你知道考acca证书可以申请移民吗?
发布时间:2020-05-03
对于很多人来说,都希望有一天能够留学海外,或者移居他国。那么,你知道考acca证书可以申请移民吗?一起来看看吧!
很多人都想移居国外但苦无机会。但ACCA资格在英联邦国家的认可程度很高,一般在取得ACCA资格后,是可以向英国、加拿大、澳大利亚等国申请技术移民的。
一、ACCA了解
ACCA资格被认为是"国际财会界的通行证"。许多国家立法许可ACCA会员从事审计、投资顾问和破产执行工作。ACCA的认可雇主已经覆盖了四大会计师事务所、商行、投行、世界五百强企业、大型国有企业和大型民营企业等知名单位,这意味着获得ACCA资质将拥有更多的移民途径。
ACCA虽然在全球大部分地区和国家都有一定的认可度,但也并非是万能的,ACCA对移民澳洲没有多少帮助。也不属于技术移民的专业范围,在澳洲只承认CPAA或者是CA。不过,ACCA对于澳洲移民没有帮助但在国内,ACCA对进四大来说却是一项加分项,都会明确表示会优先录取ACCA等持证会员。
总的来说,ACCA对于国内的会计行业来说,还是比较有优势的。即便您没有13门全过,您过了前九门科目(即AB-FM)也能证明您的能力比较强,对于找工作和跳槽都比较有优势,尤其是对国际会计准则比较依赖的合资企业和外企当中。
二、ACCA对出国留学或者移民有帮助
1、认可度高
自ACCA和牛津布鲁克斯大学合作以来,申请该学位的人数每年呈“滚雪球”式递增。这充分证明了该学位证书的市场价值,它得到了市场的认可、得到了用人单位的青睐。
2、学历加分
对想要弥补学历上的欠缺的同学来说,考ACCA顺便拿下OBU学位可谓是一箭双雕。在求职过程中,海外学历总能博得雇主更多的青睐。不仅仅是海外学历意味着应聘者拥有更全面、先进的知识体系,还因为在获取海外学历的过程中培养了学生“搜集资料、筛选资料、分析资料”等多方面的能力。ACCA凭着与牛津布鲁克斯大学的合作,补齐了学员在这方面的短板。如果你能通过学习ACCA获得OBU学位,雇主一定不会忽略你的这些能力。
3、留学跳板
如果你能拿到牛津布鲁克斯大学一等荣誉学位证书,你还可以直接进入重点大学,甚至还能享受奖学金。
国内认可程度基本及时楼上所说的,由于是国外学校的学位,所以国内教育部不能对证书做认定。
三、那如何获取OBU学位呢?
学员在通过ACCA基础阶段课程的考试并完成在线职业操守训练课程,向该校提交一份研究报告及关键技能陈述书供校方评估,就有机会获得上述学士学位。
为了有机会取得OBU学位,学员最少必须通过ACCA FR、AA、FM三科考试。如果学员这三门获得了免试,他们就不能申请该学位。在此情况下,为了获得该学位,学员可以放弃这三门的免试,参加并通过考试。
以上就是51题库考试学习网今天分享的全部内容了,想了解更多关于考试的信息,请关注51题库考试学习网哦!预祝考试顺利!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(iii) Lateral or horizontal. (3 marks)
(iii) Lateral or horizontal. Traditional communication assumes a hierarchical structure with only vertical communication,however horizontal communication has become important and necessary in less formal organisations. It takes the form. of coordination with departmental managers or supervisors meeting regularly, problem solving with department members meeting to resolve an issue or information sharing and it also describes interdepartmental sharing of ideas or conflict resolution where there is a need to resolve interdepartmental friction.
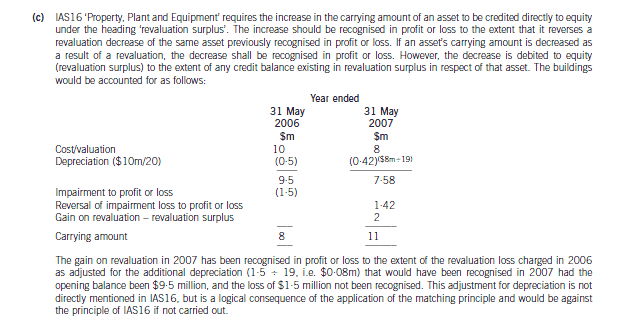
(c) Wader is reviewing the accounting treatment of its buildings. The company uses the ‘revaluation model’ for its
buildings. The buildings had originally cost $10 million on 1 June 2005 and had a useful economic life of
20 years. They are being depreciated on a straight line basis to a nil residual value. The buildings were revalued
downwards on 31 May 2006 to $8 million which was the buildings’ recoverable amount. At 31 May 2007 the
value of the buildings had risen to $11 million which is to be included in the financial statements. The company
is unsure how to treat the above events. (7 marks)
Required:
Discuss the accounting treatments of the above items in the financial statements for the year ended 31 May
2007.
Note: a discount rate of 5% should be used where necessary. Candidates should show suitable calculations where
necessary.
(c) Lamont owns a residential apartment above its head office. Until 31 December 2006 it was let for $3,000 a
month. Since 1 January 2007 it has been occupied rent-free by the senior sales executive. (6 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Lamont Co for the year ended
31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
(c) Rent-free accommodation
(i) Matters
■ The senior sales executive is a member of Lamont’s key management personnel and is therefore a related party.
■ The occupation of Lamont’s residential apartment by the senior sales executive is therefore a related party
transaction, even though no price is charged (IAS 24 Related Party Disclosures).
■ Related party transactions are material by nature and information about them should be disclosed so that users of
financial statements understand the potential effect of related party relationships on the financial statements.
■ The provision of ‘housing’ is a non-monetary benefit that should be included in the disclosure of key management
personnel compensation (within the category of short-term employee benefits).
■ The financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 should disclose the arrangement for providing the
senior sales executive with rent-free accommodation and its fair value (i.e. $3,000 per month).
Tutorial note: Since no price is charged for the transaction, rote-learned disclosures such as ‘the amount of outstanding
balances’ and ‘expense recognised in respect of bad debts’ are irrelevant.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Physical inspection of the apartment to confirm that it is occupied.
■ Written representation from the senior sales executive that he is occupying the apartment free of charge.
■ Written representation from the management board confirming that there are no related party transactions requiring
disclosure other than those that have been disclosed.
■ Inspection of the lease agreement with (or payments received from) the previous tenant to confirm the $3,000
monthly rental value.
Moonstar Co is a property development company which is planning to undertake a $200 million commercial property development. Moonstar Co has had some difficulties over the last few years, with some developments not generating the expected returns and the company has at times struggled to pay its finance costs. As a result Moonstar Co’s credit rating has been lowered, affecting the terms it can obtain for bank finance. Although Moonstar Co is listed on its local stock exchange, 75% of the share capital is held by members of the family who founded the company. The family members who are shareholders do not wish to subscribe for a rights issue and are unwilling to dilute their control over the company by authorising a new issue of equity shares. Moonstar Co’s board is therefore considering other methods of financing the development, which the directors believe will generate higher returns than other recent investments, as the country where Moonstar Co is based appears to be emerging from recession.
Securitisation proposals
One of the non-executive directors of Moonstar Co has proposed that it should raise funds by means of a securitisation process, transferring the rights to the rental income from the commercial property development to a special purpose vehicle. Her proposals assume that the leases will generate an income of 11% per annum to Moonstar Co over a ten-year period. She proposes that Moonstar Co should use 90% of the value of the investment for a collateralised loan obligation which should be structured as follows:
– 60% of the collateral value to support a tranche of A-rated floating rate loan notes offering investors LIBOR plus 150 basis points
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of B-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 12%
– 15% of the collateral value to support a tranche of C-rated fixed rate loan notes offering investors 13%
– 10% of the collateral value to support a tranche as subordinated certificates, with the return being the excess of receipts over payments from the securitisation process
The non-executive director believes that there will be sufficient demand for all tranches of the loan notes from investors. Investors will expect that the income stream from the development to be low risk, as they will expect the property market to improve with the recession coming to an end and enough potential lessees to be attracted by the new development.
The non-executive director predicts that there would be annual costs of $200,000 in administering the loan. She acknowledges that there would be interest rate risks associated with the proposal, and proposes a fixed for variable interest rate swap on the A-rated floating rate notes, exchanging LIBOR for 9·5%.
However the finance director believes that the prediction of the income from the development that the non-executive director has made is over-optimistic. He believes that it is most likely that the total value of the rental income will be 5% lower than the non-executive director has forecast. He believes that there is some risk that the returns could be so low as to jeopardise the income for the C-rated fixed rate loan note holders.
Islamic finance
Moonstar Co’s chief executive has wondered whether Sukuk finance would be a better way of funding the development than the securitisation.
Moonstar Co’s chairman has pointed out that a major bank in the country where Moonstar Co is located has begun to offer a range of Islamic financial products. The chairman has suggested that a Mudaraba contract would be the most appropriate method of providing the funds required for the investment.
Required:
(a) Calculate the amounts in $ which each of the tranches can expect to receive from the securitisation arrangement proposed by the non-executive director and discuss how the variability in rental income affects the returns from the securitisation. (11 marks)
(b) Discuss the benefits and risks for Moonstar Co associated with the securitisation arrangement that the non-executive director has proposed. (6 marks)
(c) (i) Discuss the suitability of Sukuk finance to fund the investment, including an assessment of its appeal to potential investors. (4 marks)
(ii) Discuss whether a Mudaraba contract would be an appropriate method of financing the investment and discuss why the bank may have concerns about providing finance by this method. (4 marks)
(a) An annual cash flow account compares the estimated cash flows receivable from the property against the liabilities within the securitisation process. The swap introduces leverage into the arrangement.
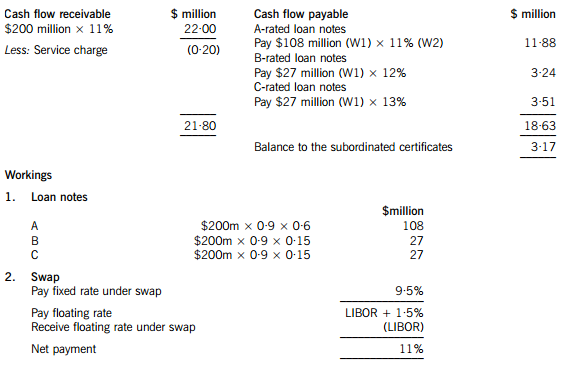
The holders of the certificates are expected to receive $3·17million on $18 million, giving them a return of 17·6%. If the cash flows are 5% lower than the non-executive director has predicted, annual revenue received will fall to $20·90 million, reducing the balance available for the subordinated certificates to $2·07 million, giving a return of 11·5% on the subordinated certificates, which is below the returns offered on the B and C-rated loan notes. The point at which the holders of the certificates will receive nothing and below which the holders of the C-rated loan notes will not receive their full income will be an annual income of $18·83 million (a return of 9·4%), which is 14·4% less than the income that the non-executive director has forecast.
(b) Benefits
The finance costs of the securitisation may be lower than the finance costs of ordinary loan capital. The cash flows from the commercial property development may be regarded as lower risk than Moonstar Co’s other revenue streams. This will impact upon the rates that Moonstar Co is able to offer borrowers.
The securitisation matches the assets of the future cash flows to the liabilities to loan note holders. The non-executive director is assuming a steady stream of lease income over the next 10 years, with the development probably being close to being fully occupied over that period.
The securitisation means that Moonstar Co is no longer concerned with the risk that the level of earnings from the properties will be insufficient to pay the finance costs. Risks have effectively been transferred to the loan note holders.
Risks
Not all of the tranches may appeal to investors. The risk-return relationship on the subordinated certificates does not look very appealing, with the return quite likely to be below what is received on the C-rated loan notes. Even the C-rated loan note holders may question the relationship between the risk and return if there is continued uncertainty in the property sector.
If Moonstar Co seeks funding from other sources for other developments, transferring out a lower risk income stream means that the residual risks associated with the rest of Moonstar Co’s portfolio will be higher. This may affect the availability and terms of other borrowing.
It appears that the size of the securitisation should be large enough for the costs to be bearable. However Moonstar Co may face unforeseen costs, possibly unexpected management or legal expenses.
(c) (i) Sukuk finance could be appropriate for the securitisation of the leasing portfolio. An asset-backed Sukuk would be the same kind of arrangement as the securitisation, where assets are transferred to a special purpose vehicle and the returns and repayments are directly financed by the income from the assets. The Sukuk holders would bear the risks and returns of the relationship.
The other type of Sukuk would be more like a sale and leaseback of the development. Here the Sukuk holders would be guaranteed a rental, so it would seem less appropriate for Moonstar Co if there is significant uncertainty about the returns from the development.
The main issue with the asset-backed Sukuk finance is whether it would be as appealing as certainly the A-tranche of the securitisation arrangement which the non-executive director has proposed. The safer income that the securitisation offers A-tranche investors may be more appealing to investors than a marginally better return from the Sukuk. There will also be costs involved in establishing and gaining approval for the Sukuk, although these costs may be less than for the securitisation arrangement described above.
(ii) A Mudaraba contract would involve the bank providing capital for Moonstar Co to invest in the development. Moonstar Co would manage the investment which the capital funded. Profits from the investment would be shared with the bank, but losses would be solely borne by the bank. A Mudaraba contract is essentially an equity partnership, so Moonstar Co might not face the threat to its credit rating which it would if it obtained ordinary loan finance for the development. A Mudaraba contract would also represent a diversification of sources of finance. It would not require the commitment to pay interest that loan finance would involve.
Moonstar Co would maintain control over the running of the project. A Mudaraba contract would offer a method of obtaining equity funding without the dilution of control which an issue of shares to external shareholders would bring. This is likely to make it appealing to Moonstar Co’s directors, given their desire to maintain a dominant influence over the business.
The bank would be concerned about the uncertainties regarding the rental income from the development. Although the lack of involvement by the bank might appeal to Moonstar Co's directors, the bank might not find it so attractive. The bank might be concerned about information asymmetry – that Moonstar Co’s management might be reluctant to supply the bank with the information it needs to judge how well its investment is performing.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2021-06-30
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-04-01
- 2019-12-06
- 2021-08-29
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-11
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-01-02
- 2021-06-26
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-25
- 2020-03-15
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-02
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-04
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-13
- 2020-01-10