看过来:2020年湖南ACCA考试成绩查询有关通知
发布时间:2020-10-19
最近各位小伙伴都在关心ACCA考试成绩查询时间,为了帮助大家有个清晰的了解,现将有关内容分享如下,一起来看看吧。
2020年9月ACCA考试成绩已公布,考生现在登录ACCA官网即可查询。
ACCA考试成绩查询方式一共有三种,分别是:手机短信通知、邮件通知、在线查询。
(一)手机短信通知
(二)邮件通知
ACCA官方会根据所有考生的预留手机号和注册邮箱地址,通过短信和电子邮件的形式将成绩单发送给各位考生。不过,要实现这一功能,需要学员自行登录My ACCA账户中,设置邮件或短信通知成绩这一选项。
(三)在线查询
1. 进入ACCA官网http://www.accaglobal.com/hk/en.html 点击右上角My ACCA进行登录;
2. 输入账号、密码登录后进入主页面,点击Exam
status & Results;
3. 跳转页面后选择View your
status report;
ACCA成绩查询结果显示:
到ACCA全球官方网站http://www.accaglobal.com/hk/en.html;点击Myacca登陆,点左面框架里的“EXAMS”进入页面,中间有一段:
EXAM STATUS REPORT Your status report
provides details of the ACCA exams you have already passed and those you have
still to complete EXAM STATUS REPORT Your status report provides details of the
ACCA exams you have already passed and those you have still to complete View
your status report——这个是超级链接,点击进入就可以查看学员全部的考试分数记录。
9月ACCA考试成绩常见问题:
1、ACCA成绩有效期
ACCA 应用知识和技能课程阶段的成绩永久有效,但战略阶段课程成绩仅7年内有效。即:从学员通过战略阶段的第一门科目开始,7年内需完成战略阶段所要求的所有科目,否则从第8年开始第1年所考过的战略阶段科目成绩将会被视为过期作废。
此政策实行滚动式废除,也就是说不会在第8年时把之前7年所有考过的P阶段科目成绩都废除,只会废除第1年考过的战略阶段科目成绩,第9年会废除前2年所通过的战略阶段科目成绩,以此类推。
2、何时申请成绩复议,具体步骤
学员须在考试成绩发布日后的15个工作日内提出复议申请,具体申请的步骤为:
(1):登录进入Myacca;
(2):点击“Exam Status
and Results”里面有“Administrative Review”;
(3):填写和提交表格即可。
一旦成绩有误,那么学员会在下次报考截止日期前收到改正后的考试成绩。
说明:因考试政策、内容不断变化与调整,51题库考试学习网提供的考试信息仅供参考,如有异议,请考生以权威部门公布的内容为准!
以上就是今日51题库考试学习网分享的全部内容,小伙伴赶紧行动起来查询成绩吧。如查询期间遇到问题,可向51题库考试学习网咨询。更多ACCA考试相关内容尽在51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) Comment briefly on how divisional managers might respond to the results achieved and ONE potential
problem that might be experienced by Our Timbers Ltd. (2 marks)
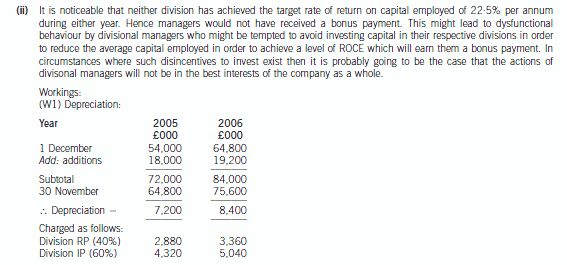
3 Joe Lawson is founder and Managing Director of Lawson Engineering, a medium sized, privately owned family
business specialising in the design and manufacture of precision engineering products. Its customers are major
industrial customers in the aerospace, automotive and chemical industries, many of which are globally recognised
companies. Lawson prides itself on the long-term relationships it has built up with these high profile customers. The
strength of these relationships is built on Lawson’s worldwide reputation for engineering excellence, which has
tangible recognition in its gaining prestigious international awards for product and process innovation and quality
performance. Lawson Engineering is a company name well known in its chosen international markets. Its reputation
has been enhanced by the awarding of a significant number of worldwide patents for the highly innovative products
it has designed. This in turn reflects the commitment to recruiting highly skilled engineers, facilitating positive staff
development and investing in significant research and development.
Its products command premium prices and are key to the superior performance of its customers’ products. Lawson
Engineering has also established long-term relationships with its main suppliers, particularly those making the exotic
materials built into their advanced products. Such relationships are crucial in research and development projects,
some of which take a number of years to come to fruition. Joe Lawson epitomises the ‘can do’ philosophy of the
company, always willing to take on the complex engineering challenges presented by his demanding customers.
Lawson Engineering now faces problems caused by its own success. Its current location, premises and facilities are
inadequate to allow the continued growth of the company. Joe is faced with the need to fund a new, expensive,
purpose-built facility on a new industrial estate. Although successful against a number of performance criteria, Lawson
Engineering’s performance against traditional financial measures has been relatively modest and unlikely to impress
the financial backers Joe wants to provide the necessary long-term capital.
Joe has become aware of the increasing attention paid to the intangible resources of a firm in a business. He
understands that you, as a strategy consultant, can advise him on the best way to show that his business should be
judged on the complete range of assets it possesses.
Required:
(a) Using models where appropriate, provide Joe with a resource analysis showing why the company’s intangible
resources and related capabilities should be taken into account when assessing Lawson Engineering’s case
for financial support. (12 marks)
(a) To: Joe Lawson, Managing Director, Lawson Engineering
From:
Business case for financial support
The treatment of intangible resources is an area of considerable concern to the financial community and in many ways the
situation that Lawson Engineering finds itself, is typical of the current confusion surrounding the value placed on intangible
resources. This in turn reflects a traditional concern that the strategic health and the financial health of a business are not
one and the same thing. Intangible resources cover a wide variety of assets and skills found in the business. These include
the intellectual property rights of patents; brands; trademarks; trade secrets etc through to people-determined assets such as
know-how; internal and external networks; organisational culture and the reputation of the company.
It is important for you to present a case which shows how the investment in intangible resources is just as important a source
of value creation for the customer as is investment in tangible assets such as plant and finance which are traditionally focused
on in financial statements of the firm’s well being. As one source expresses it, ‘for most companies, intangible resources
contribute much more to total asset value’. Kaplan and Norton in a 2004 article on intangible assets go further and argue
that ‘measuring the value of such intangible assets is the holy grail of accounting’. The increasing importance of service
businesses and service activities in the firm’s value chain compound the problems faced in getting a true reflection of the
firm’s ability to create value. One view is that the key value creation activity lies in the relationships a firm has with its key
stakeholders – its customers, suppliers and employees. These relationships develop into distinctive capabilities, defined as
‘something it can do that its competitors cannot’. These distinctive capabilities only become competitive advantage(s) when
the capability is applied to a relevant market. Firms attain a sustainable competitive advantage when they consistently
produce products or services with attributes that align with the key buying criteria for the majority of customers in the chosen
market.
Competitive advantage, to be strategically significant, must have the twin virtues of sustainability and appropriability.
Sustainability means the ability to sustain an advantage over a period of time. Fairly obviously, assets such as plant and
technology may be easily obtainable in the open market, however it is only when they are combined with less tangible
resources that advantages become sustainable over time because competitors cannot easily copy them. Equally significant
are intangible resources such as reputation and organisational culture in that they influence the firm’s ability to hold on to
or appropriate some of the value it creates. If other stakeholders both inside and outside the firm are able to take more than
their fair share of value created – for example customers forcing down prices or employees demanding excessive wage
increases – this will reduce the funds available for the firm to invest in further development of its intangible resources, and
as a consequence begin to weaken its competitive advantage.
Essentially, intangible resources can be separated into those capabilities that are based on assets and those that are based
on skills. As one source puts it asset based advantages are derived from ‘having’ a particular asset and skills based advantages
stem from the ability to be ‘doing’ things competitors are unable to do. Assets are those things that the firms ‘owns’ – the
intellectual property as embodied in patents, trademarks and associated brands, copyrights, recognised by law and
defendable against copying under that law. It is worth noting the effort and investment that many companies are putting into
defending their intellectual property against the threat of copying and piracy. A more recent asset that many firms spend
considerable time and effort in developing are databases on key activities in the firm’s value chain – customer databases are
only one of the possible sources of firm information and know-how. One of the most prized intangible assets is that of the
firm’s reputation which may reflect the power of the brands it has created. Reputation may be easier to maintain than create
and meets the key tests of sustainability. The capability to produce innovation consistently may be instrumental in creating
in the minds of customers the longer-term competitive advantage of reputation. Reputation is argued to represent the
knowledge and emotions the customer may associate with a firm’s product range and can therefore be a major factor in
securing the competitive advantage derived through effective differentiation.
A positive organisational culture, staff know-how and networks are equally important intangible sources of competitive
advantage. These by their very nature may be more dynamic than asset based intangibles and the know-how of employees
in particular is an intangible resource that results in the distinctive capabilities which differentiate the firm from its competitors.
Much has been written about the significance of organisational culture and the way it reflects the style. of top management,
the ‘can do’ culture of Lawson Engineering clearly creates a competitive advantage. One interesting study of how chief
executive officers rate their intangible resources in terms of their contribution to the overall success of the business showed
that company reputation, product reputation and employee know-how were the most highly regarded intangible resources.
Hamel and Prahalad argue that core competences rather than market position are the real source of competitive advantage.
They gave three tests to identify a core competence – firstly the competence should provide potential access to a wide variety
of markets and thus be capable of being leveraged to good effect, secondly, it should be relevant to the customer’s key buying
criteria and thirdly, it should be difficult for competitors to imitate.
The disadvantages of intangibles stem from the differing value placed on such assets and competences by the various
interested stakeholders. How should a company’s reputation be measured? How long will that reputation yield competitive
advantage, particularly in view of how swiftly such reputations can disappear? It seems likely that the financial markets with
their ability to reflect all knowledge and information about the firm in its share price increasingly will take the contribution of
intangibles into account.
Overall the case should be clearly made that the strengths of the company rests in its unique combination of intangible
resources and the capabilities – both internal and external – that it has. Financial health is not always the same as strategichealth and by any objective measure Lawson Engineering is worthy of support.
Yours,
Strategy consultant
(c) You have been making preliminary inquiries regarding matters arising from the previous year’s audit of Di Rollo.
It has been revealed that no action has been taken in response to the management letter prepared by the previous
auditors. Di Rollo’s management has explained that this was because it was ‘poorly prepared’ and ‘unhelpful’.
Required:
Briefly describe various criteria against which the effectiveness of a management letter may be assessed.
(7 marks)
(c) Management letter effectiveness criteria
Tutorial note: Candidates at this level must know that a management letter is a letter of weakness (also called post-audit
letter). NO marks will be awarded for consideration of any other letters (e.g. management representation letters, engagement
letters).
■ Timeliness – a management letter should be issued as soon as possible after completion of the audit procedures giving
rise to comment. This is particularly important when audit work is carried out on more than one audit visit and where
it is a matter of urgency that management make improvements to their procedures (e.g. where there is evidence of
serious weakness).
■ Clarity – wording must be clear so that recipients understand the significance of weaknesses that are being drawn to
their attention. It is particularly important that implications are explained clearly in terms that will prompt management
to respond positively (e.g. drawing attention to the risks of financial loss arising).
■ Illustrative – specific illustrative examples (e.g. of where controls have not been evidenced) should aid management in
understanding the nature of the problem(s).
■ Constructive comments/advice – recommendations for improvements must be practicable (i.e. appropriate and costeffective
in the light of the client’s resources) if the client is to take corrective action.
■ Conciseness – unnecessary volume will distract management from new/additional matters that require their attention.
For example, matters adequately dealt with in the internal auditor’s report should not be repeated.
■ Factual accuracy is essential. Inaccuracies will not only aggravate the client and appear unprofessional but could, in rare
circumstances, result in liability. Similarly, the letter should not criticise (or ‘cast aspersions’) on individual staff members
if it is the system that is inadequate.
■ A suitable structure – for example ‘tiered’, where the report contains matters of varying levels of significance. By directing
different classes of matters to the appropriate level or area of responsibility action by management can be taken more
speedily and constructively.
Tutorial note: An alternative structure might be one that sequences those recommendations that improve
profitability/cash flows before those that deal with information systems.
■ Inclusion of staff responses – both to advise senior management of action proposed/being taken by their staff and to give
credit to recommendations for improvements where it is due (e.g. where client’s staff have proposed recommendations).
■ Inclusion of management’s response – an indication of the actions that management intends to take is more likely to
result in action being taken. Discussing findings with management first should also ensure their factual accuracy.
■ Client’s perspective – implications from the client’s viewpoint (e.g. in terms of cost savings) are more likely to be acted
on than those expressed from an audit perspective (e.g. in terms of lowered audit risk).
■ Professional tone – should not be offensive. Comments that fault management’s knowledge, competence, motives or
integrity are likely to provoke defensive reactions. Comments should be positive/constructive by emphasising
solutions/benefits.
Tutorial notes: Other points that candidates may include:
■ Inclusion of matters of future relevance
■ Cost effectiveness – minutes of discussions with management instead of a formal weakness letter
■ Not raising ‘people problems’ in such a formal communication (a confidential discussion is preferable).
(b) Calculate the percentage of maximum capacity at which the zoo will break even during the year ending
30 November 2007. You should assume that 50% of the revenue from sales of ticket type ZC is attributable
to the zoo. (7 marks)

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-08-12
- 2020-02-23
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-01
- 2021-04-07
- 2020-08-12
- 2021-01-06
- 2019-03-20
- 2019-01-05
- 2020-09-05
- 2021-04-07
- 2019-03-20
- 2020-08-12
- 2020-08-12
- 2021-01-06
- 2021-01-08
- 2020-08-17
- 2021-01-06
- 2019-03-20
- 2020-08-12
- 2020-09-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-09-05
- 2020-08-12
- 2021-04-04
- 2020-10-18
- 2019-03-20
- 2019-03-20
- 2021-04-04