听说ACCA考试挺难,是真的吗?
发布时间:2019-07-21
很多同学一听到ACCA考试科目一共有14门在加上全英文的,就觉得考试很难。那么ACCA难考吗?ACCA全球通过率高吗?通过率是多少?报名ACCA需要准备什么材料?这些问题对于一个准备报考ACCA的小伙伴来说一定是在心里徘徊已久的问题了。为此小编特地整理了如下内容。
一、ACCA考试难度
ACCA是全英文考试,教材有非常厚,有几十本,考试科目也非常多,有13门。这些因素凑在一块,无疑不在加深ACCA的难度。不过,ACCA考试的难度是以英国大学学位考试的难度为标准。具体而言,第一(f1-f3)、第二部分(f4-f9)的难度分别相当于学士学位高年级课程的考试难度,第三部分的考试相当于硕士学位最后阶段的考试。
第一部分的每门考试只是测试本门课程所包含的知识,着重于为后两个部分中实务性的课程所要运用的理论和技能打下基础。
第二部分的考试除了本门课程的内容之外,还会考到第一部分的一些知识,着重培养学员的分析能力。
第三部分的考试要求学员综合运用学到的知识、技能和决断力。不仅会考到以前的课程内容,还会考到邻近科目的内容。
二、ACCA全球单科通过率
ACCA全球单科通过率基本在30-40%左右,中国学员通过率为50-60%。
ACCA作为国际注册会计师,逐渐受到了越来越多财务人士的认可。ACCA证书的含金量比较高,但是它的报考门槛却不高,凡具有国家教育局认可的大专以上学历即可报名参加考试。
三、在线注册报名考试的时候,需要准备哪些资料呢?
1.学历/ 学位证明(高校在校生需提交学校出具的在校证明函及第一年所有课程考试合格的成绩单)的原件、复印件和译文;外地申请者不要邮寄原件,请把您的申请材料复印件加盖公司或学校公章,或邮寄公证件既可。
2.身份证的原件、复印件和译文;或提供护照,不需提交翻译件。
3.两张张两寸照片;(黑白彩色均可)
4.注册报名费(银行汇票或信用卡支付),请确认信用卡可以从国外付款,否则会影响您的注册返回时间;如果不能确定建议您用汇票交纳注册费。(信用卡支付请在英文网站上注册时直接输入信用卡详细信息,英国总部收到您的书面注册材料后才会从您的信用卡上划帐)。
综上所述就是关于ACCA问题的解答,希望对于各位小伙伴有用,小编将持续为大家更新ACCA相关内容。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Discuss how management’s judgement and the financial reporting infrastructure of a country can have a
significant impact on financial statements prepared under IFRS. (6 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
(b) Management judgement may have a greater impact under IFRS than generally was the case under national GAAP. IFRS
utilises fair values extensively. Management have to use their judgement in selecting valuation methods and formulating
assumptions when dealing with such areas as onerous contracts, share-based payments, pensions, intangible assets acquired
in business combinations and impairment of assets. Differences in methods or assumptions can have a major impact on
amounts recognised in financial statements. IAS1 expects companies to disclose the sensitivity of carrying amounts to the
methods, assumptions and estimates underpinning their calculation where there is a significant risk of material adjustment
to their carrying amounts within the next financial year. Often management’s judgement is that there is no ‘significant risk’
and they often fail to disclose the degree of estimation or uncertainty and thus comparability is affected.
In addition to the IFRSs themselves, a sound financial reporting infrastructure is required. This implies effective corporate
governance practices, high quality auditing standards and practices, and an effective enforcement or oversight mechanism.
Therefore, consistency and comparability of IFRS financial statements will also depend on the robust nature of the other
elements of the financial reporting infrastructure.
Many preparers of financial statements will have been trained in national GAAP and may not have been trained in the
principles underlying IFRS and this can lead to unintended inconsistencies when implementing IFRS especially where the
accounting profession does not have a CPD requirement. Additionally where the regulatory system of a country is not well
developed, there may not be sufficient market information to utilise fair value measurements and thus this could lead to
hypothetical markets being created or the use of mathematical modelling which again can lead to inconsistencies because of
lack of experience in those countries of utilising these techniques. This problem applies to other assessments or estimates
relating to such things as actuarial valuations, investment property valuations, impairment testing, etc.
The transition to IFRS can bring significant improvement to the quality of financial performance and improve comparability
worldwide. However, there are issues still remaining which can lead to inconsistency and lack of comparability with those
financial statements.
(c) Critically discuss FOUR principal roles of non-executive directors and explain the potential tensions between
these roles that WM’s non-executive directors may experience in advising on the disclosure of the
overestimation of the mallerite reserve. (12 marks)
(c) Non-executive directors
Roles of NEDs
Non-executive directors have four principal roles.
The strategy role recognises that NEDs are full members of the board and thus have the right and responsibility to contribute
to the strategic success of the organisation for the benefit of shareholders. The enterprise must have a clear strategic direction
and NEDs should be able to bring considerable experience from their lives and business experience to bear on ensuring that
chosen strategies are sound. In this role they may challenge any aspect of strategy they see fit and offer advice or input to
help to develop successful strategy.
In the scrutinising or performance role, NEDs are required to hold executive colleagues to account for decisions taken and
company performance. In this respect they are required to represent the shareholders’ interests against the possibility that
agency issues arise to reduce shareholder value.
The risk role involves NEDs ensuring the company has an adequate system of internal controls and systems of risk
management in place. This is often informed by prescribed codes (such as Turnbull in the UK) but some industries, such as
chemicals, have other systems in place, some of which fall under ISO standards. In this role, NEDs should satisfy themselves
on the integrity of financial information and that financial controls and systems of risk management are robust and defensible.
Finally, the ‘people’ role involves NEDs overseeing a range of responsibilities with regard to the management of the executive
members of the board. This typically involves issues on appointments and remuneration, but might also involve contractual
or disciplinary issues and succession planning.
Tutorial note: these four roles are as described in the UK Higgs Report and are also contained in the Combined Code 2003.
Tensions in NED roles in the case
This refers to a potential tension in the loyalties of the NEDs. Although the NED is accountable, through the chairman to the
shareholders and thus must always act in the economic best interests of the shareholders, he or she is also a part of the board
of the company and they may, in some situations, advise discretion. Withholding information might be judged correct because
of strategic considerations or longer-term shareholder interests. In most situations, NEDs will argue for greater transparency,
less concealment and more clarity of how and why a given action will be in the interests of shareholders.
The case of mallerite overestimation places the WM NEDs in a position of some tension. Any instinct to conceal the full extent
of the overestimate of the reserve for the possible protection of the company’s short-term value must be balanced against the
duty to serve longer-term strategic interests and the public interest. Whilst concealment would protect the company’s
reputation and share price in the short term, it would be a duty of the NEDs to point out that WM should observe transparency
as far as possible in its dealing with the shareholders and other capital market participants.
The following statements have been made about life cycle costing:
(i) It focuses on the short-term by identifying costs at the beginning of a product’s life cycle
(ii) It identifies all costs which arise in relation to the product each year and then calculates the product’s profitability on an annual basis
(iii) It accumulates a product’s costs over its whole life time and works out the overall profitability of a product
(iv) It allocates costs to each stage of a product’s life cycle and writes them off at the end of each stage
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A.(i) and (iii)
B.(iii) only
C.(i) and (iv)
D.(ii) only
All of the statements are false except statement (iii).
(iii) State how your answer in (ii) would differ if the sale were to be delayed until August 2006. (3 marks)
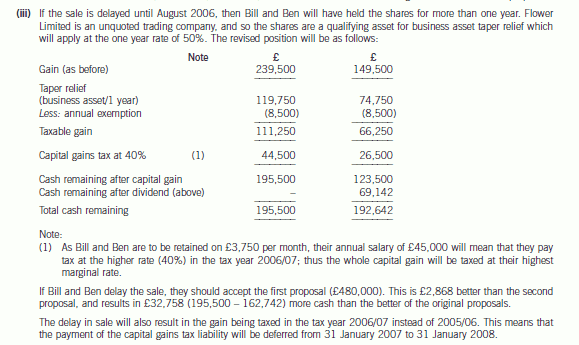
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-18
- 2020-04-09
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-04-04
- 2020-04-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-02
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-18
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-03-17
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-03-30
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-05-05
- 2021-05-14
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10