免试1门课程;
5)MPAcc专业(获得MPAcc学位或完成MPAcc大纲规定的所有课程、只有论文待完成) 免试5门课程*;
6)MBA - 获得MBA学位 免试3门课程;
7)非相关专业 无免试课程。
*注:部分院校的MPAcc专业已专门申请ACCA总部的免试审核,因此有多于5门的免试,具体请查询 ACCA总部官网。
教育部认可高校在校生(本科)
1)会计学专业 - 完成第一学年课程 可以注册为ACCA正式学员 无免试;
2)会计学专业 - 完成第二学年课程 免试3门课程;
3)其他专业 - 在校生 ACCA全球网站查询。
中国注册会计师资格
1)CICPA - 2009年“6+1”制度前获得全科合格证或者会员资格证 免试5门课程;
2)CICPA - 2009年“6+1”制度后获得全科合格证或者会员资格证 免试9门课程;
3)FIA(Foundation in
Accountancy) 通过FIA(Foundation in Accountancy)所有考试并取得相关工作经验 免试4门课程。
关于ACCA有效期的介绍
ACCA考试期限跟CPA一样实行轮废制,即需要在一定的时间里面考完规定的科目,否则成绩将会无效。那么这个时间怎么算的呢?
根据以前的规则,学员必须在首次报名注册后10年内通过所有考试,否则将注销其学员资格。后特许公认会计师公会ACCA对学员通过ACCA资格认证所有考试的时限做出了重要调整。F段成绩永久有效,P段要在7年内考完。根据新规则,专业阶段考试的时限将为7年。因此,国际财会基础资格(Foundations in Accountancy,简称FIA)的考试以及ACCA资格考试的基础阶段F1-F9考试将不再有通过时限。
“7年政策”意味着从你通过P阶段的第一门科目开始,7年内需完成P阶段所要求的所有ACCA考试科目。否则,从第8年开始,你第1年所考过的P阶段科目成绩将会被视为过期作废,须重新考试。
以上就是关于ACCA考试的相关信息,51题库考试学习网想告诉大家的是,其实一个证书好不好考并不是绝对的,这取决于你自己的努力程度。俗话说,有志者事竟成,相信只要通过自己的不懈努力,通过看似很困难的ACCA考试也不是太大的问题。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
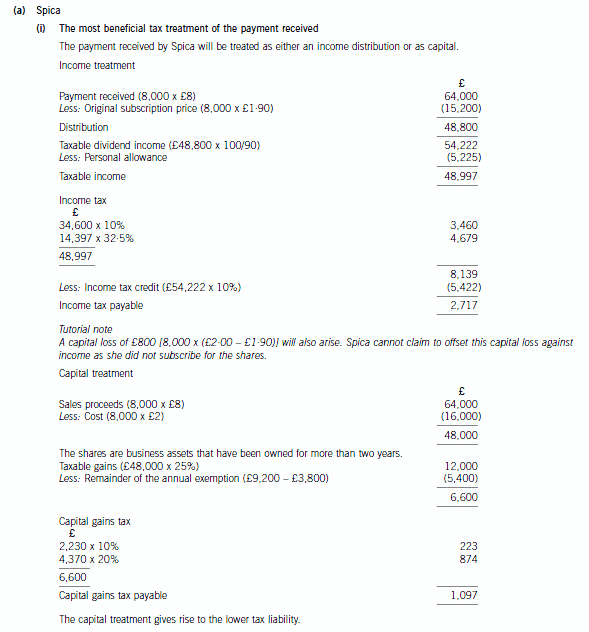
3 Spica, one of the director shareholders of Acrux Ltd, has been in dispute with the other shareholders over plans to
expand the company’s activities overseas. In order to resolve the position it has been agreed that Spica will sell her
shares back to the company. Once the purchase of her shares has taken place, the company intends to establish a
number of branches overseas and acquire a shareholding in a number of companies that are resident and trade in
overseas countries.
The following information has been obtained from client files and meetings with the parties involved.
Acrux Ltd:
– An unquoted UK resident company.
– Share capital consists of 50,000 ordinary shares issued at £1·90 per share in July 2000.
– None of the other shareholders has any connection with Spica.
The purchase of own shares:
– The company will purchase all of Spica’s shares for £8 per share.
– The transaction will take place by the end of 2008.
Spica:
– Purchased 8,000 shares in Acrux Ltd for £2 per share on 30 September 2003.
– Has no income in the tax year 2008/09.
– Has chargeable capital gains in the tax year 2008/09 of £3,800.
– Has houses in the UK and the country of Solaris and divides her time between them.
Investment in non-UK resident companies:
– Acrux Ltd will acquire between 15% and 20% of each of the non-UK resident companies.
– The companies will not be controlled foreign companies as the rates of tax in the overseas countries will be
between 23% and 42%.
– There may or may not be a double tax treaty between the UK and the overseas countries in which the companies
are resident. Where there is a treaty, it will be based on the OECD model treaty.
– None of the countries concerned levy withholding tax on dividends paid to UK companies.
– The directors of Acrux Ltd are concerned that the rate of tax suffered on the profits of the overseas companies
will be very high as they will be taxed in both the overseas country and in the UK.
Required:
(a) (i) Prepare detailed calculations to determine the most beneficial tax treatment of the payment Spica will
receive for her shares; (7 marks)
1 Your client, Island Co, is a manufacturer of machinery used in the coal extraction industry. You are currently planning
the audit of the financial statements for the year ended 30 November 2007. The draft financial statements show
revenue of $125 million (2006 – $103 million), profit before tax of $5·6 million (2006 – $5·1 million) and total
assets of $95 million (2006 – $90 million). Your firm was appointed as auditor to Island Co for the first time in June
2007.
Island Co designs, constructs and installs machinery for five key customers. Payment is due in three instalments: 50%
is due when the order is confirmed (stage one), 25% on delivery of the machinery (stage two), and 25% on successful
installation in the customer’s coal mine (stage three). Generally it takes six months from the order being finalised until
the final installation.
At 30 November, there is an amount outstanding of $2·85 million from Jacks Mine Co. The amount is a disputed
stage three payment. Jacks Mine Co is refusing to pay until the machinery, which was installed in August 2007, is
running at 100% efficiency.
One customer, Sawyer Co, communicated in November 2007, via its lawyers with Island Co, claiming damages for
injuries suffered by a drilling machine operator whose arm was severely injured when a machine malfunctioned. Kate
Shannon, the chief executive officer of Island Co, has told you that the claim is being ignored as it is generally known
that Sawyer Co has a poor health and safety record, and thus the accident was their fault. Two orders which were
placed by Sawyer Co in October 2007 have been cancelled.
Work in progress is valued at $8·5 million at 30 November 2007. A physical inventory count was held on
17 November 2007. The chief engineer estimated the stage of completion of each machine at that date. One of the
major components included in the coal extracting machinery is now being sourced from overseas. The new supplier,
Locke Co, is located in Spain and invoices Island Co in euros. There is a trade payable of $1·5 million owing to Locke
Co recorded within current liabilities.
All machines are supplied carrying a one year warranty. A warranty provision is recognised on the balance sheet at
$2·5 million (2006 – $2·4 million). Kate Shannon estimates the cost of repairing defective machinery reported by
customers, and this estimate forms the basis of the provision.
Kate Shannon owns 60% of the shares in Island Co. She also owns 55% of Pacific Co, which leases a head office to
Island Co. Kate is considering selling some of her shares in Island Co in late January 2008, and would like the audit
to be finished by that time.
Required:
(a) Using the information provided, identify and explain the principal audit risks, and any other matters to be
considered when planning the final audit for Island Co for the year ended 30 November 2007.
Note: your answer should be presented in the format of briefing notes to be used at a planning meeting.
Requirement (a) includes 2 professional marks. (13 marks)
1 ISLAND CO
(a) Briefing Notes
Subject: Principal Audit Risks – Island Co
Revenue Recognition – timing
Island Co raises sales invoices in three stages. There is potential for breach of IAS 18 Revenue, which states that revenue
should only be recognised once the seller has the right to receive it, in other words the seller has performed its contractual
obligations. This right does not necessarily correspond to amounts falling due for payment in accordance with an invoice
schedule agreed with a customer as part of a contract. Island Co appears to receive payment from its customers in advance
of performing any obligation, as the stage one invoice is raised when an order is confirmed i.e. before any work has actually
taken place. This creates the potential for revenue to be recognised too early, in advance of any performance of contractual
obligation. When a payment is received in advance of performance, a liability should be recognised equal to the amount
received, representing the obligation under the contract. Therefore a significant risk is that revenue is overstated and liabilities
understated.
Tutorial note: Equivalent guidance is also provided in IAS 11 Construction Contracts and credit will be awarded where
candidates discuss revenue recognition under IAS 11 as Island Co is providing a single substantial asset for a customer
under the terms of a contract.
Disputed receivable
The amount owed from Jacks Mine Co is highly material as it represents 50·9% of profit before tax, 2·3% of revenue, and
3% of total assets. The risk is that the receivable is overstated if no impairment of the disputed receivable is recognised.
Legal claim
The claim should be investigated seriously by Island Co. The chief executive officer’s (CEO) opinion that the claim will not
result in any financial consequence for Island Co is na?ve and flippant. Damages could be awarded against Island Co if it is
found that the machinery is faulty. The recurring high level of warranty provision implies that machinery faults are fairly
common and therefore the accident could be the result of a defective machine being supplied to Sawyer Co. The risk is that
no provision is created for the potential damages under IAS 37 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets, if the
likelihood of paying damages is considered probable. Alternatively, if the likelihood of damages being paid to Sawyer Co is
considered a possibility then a disclosure note should be made in the financial statements describing the nature and possible
financial effect of the contingent liability. As discussed below, the CEO, Kate Shannon, has an incentive not to make a
provision or disclose a contingent liability due to the planned share sale post year end.
A further risk is that any legal fees associated with the claim have not been accrued within the financial statements. As the
claim has arisen during the year, the expense must be included in this year’s income statement, even if the claim is still ongoing
at the year end.
The fact that the legal claim is effectively being ignored may cast doubts on the overall integrity of senior management, and
on the integrity of the financial statements. Management representations should be approached with a degree of professional
scepticism during the audit.
Sawyer Co has cancelled two orders. If the amounts are still outstanding at the year end then it is highly likely that Sawyer
Co will not pay the invoiced amounts, and thus receivables are overstated. If the stage one payments have already been made,
then Sawyer Co may claim a refund, in which case a provision should be made to repay the amount, or a contingent liability
disclosed in a note to the financial statements.
Sawyer Co is one of only five major customers, and losing this customer could have future going concern implications for
Island Co if a new source of revenue cannot be found to replace the lost income stream from Sawyer Co. If the legal claim
becomes public knowledge, and if Island Co is found to have supplied faulty machinery, then it will be difficult to attract new
customers.
A case of this nature could bring bad publicity to Island Co, a potential going concern issue if it results in any of the five key
customers terminating orders with Island Co. The auditors should plan to extend the going concern work programme to
incorporate the issues noted above.
Inventories
Work in progress is material to the financial statements, representing 8·9% of total assets. The inventory count was held two
weeks prior to the year end. There is an inherent risk that the valuation has not been correctly rolled forward to a year end
position.
The key risk is the estimation of the stage of completion of work in progress. This is subjective, and knowledge appears to
be confined to the chief engineer. Inventory could be overvalued if the machines are assessed to be more complete than they
actually are at the year end. Absorption of labour costs and overheads into each machine is a complex calculation and must
be done consistently with previous years.
It will also be important that consumable inventories not yet utilised on a machine, e.g. screws, nuts and bolts, are correctly
valued and included as inventories of raw materials within current assets.
Overseas supplier
As the supplier is new, controls may not yet have been established over the recording of foreign currency transactions.
Inherent risk is high as the trade payable should be retranslated using the year end exchange rate per IAS 21 The Effects of
Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates. If the retranslation is not performed at the year end, the trade payable could be
significantly over or under valued, depending on the movement of the dollar to euro exchange rate between the purchase date
and the year end. The components should remain at historic cost within inventory valuation and should not be retranslated
at the year end.
Warranty provision
The warranty provision is material at 2·6% of total assets (2006 – 2·7%). The provision has increased by only $100,000,
an increase of 4·2%, compared to a revenue increase of 21·4%. This could indicate an underprovision as the percentage
change in revenue would be expected to be in line with the percentage change in the warranty provision, unless significant
improvements had been made to the quality of machines installed for customers during the year. This appears unlikely given
the legal claim by Sawyer Co, and the machines installed at Jacks Mine Co operating inefficiently. The basis of the estimate
could be understated to avoid charging the increase in the provision as an expense through the income statement. This is of
special concern given that it is the CEO and majority shareholder who estimates the warranty provision.
Majority shareholder
Kate Shannon exerts control over Island Co via a majority shareholding, and by holding the position of CEO. This greatly
increases the inherent risk that the financial statements could be deliberately misstated, i.e. overvaluation of assets,
undervaluation of liabilities, and thus overstatement of profits. The risk is severe at this year end as Kate Shannon is hoping
to sell some Island Co shares post year end. As the price that she receives for these shares will be to a large extent influenced
by the balance sheet position of the company at 30 November 2007, she has a definite interest in manipulating the financial
statements for her own personal benefit. For example:
– Not recognising a provision or contingent liability for the legal claim from Sawyer Co
– Not providing for the potentially irrecoverable receivable from Jacks Mines Co
– Not increasing the warranty provision
– Recognising revenue earlier than permitted by IAS 18 Revenue.
Related party transactions
Kate Shannon controls Island Co and also controls Pacific Co. Transactions between the two companies should be disclosed
per IAS 24 Related Party Disclosures. There is risk that not all transactions have been disclosed, or that a transaction has
been disclosed at an inappropriate value. Details of the lease contract between the two companies should be disclosed within
a note to the financial statements, in particular, any amounts owed from Island Co to Pacific Co at 30 November 2007 should
be disclosed.
Other issues
– Kate Shannon wants the audit to be completed as soon as possible, which brings forward the deadline for completion
of the audit. The audit team may not have time to complete all necessary procedures, or there may not be time for
adequate reviews to be carried out on the work performed. Detection risk, and thus audit risk is increased, and the
overall quality of the audit could be jeopardised.
– This is especially important given that this is the first year audit and therefore the audit team will be working with a
steep learning curve. Audit procedures may take longer than originally planned, yet there is little time to extend
procedures where necessary.
– Kate Shannon may also exert considerable influence on the members of the audit team to ensure that the financial
statements show the best possible position of Island Co in view of her share sale. It is crucial that the audit team
members adhere strictly to ethical guidelines and that independence is beyond question.
– Due to the seriousness of the matters noted above, a final matter to be considered at the planning stage is that a second
partner review (Engagement Quality Control Review) should be considered for the audit this year end. A suitable
independent reviewer should be indentified, and time planned and budgeted for at the end of the assignment.
Conclusion
From the range of issues discussed in these briefing notes, it can be seen that the audit of Island Co will be a relatively high
risk engagement.
(ii) Advise Mr Fencer of the income tax implications of the proposed financing arrangements. (2 marks)
(ii) The income tax implications of the proposed financing arrangements
Mr Fencer has borrowed money from a UK bank in order to make a loan to Rapier Ltd, a close company. The interest
paid by Mr Fencer to the bank will be an allowable charge on income as long as he continues to hold more than 5% of
Rapier Ltd. Charges on income are deductible in arriving at an individual’s statutory total income.
Mr Fencer will receive interest from Rapier Ltd net of 20% income tax. The gross amount of interest will be subject to
income tax at either 10%, 20% or 40% depending on whether the income falls into Mr Fencer’s starting rate, basic rate
or higher rate tax band. Mr Fencer will obtain a tax credit for the 20% income tax suffered at source.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-01-01
- 2021-08-12
- 2020-04-14
- 2020-03-26
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-15
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-27
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-14
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-05-17
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-04-18
- 2019-03-27
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-05-17