2019ACCA这些免考福利政策你都清楚了吗?
发布时间:2019-07-19
据2019年ACCA官网信息了解到,2019-2020年部分财务相关专业大学在校或毕业学生,在参加ACCA考试注册时,将获得一定科目的免试权。ACCA对于参加专业会计师考试(ACCA)的中国学员的免试政策详情如下:
一、ACCA对中国教育部认可的全日制大学在读生(会计或金融专业)设置的免试政策
1. 会计学或金融学(完成第一学年课程):可以注册为ACCA正式学员,无免试
2. 会计学或金融学(完成第二学年课程):免试3门课程(F1-F3)
3. 会计学或金融学(完成第三学年课程):免试3门课程(F1-F3)
4. 其他专业(在校生完成大一后):可以注册但无免试
*大学在读考生准备时间相对充足,可以每次报考三门课程,不建议报考四门,科目可以以F5/F6/F7三门计算类科目为主,通过逐步的学习加强英文能力,然后再学习F4、F8、F9有文字写作要求的科目。
二、ACCA对中国教育部认可高校毕业生设置的免试政策
1. 会计学(获得学士学位):免试5门课程(F1-F5)
2. 会计学(辅修专业):免试3门课程(F1-F3)
3. 金融专业:免试5门课程(F1-F5)
4. 法律专业:免试1门课程(F4)
5. 商务及管理专业:免试1门课程(F1)
6. MPAcc专业(获得MPAcc学位或完成MPAcc大纲规定的所有课程、只有论文待完成):原则上免试九门课程(F1–F9),其中F6(税务)的免试条件:CICPA全科通过或MPAcc课程中选修了"中国税制"课程。
7. MBA学位(获得MBA学位):免试3门课程(F1-F3)
8. 非相关专业:无免试
高校毕业生(即:在职人士),可以每次报考两门课程,小编建议不要超过三门课程,科目可以F5/F6/F7三门计算类科目为主,通过逐步的学习加强英文能力,然后再学习F4、F8、F9有文字写作要求的科目。
三、注册会计师考生
1. 2009年CICPA"6+1"新制度实行之前获得CICPA全科通过的人员:免试5门课程(F1-F4和F6)
2. 2009年CICPA"6+1"新制度实行之后获得CICPA全科通过的人员:免试9们课程(F1-F9)
3. 如果在学习ACCA基础阶段科目的过程中获得了CICPA全科合格证(须2009年"6+1"制度实行后的新版证书),可以自行决定是否申请追加免试。
*通过注会考试的考生对于财务知识基础相对好,一般F7、F8、F9通过率比其他考生高很多,建议从这些科目入手,加强英语的阅读和写作能力,注会考试大纲与ACCA考试大纲类似,只其是在审计及财务管理类的科目上,基本上知识点是相通的。F7会计科目中国际会计准则会计处理上略有不同。
四、其他
1. CMA(美国注册管理会计师)全科通过并取得证书:免试F1-F5、F8、F9(共免7门)
2. USCPA(美国注册会计师)全科通过:免试F1-F6、F8、F9(共免8门)
五、注意事项
1.在校生只有顺利通过整学年的课程才能够申请免试。
2.针对在校生的部分课程免试政策只适用于会计学专业全日制大学本科的在读学生,而不适用于硕士学位或大专学历的在读学生。
3.已完成MPAcc学位大纲规定课程,还需完成论文的学员也可注册并申请免试。但须提交由学校出具的通过所有MPAcc学位大纲规定课程的成绩单,并附注"该学员已通过所有MPAcc学位大纲规定课程,论文待完成"的说明。
4.特许学位(即海外大学与中国本地大学合作而授予海外大学学位的项目)— 部分完成时不能申请免试。
5.政策适用于在中国教育部认可的高等院校全部完成或部分完成本科课程的学生,而不考虑目前居住地点。
6.欲申请牛津•布鲁克斯大学学士学位的学员需放弃F7-F9的免试。
综合以上就是关于2019ACCA免试政策的全部内容,希望对于正在备考的小伙伴么有帮助,小编将持续更新相关ACCA的相关资讯。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
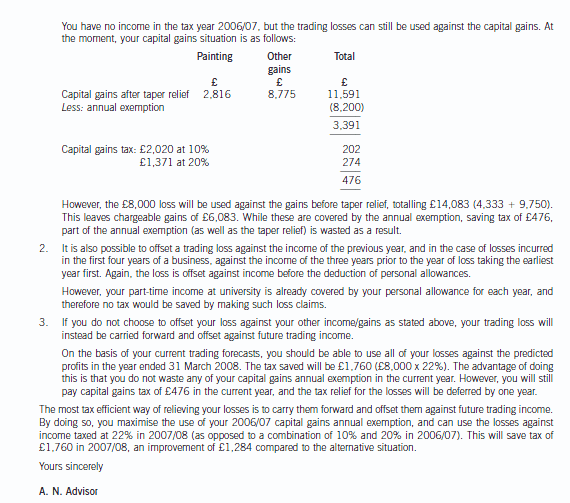
(ii) Write a letter to Donald advising him on the most tax efficient manner in which he can relieve the loss
incurred in the year to 31 March 2007. Your letter should briefly outline the types of loss relief available
and explain their relative merits in Donald’s situation. Assume that Donald will have no source of income
other than the business in the year of assessment 2006/07 and that any income he earned on a parttime
basis while at university was always less than his annual personal allowance. (9 marks)
Assume that the corporation tax rates and allowances for the financial year 2004 and the income tax rates
and allowances for 2004/05 apply throughout this question.
Relevant retail price index figures are:
January 1998 159·5
April 1998 162·6
(ii) [Donald’s address] [Firm’s address]
Dear Donald [Date]
I understand that you have incurred a tax loss in your first year of trading. The following options are available in respect
of this loss.
1. The first option is to use the trading loss against other forms of income in the same year. If such a claim is made,
losses are offset against income before personal allowances.
Any excess loss can still be offset against capital gains of the year. However, any offset against capital gains is
before both taper relief and annual exemptions.
(c) Discuss how the manipulation of financial statements by company accountants is inconsistent with their
responsibilities as members of the accounting profession setting out the distinguishing features of a
profession and the privileges that society gives to a profession. (Your answer should include reference to the
above scenario.) (7 marks)
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 marks for the quality of the discussion.
(c) Accounting and ethical implications of sale of inventory
Manipulation of financial statements often does not involve breaking laws but the purpose of financial statements is to present
a fair representation of the company’s position, and if the financial statements are misrepresented on purpose then this could
be deemed unethical. The financial statements in this case are being manipulated to show a certain outcome so that Hall
may be shown to be in a better financial position if the company is sold. The retained earnings of Hall will be increased by
$4 million, and the cash received would improve liquidity. Additionally this type of transaction was going to be carried out
again in the interim accounts if Hall was not sold. Accountants have the responsibility to issue financial statements that do
not mislead the public as the public assumes that such professionals are acting in an ethical capacity, thus giving the financial
statements credibility.
A profession is distinguished by having a:
(i) specialised body of knowledge
(ii) commitment to the social good
(iii) ability to regulate itself
(iv) high social status
Accountants should seek to promote or preserve the public interest. If the idea of a profession is to have any significance,
then it must make a bargain with society in which they promise conscientiously to serve the public interest. In return, society
allocates certain privileges. These might include one or more of the following:
– the right to engage in self-regulation
– the exclusive right to perform. particular functions
– special status
There is more to being an accountant than is captured by the definition of the professional. It can be argued that accountants
should have the presentation of truth, in a fair and accurate manner, as a goal.
3 Assume that today’s date is 10 May 2005.
You have recently been approached by Fred Flop. Fred is the managing director and 100% shareholder of Flop
Limited, a UK trading company with one wholly owned subsidiary. Both companies have a 31 March year-end.
Fred informs you that he is experiencing problems in dealing with aspects of his company tax returns. The company
accountant has been unable to keep up to date with matters, and Fred also believes that mistakes have been made
in the past. Fred needs assistance and tells you the following:
Year ended 31 March 2003
The corporation tax return for this period was not submitted until 2 November 2004, and corporation tax of £123,500
was paid at the same time. Profits chargeable to corporation tax were stated as £704,300.
A formal notice (CT203) requiring the company to file a self-assessment corporation tax return (dated 1 February
2004) had been received by the company on 4 February 2004.
A detailed examination of the accounts and tax computation has revealed the following.
– Computer equipment totalling £50,000 had been expensed in the accounts. No adjustment has been made in
the tax computation.
– A provision of £10,000 was made for repairs, but there is no evidence of supporting information.
– Legal and professional fees totalling £46,500 were allowed in full without any explanation. Fred has
subsequently produced the following analysis:
Analysis of legal & professional fees
£
Legal fees on a failed attempt to secure a trading loan 15,000
Debt collection agency fees 12,800
Obtaining planning consent for building extension 15,700
Accountant’s fees for preparing accounts 14,000
Legal fees relating to a trade dispute 19,000
– No enquiry has yet been raised by the Inland Revenue.
– Flop Ltd was a large company in terms of the Companies Act definition for the year in question.
– Flop Ltd had taxable profits of £595,000 in the previous year.
Year ended 31 March 2004
The corporation tax return has not yet been submitted for this year. The accounts are late and nearing completion,
with only one change still to be made. A notice requiring the company to file a self-assessment corporation tax return
(CT203) dated 27 July 2004 was received on 1 August 2004. No corporation tax has yet been paid.
1 – The computation currently shows profits chargeable to corporation tax of £815,000 before accounting
adjustments, and any adjustments for prior years.
– A company owing Flop Ltd £50,000 (excluding VAT) has gone into liquidation, and it is unlikely that any of this
money will be paid. The money has been outstanding since 3 September 2003, and the bad debt will need to
be included in the accounts.
1 Fred also believes there are problems in relation to the company’s VAT administration. The VAT return for the quarter
ended 31 March 2005 was submitted on 5 May 2005, and VAT of £24,000 was paid at the same time. The previous
return to 31 December 2004 was also submitted late. In addition, no account has been made for the VAT on the bad
debt. The VAT return for 30 June 2005 may also be late. Fred estimates the VAT liability for that quarter to be £8,250.
Required:
(a) (i) Calculate the revised corporation tax (CT) payable for the accounting periods ending 31 March 2003
and 2004 respectively. Your answer should include an explanation of the adjustments made as a result
of the information which has now come to light. (7 marks)
(ii) State, giving reasons, the due payment date of the corporation tax (CT) and the filing date of the
corporation tax return for each period, and identify any interest and penalties which may have arisen to
date. (8 marks)
(a) Calculation of corporation tax
Year ended 31 March 2003
Corporation tax payable
There are three adjusting items:.
(i) The computers are capital items, as they have an enduring benefit. These need to be added back in the Schedule D
Case I calculation, and capital allowances claimed instead. The company is not small or medium by Companies Act
definitions and therefore no first year allowances are available. Allowances of £12,500 (50,000 x 25%) can be claimed,
leaving a TWDV of £37,500.
(ii) The provision appears to be general in nature. In addition there is insufficient information to justify the provision and it
should be disallowed until such times as it is released or utilised.
(iii) Costs relating to trading loan relationships are allowable, as are costs relating to the trade (debt collection, trade disputes
and accounting work). Costs relating to capital items (£5,700) are not allowable so will have to be added back.
Total profit chargeable to corporation tax is therefore £704,300 + 50,000 – 12,500 + 10,000 + 5,700 = 757,500. There are two associates, and therefore the 30% tax rate starts at £1,500,000/2 = £750,000. Corporation tax payable is 30% x£757,500 = £227,250.
Payment date
Although the rate of tax is 30% and the company ‘large’, quarterly payments will not apply, as the company was not large in the previous year. The due date for payment of tax is therefore nine months and one day after the end of the tax accounting period (31 March 2003) i.e. 1 January 2004.
Filing date
This is the later of:
– 12 months after the end of the period of account: 31 March 2004
– 3 months after the date of the notice requiring the return 1 May 2004
i.e. 1 May 2004.

声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-03-21
- 2020-05-20
- 2020-05-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-11
- 2021-05-23
- 2020-04-07
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-05-14
- 2020-03-24
- 2020-03-18
- 2019-12-29
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-03-21
- 2020-04-22
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-02-12
- 2020-01-30
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-29
- 2019-07-19
- 2020-02-04
- 2020-04-16
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-19
- 2020-03-22
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-01