云南省考生:ACCA国际会计师是什么证书?好考吗?
发布时间:2020-01-09
随着时代的更替,相信有越来越多的人听说过ACCA证书吧,也有很多人知晓其含金量和社会认可度是逐年在增加;因此,有不少人慕名前来咨询关于ACCA证书的相关事宜。今天51题库考试学习网就统一为大家介绍一下什么是ACCA?以及它的难易程度,感兴趣的同学可以收藏起来~
首先,何为ACCA呢?ACCA在国内称为"国际注册会计师",实际上是特许公认会计师公会(The Association Of Chartered Certified Accountants)的缩写,它是英国具有特许头衔的4家注册会计师协会之一,总部设立在英国,也是当今最知名的国际性会计师组织之一。ACCA资格被认为是"国际财会界的通行证"。许多国家立法许可ACCA会员从事审计、投资顾问和破产执行工作。它最有价值的地方是这个证书是全球都认可的,无论是你加入国企还是海外企业,相信这个证书一定会为你的履历上增添一抹光彩,从而增加你应试成功的几率。
ACCA目前在全球拥有近101个办事处和超过7400多家的认可雇主企业。覆盖事务所、金融服务、科技、制造等热门行业。可以说,拥有ACCA会员资格,就拥有了在世界各地就业的“通行证”。由此可见,ACCA证书的含金量是有多高。
因此ACCA证书也被会计界人士亲切地叫做:含着“金钥匙”的证书
那么ACCA持证者的就业方向,主要分为以下三大类:
一、金融服务类
大型银行和投资银行:无论是大型国有、股份制银行还是投资银行,都认可ACCA的国际资质,毕竟由于目前持有ACCA证书的人数还较少,能成功拿到ACCA证书的人想必一定是各方面能力都很突出的佼佼者。
二、事务所及咨询类
咨询企业:如麦肯锡、埃森哲等国际大牌咨询机构。
会计师事务所:国际四大会计师事务所:普华永道、毕马威、德勤、安永。国内八大会计师事务所:瑞华、立信、天健、信永中和、大华、大信、致同和天职国际。
这一部分对会计审计计算方面要求较高的,持有ACCA证书的人经过国际考核,认可度还是比较高的。
三、知名企业类
世界五百强:比如壳牌、英特尔、强生医疗、联合利华、百事食品等。
国内大中型企业或国企:比如中国中化、联想、中国移动、阿里巴巴、华为等。
这一部分的工作就比较强调语言交流能力,持有ACCA考试证书的人无论是英语交流还是中文交流相信都是手到擒来的。
在工作中ACCA会员会担任各类要职,其中担任公司副总裁/合伙人的就有5%,企业CFO有10%,财务总监的占12%,风控、审计、税务筹划经理各占9%、23%、16%。
说了这么多ACCA证书的好处,那么它好考吗?或许这是目前很多人关心的话题吧
首先,要给大家解释一下的是:ACCA是全英文的考试,包括考试题目、材料等都是英文这就是与国内考试的最大的区别。
其次,在于它的考试科目:多达13科目,在于从F阶段到P阶段简直是质的突破,不过通过率还是挺高的,所以想报的还是建议报考的。
(温馨提示:ACCA考试一个考季只能报考最多4个科目,且必须要F阶段全部科目通过之后才可以报考P阶段的)
虽然ACCA考试科目众多,但ACCA每个阶段完成后,ACCA官方协会都会颁发相应的证书鼓励ACCA考试小伙伴继续考下去,同时这些证书都可以帮助你找实习找工作、show给你的老板升职加薪、申请国外留学等等
以上就是关于ACCA考试的相关信息,51题库考试学习网想告诉大家的是,其实一个证书好不好考并不是绝对的,这取决于你自己的努力程度。俗话说,有志者事竟成,相信只要通过自己的不懈努力,通过看似很困难的ACCA考试也不是太大的问题。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(ii) How existing standards could be modified to meet the needs of SMEs. (6 marks
(ii) The development of IFRSs for SMEs as a modification of existing IFRSs
Most SMEs have a narrower range of users than listed entities. The main groups of users are likely to be the owners,
suppliers and lenders. In deciding upon the modifications to make to IFRS, the needs of the users will need to be taken
into account as well as the costs and other burdens imposed upon SMEs by the IFRS. There will have to be a relaxation
of some of the measurement and recognition criteria in IFRS in order to achieve the reduction in the costs and the
burdens. Some disclosure requirements, such as segmental reports and earnings per share, are intended to meet the
needs of listed entities, or to assist users in making forecasts of the future. Users of financial statements of SMEs often
do not make such kinds of forecasts. Thus these disclosures may not be relevant to SMEs, and a review of all of the
disclosure requirements in IFRS will be required to assess their appropriateness for SMEs.
The difficulty is determining which information is relevant to SMEs without making the information disclosed
meaningless or too narrow/restricted. It may mean that measurement requirements of a complex nature may have to be
omitted.
There are, however, rational grounds for justifying different treatments because of the different nature of the entities and
the existence of established practices at the time of the issue of an IFRS.
5 Jones and Cousin, a public quoted company, operate in twenty seven different countries and earn revenue and incur
costs in several currencies. The group develops, manufactures and markets products in the medical sector. The growth
of the group has been achieved by investment and acquisition. It is organised into three global business units which
manage their sales in international markets, and take full responsibility for strategy and business performance. Only
five per cent of the business is in the country of incorporation. Competition in the sector is quite fierce.
The group competes across a wide range of geographic and product markets and encourages its subsidiaries to
enhance local communities by reinvestment of profits in local educational projects. The group’s share of revenue in a
market sector is often determined by government policy. The markets contain a number of different competitors
including specialised and large international corporations. At present the group is awaiting regulatory approval for a
range of new products to grow its market share. The group lodges its patents for products and enters into legal
proceedings where necessary to protect patents. The products are sourced from a wide range of suppliers, who, once
approved both from a qualitative and ethical perspective, are generally given a long term contract for the supply of
goods. Obsolete products are disposed of with concern for the environment and the health of its customers, with
reusable materials normally being used. The industry is highly regulated in terms of medical and environmental laws
and regulations. The products normally carry a low health risk.
The Group has developed a set of corporate and social responsibility principles during the period which is the
responsibility of the Board of Directors. The Managing Director manages the risks arising from corporate and social
responsibility issues. The group wishes to retain and attract employees and follows policies which ensure equal
opportunity for all the employees. Employees are informed of management policies, and regularly receive in-house
training.
The Group enters into contracts for fixed rate currency swaps and uses floating to fixed rate interest rate swaps. The
cash flow effects of these swaps match the cash flows on the underlying financial instruments. All financial
instruments are accounted for as cash flow hedges. A significant amount of trading activity is denominated in the
Dinar and the Euro. The dollar is its functional currency.
Required:
(a) Describe the principles behind the Management Commentary discussing whether the commentary should be
mandatory or whether directors should be free to use their judgement as to what should be included in such
a commentary. (13 marks)
(a) The purpose of the Management Commentary (MC) is to present a balanced and comprehensive analysis of the development
position and performance of the entity in the year. Additionally, it deals with the main trends and factors behind the
development, position and performance of the entity during the financial year and those factors which are likely to affect the
entity in the future. The MC should enable users to assess the strategies adopted by the entity and the potential success of
those strategies. The key principles are as follows:
– The MC should be seen through the eyes of the directors and should focus on those matters relevant to the members of
the company.
– The review should look forward, identifying trends and factors relevant to the assessment of the current and future
performance of the entity.
– The MC should supplement and complement the financial statements so as to improve disclosure by providing additional
financial and non-financial information.
– The review should be comprehensive, understandable, reliable, relevant and represent faithfully the underlying strategies
and trends.
– Both good and bad aspects of the position of the entity should be discussed in a balanced and neutral way.
– The MC should be comparable over time, and the information should be supportable and consistent with the financial
statements to which it relates.
The increase in transparency and accountability improves the links between strategy, performance and risk, and the
evaluation of directors, and how they are paid.
A mandatory MC would make it easier for companies to judge the content of the reports and the necessary standard of
reporting, and would mean that the reports may be more robust and comparable. If the MC is not mandatory then this could
lead to uncertainty, risks of non compliance and possible mis-information being shown in the review. Directors may adopt a
policy of stating the minimum amount of disclosure which will frustrate the significant benefits to be gained from using
financial reporting as a strategic communication tool. ‘Necessity to report’ decisions will become subjective with possible legal
outcomes. The minimalist approach may also prove problematic if directors’ insurers reject claims because of ‘non-disclosure’
of information. Senior executives and the company board will play a more prominent role in deciding upon matters of MC
content than will be the case with mandatory reporting practice. Influential factors driving MC disclosure practice may become
the following rather than the broader issues:
(1) those expected to have short-term financial impact,
(2) whether shareholder decisions may be influenced,
(3) issues of risk management.
However, it can be argued that a mandatory MC could produce stereo-typed reports which would be based on a checklist
approach. Thus innovation in corporate reporting would be stifled. The power of market forces could be enough to ensure
that entities produce relevant and reliable information. Every company is different as are their challenges and risks and in anon-mandatory environment, companies could produce individual MCs to reflect those challenges and risks.
JJG Co is planning to raise $15 million of new finance for a major expansion of existing business and is considering a rights issue, a placing or an issue of bonds. The corporate objectives of JJG Co, as stated in its Annual Report, are to maximise the wealth of its shareholders and to achieve continuous growth in earnings per share. Recent financial information on JJG Co is as follows:
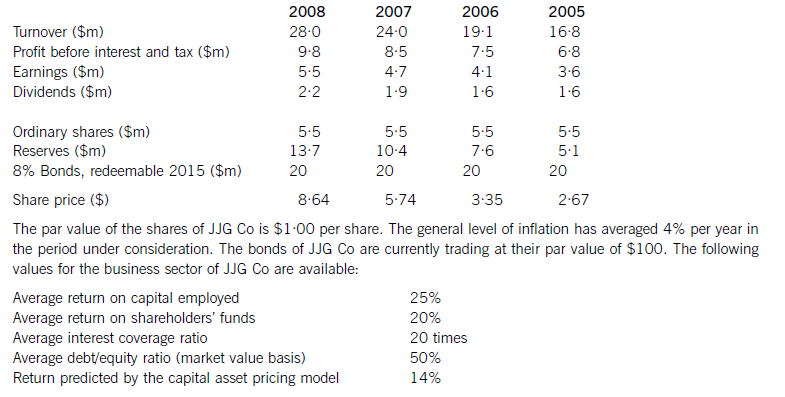
Required:
(a) Evaluate the financial performance of JJG Co, and analyse and discuss the extent to which the company has achieved its stated corporate objectives of:
(i) maximising the wealth of its shareholders;
(ii) achieving continuous growth in earnings per share.
Note: up to 7 marks are available for financial analysis.(12 marks)
(b) If the new finance is raised via a rights issue at $7·50 per share and the major expansion of business has
not yet begun, calculate and comment on the effect of the rights issue on:
(i) the share price of JJG Co;
(ii) the earnings per share of the company; and
(iii) the debt/equity ratio. (6 marks)
(c) Analyse and discuss the relative merits of a rights issue, a placing and an issue of bonds as ways of raising the finance for the expansion. (7 marks)
AchievementofcorporateobjectivesJJGCohasshareholderwealthmaximisationasanobjective.Thewealthofshareholdersisincreasedbydividendsreceivedandcapitalgainsonsharesowned.Totalshareholderreturncomparesthesumofthedividendreceivedandthecapitalgainwiththeopeningshareprice.TheshareholdersofJJGCohadareturnof58%in2008,comparedwithareturnpredictedbythecapitalassetpricingmodelof14%.Thelowestreturnshareholdershavereceivedwas21%andthehighestreturnwas82%.Onthisbasis,theshareholdersofthecompanyhaveexperiencedasignificantincreaseinwealth.Itisdebatablewhetherthishasbeenasaresultoftheactionsofthecompany,however.Sharepricesmayincreaseirrespectiveoftheactionsanddecisionsofmanagers,orevendespitethem.Infact,lookingatthedividendpersharehistoryofthecompany,therewasoneyear(2006)wheredividendswereconstant,eventhoughearningspershareincreased.Itisalsodifficulttoknowwhenwealthhasbeenmaximised.Anotherobjectiveofthecompanywastoachieveacontinuousincreaseinearningspershare.Analysisshowsthatearningspershareincreasedeveryyear,withanaverageincreaseof14·9%.Thisobjectiveappearstohavebeenachieved.CommentonfinancialperformanceReturnoncapitalemployed(ROCE)hasbeengrowingtowardsthesectoraverageof25%onayear-by-yearbasisfrom22%in2005.Thissteadygrowthintheprimaryaccountingratiocanbecontrastedwithirregulargrowthinturnover,thereasonsforwhichareunknown.Returnonshareholders’fundshasbeenconsistentlyhigherthantheaverageforthesector.ThismaybeduemoretothecapitalstructureofJJGCothantogoodperformancebythecompany,however,inthesensethatshareholders’fundsaresmalleronabookvaluebasisthanthelong-termdebtcapital.Ineverypreviousyearbut2008thegearingofthecompanywashigherthanthesectoraverage.(b)CalculationoftheoreticalexrightspershareCurrentshareprice=$8·64pershareCurrentnumberofshares=5·5millionsharesFinancetoberaised=$15mRightsissueprice=$7·50pershareNumberofsharesissued=15m/7·50=2millionsharesTheoreticalexrightspricepershare=((5·5mx8·64)+(2mx7·50))/7·5m=$8·34pershareThesharepricewouldfallfrom$8·64to$8·34pershareHowever,therewouldbenoeffectonshareholderwealthEffectofrightsissueonearningspershareCurrentEPS=100centspershareRevisedEPS=100x5·5m/7·5m=73centspershareTheEPSwouldfallfrom100centspershareto73centspershareHowever,asmentionedearlier,therewouldbenoeffectonshareholderwealthEffectofrightsissueonthedebt/equityratioCurrentdebt/equityratio=100x20/47·5=42%Revisedmarketvalueofequity=7·5mx8·34=$62·55millionReviseddebt/equityratio=100x20/62·55=32%Thedebt/equityratiowouldfallfrom42%to32%,whichiswellbelowthesectoraveragevalueandwouldsignalareductioninfinancialrisk(c)Thecurrentdebt/equityratioofJJGCois42%(20/47·5).Althoughthisislessthanthesectoraveragevalueof50%,itismoreusefulfromafinancialriskperspectivetolookattheextenttowhichinterestpaymentsarecoveredbyprofits.Theinterestonthebondissueis$1·6million(8%of$20m),givinganinterestcoverageratioof6·1times.IfJJGCohasoverdraftfinance,theinterestcoverageratiowillbelowerthanthis,butthereisinsufficientinformationtodetermineifanoverdraftexists.Theinterestcoverageratioisnotonlybelowthesectoraverage,itisalsolowenoughtobeacauseforconcern.Whiletheratioshowsanupwardtrendovertheperiodunderconsideration,itstillindicatesthatanissueoffurtherdebtwouldbeunwise.Aplacing,oranyissueofnewsharessuchasarightsissueorapublicoffer,woulddecreasegearing.Iftheexpansionofbusinessresultsinanincreaseinprofitbeforeinterestandtax,theinterestcoverageratiowillincreaseandfinancialriskwillfall.GiventhecurrentfinancialpositionofJJGCo,adecreaseinfinancialriskiscertainlypreferabletoanincrease.Aplacingwilldiluteownershipandcontrol,providingthenewequityissueistakenupbynewinstitutionalshareholders,whilearightsissuewillnotdiluteownershipandcontrol,providingexistingshareholderstakeuptheirrights.Abondissuedoesnothaveownershipandcontrolimplications,althoughrestrictiveornegativecovenantsinbondissuedocumentscanlimittheactionsofacompanyanditsmanagers.Allthreefinancingchoicesarelong-termsourcesoffinanceandsoareappropriateforalong-terminvestmentsuchastheproposedexpansionofexistingbusiness.Equityissuessuchasaplacingandarightsissuedonotrequiresecurity.Noinformationisprovidedonthenon-currentassetsofJJGCo,butitislikelythattheexistingbondissueissecured.Ifanewbondissuewasbeingconsidered,JJGCowouldneedtoconsiderwhetherithadsufficientnon-currentassetstoofferassecurity,althoughitislikelythatnewnon-currentassetswouldbeboughtaspartofthebusinessexpansion.
(c) The Shirtmaster division and Corporate Clothing division, though being part of the same group, operate largely
independently of one another.
Assess the costs and benefits of the two divisions continuing to operate independently of one another.
(15 marks)
(c) The Shirtmaster Group has decided to structure itself using two divisions who are dealing with very different markets,
customers and buying behaviours. In so doing the intention is to provide more value to the customer through a better
understanding of their needs. The existence of the two divisions also reflects the origins of the two family businesses.
Mintzberg in his work on organisation design and structure sees divisional configurations as being appropriate in relatively
simple and static environments where significant strategic power is delegated from the ‘strategic apex’ to the ‘middle line‘
general managers with responsibility for the performance of the division. Indeed one of the benefits cited for divisionalised
companies is their ability to provide a good training ground in strategic decision making for general managers who can then
progress to senior positions at company headquarters. Tony Masters’s reluctance to delegate real strategic decision making
power to the senior managers in the Shirtmaster division may be preventing those managers developing key managerial skills.
Using the Boston Box model one could classify the Shirtmaster division as a ‘dog’ with low market share in a market exhibiting
change but little growth. The Corporate Clothing division, by contrast, can be regarded as a ‘problem child’ having a small
share but of a growing market. Porter’s ‘better-off test’ needs to be met – are the two divisions better off being in the same
Group? As it stands there seems little synergy between the two divisions – there seems to be little evidence of the two divisions
sharing resources or transferring skills or learning between the two divisions. Their two value chains and systems are both
separate and different though on the face of it there are many activities that are similar. Operating independently may
encourage healthy competition between the two divisions and consequently better performance through better motivated staff.
Specialised competences such as Corporate Clothing division’s on-line response to customer orders and design changes are
more easily developed within a divisionalised structure. Performance can be clearly identified and controlled and resources
channelled to those areas showing potential. However, this may be at the expense of costly duplication of resources and an
inability to get the necessary scale to compete in either of their separate markets. Certainly, the lack of co-operation betweenthe divisions in areas such as information systems may lead to higher costs and poorer performance.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2019-12-31
- 2020-02-18
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-03-21
- 2020-05-17
- 2020-04-30
- 2019-12-28
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-08
- 2020-05-16
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-02-02
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-14
- 2020-03-27
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-18
- 2020-01-10