广西2020年ACCA国际会计师报考指南
发布时间:2020-01-08
对于近些年才映入大众眼球的ACCA证书,想必大家也是处于一知半解的状态吧,那么ACCA国际注册会计师证到底有什么用?适用的报考的人群又是哪些呢?这些问题一直困扰着大部分准备报考ACCA的同学们,不用担心,51题库考试学习网在这为大家解答疑惑,这些报考指南宝典要收藏哟~
首先大家先看看最新的免试政策,看看你符合哪个条件,到底能免试几个科目:
1.哪些人适合报考ACCA?
在校大学生(金融、会计、管理专业的)
有意向从事财务、金融、管理领域相关职业,教育部认可的高等院校在读学生,建议从大一开始学习ACCA。但需要你完成了大一整个学年的学习才可以报考ACCA。
大专及以上学历者
有意向从事财务、金融、管理领域相关职业,希望提升自身的学历水平和专业技能,扩大自己的人脉圈,ACCA可助你学历跟职业竞争力双丰收。
财务专业人士
正在从事或准备从事财会工作的专业人士,适合财务经理、财务主管、财务分析、财务顾问、投资经理等岗位人员。这一部分的人学习ACCA相比较前两者有优势的地方在于目前从事的工作与ACCA考试基础阶段的知识要点或多或少有重叠部分
高级管理人员
需要提升国际化思维能力,综合运用财务与管理知识做出战略决策的企业中高层管理者,高级管理人员对自身要求将会更高,而ACCA考试正是一个全方面对自己能力的考核的考试。例如公司总裁、财务总监、董秘等。
2.ACCA的效力?
ACCA一般用来和CPA相比。各自又有各自的优势,虽然对于大部分企业(各种集团和四大)而言,二者可以互换(作为会计知识水平的证明)。但前者作为全英文考试,更受外企喜爱;后者在国内有签字权(财务报告或审计报告签字),因而国内内资会计师事务所略看重一些。
3.ACCA考试改革具体的变化有哪些?
ACCA对其专业资格最高阶段的考试进行了创新设计,已于2018年9月以全新的战略专业阶段(Strategic Professional)考试取代之前的专业阶段考试体系,更加注重就业能力与核心技能在现代工作场所中的实际应用。更加注重培养理论和实践都杰出的人才
全新的战略专业阶段包括:
●战略商业领袖 (Strategic Business Leader)——这是一门基于现实商业情境的创新案例考试,考试时长为4小时。
●战略商业报告(Strategic Business Reporting)——这门新型考试将使学员接触到更广泛的财务和商业报告情境,培养他们的重要技能,从而向利益相关方解释和传达商业交易与报告的意义和影响。
●职业道德与专业技能模块(Ethics and Professional Skills
module)——作为首家在2008年向学员开设职业道德模块的专业会计师组织,ACCA对当前的职业道德模块进行了重新构建。新模块已上线。
这一阶段的考试不仅仅是对考试理论层面的考核,还必须要结合实践,所以此类改革更加完备了ACCA考核的标准,让ACCA证书的含金量更上一层楼~
4.ACCA和学校学习之间的关系?
首先,由于ACCA是英文版的国际会计课程,所以在很多课程上会出现ACCA先讲过课内再讲,亦或者相反。总体而言,ACCA的课程比学校课程更加靠近时代,理论层次稍高。同时,ACCA对于四大的大一大二大三的项目、实习项目和企业的实习项目也有一定的帮助。但如果是在大学期间报考ACCA考试的话,一定要协调好ACCA考试和学校课程的关系,比较学校课程的成绩和绩点与自身的毕业证书有关。
总结,这些报考宝典你Get到了吗?最后,还是希望大家能明白,Pass,Fail本身并无好坏,成绩只是结果,关键是我们如何以平静的心态去面对考试,去面对考试结果。不论Pass or Fail,我们都要真确应对!最后,51题库考试学习网预祝大家在三月份的考试全部PASS!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(a) The following information relates to Crosswire a publicly listed company.
Summarised statements of financial position as at:
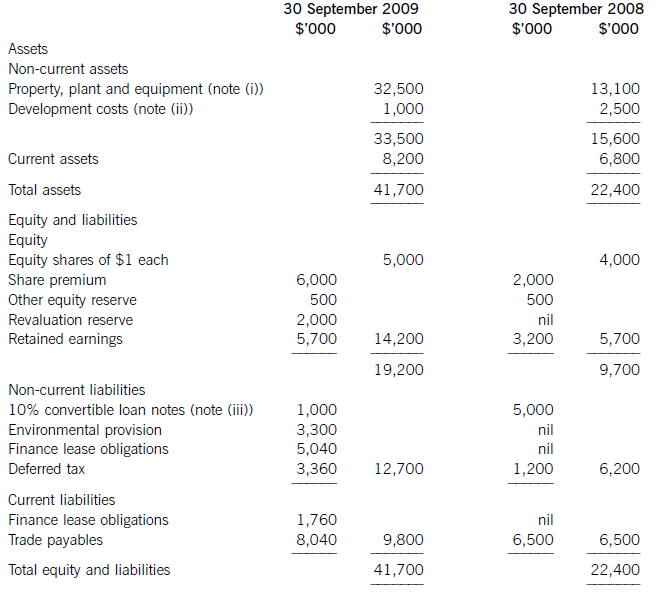
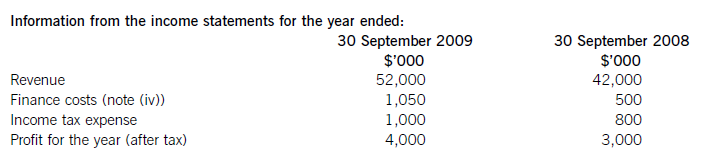
The following information is available:
(i) During the year to 30 September 2009, Crosswire embarked on a replacement and expansion programme for its non-current assets. The details of this programme are:
On 1 October 2008 Crosswire acquired a platinum mine at a cost of $5 million. A condition of mining the
platinum is a requirement to landscape the mining site at the end of its estimated life of ten years. The
present value of this cost at the date of the purchase was calculated at $3 million (in addition to the
purchase price of the mine of $5 million).
Also on 1 October 2008 Crosswire revalued its freehold land for the first time. The credit in the revaluation
reserve is the net amount of the revaluation after a transfer to deferred tax on the gain. The tax rate applicable to Crosswire for deferred tax is 20% per annum.
On 1 April 2009 Crosswire took out a finance lease for some new plant. The fair value of the plant was
$10 million. The lease agreement provided for an initial payment on 1 April 2009 of $2·4 million followed
by eight six-monthly payments of $1·2 million commencing 30 September 2009.
Plant disposed of during the year had a carrying amount of $500,000 and was sold for $1·2 million. The
remaining movement on the property, plant and equipment, after charging depreciation of $3 million, was
the cost of replacing plant.
(ii) From 1 October 2008 to 31 March 2009 a further $500,000 was spent completing the development
project at which date marketing and production started. The sales of the new product proved disappointing
and on 30 September 2009 the development costs were written down to $1 million via an impairment
charge.
(iii) During the year ended 30 September 2009, $4 million of the 10% convertible loan notes matured. The
loan note holders had the option of redemption at par in cash or to exchange them for equity shares on the
basis of 20 new shares for each $100 of loan notes. 75% of the loan-note holders chose the equity option.
Ignore any effect of this on the other equity reserve.
All the above items have been treated correctly according to International Financial Reporting Standards.
(iv) The finance costs are made up of:
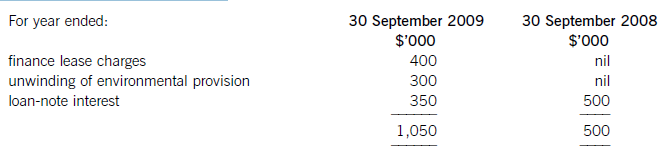
Required:
(i) Prepare a statement of the movements in the carrying amount of Crosswire’s non-current assets for the
year ended 30 September 2009; (9 marks)
(ii) Calculate the amounts that would appear under the headings of ‘cash flows from investing activities’
and ‘cash flows from financing activities’ in the statement of cash flows for Crosswire for the year ended
30 September 2009.
Note: Crosswire includes finance costs paid as a financing activity. (8 marks)
(b) A substantial shareholder has written to the directors of Crosswire expressing particular concern over the
deterioration of the company’s return on capital employed (ROCE)
Required:
Calculate Crosswire’s ROCE for the two years ended 30 September 2008 and 2009 and comment on the
apparent cause of its deterioration.
Note: ROCE should be taken as profit before interest on long-term borrowings and tax as a percentage of equity plus loan notes and finance lease obligations (at the year end). (8 marks)
(i)Thecashelementsoftheincreaseinproperty,plantandequipmentare$5millionforthemine(thecapitalisedenvironmentalprovisionisnotacashflow)and$2·4millionforthereplacementplantmakingatotalof$7·4million.(ii)Ofthe$4millionconvertibleloannotes(5,000–1,000)thatwereredeemedduringtheyear,75%($3million)ofthesewereexchangedforequitysharesonthebasisof20newsharesforeach$100inloannotes.Thiswouldcreate600,000(3,000/100x20)newsharesof$1eachandsharepremiumof$2·4million(3,000–600).As1million(5,000–4,000)newshareswereissuedintotal,400,000musthavebeenforcash.Theremainingincrease(aftertheeffectoftheconversion)inthesharepremiumof$1·6million(6,000–2,000b/f–2,400conversion)mustrelatetothecashissueofshares,thuscashproceedsfromtheissueofsharesis$2million(400nominalvalue+1,600premium).(iii)Theinitialleaseobligationis$10million(thefairvalueoftheplant).At30September2009totalleaseobligationsare$6·8million(5,040+1,760),thusrepaymentsintheyearwere$3·2million(10,000–6,800).(b)TakingthedefinitionofROCEfromthequestion:Fromtheaboveitcanbeclearlyseenthatthe2009operatingmarginhasimprovedbynearly1%point,despitethe$2millionimpairmentchargeonthewritedownofthedevelopmentproject.ThismeansthedeteriorationintheROCEisduetopoorerassetturnover.Thisimpliestherehasbeenadecreaseintheefficiencyintheuseofthecompany’sassetsthisyearcomparedtolastyear.Lookingatthemovementinthenon-currentassetsduringtheyearrevealssomemitigatingpoints:Thelandrevaluationhasincreasedthecarryingamountofproperty,plantandequipmentwithoutanyphysicalincreaseincapacity.Thisunfavourablydistortsthecurrentyear’sassetturnoverandROCEfigures.TheacquisitionoftheplatinummineappearstobeanewareaofoperationforCrosswirewhichmayhaveadifferent(perhapslower)ROCEtootherpreviousactivitiesoritmaybethatitwilltakesometimefortheminetocometofullproductioncapacity.Thesubstantialacquisitionoftheleasedplantwashalf-waythroughtheyearandcanonlyhavecontributedtotheyear’sresultsforsixmonthsatbest.Infutureperiodsafullyear’scontributioncanbeexpectedfromthisnewinvestmentinplantandthisshouldimprovebothassetturnoverandROCE.Insummary,thefallintheROCEmaybeduelargelytotheabovefactors(effectivelythereplacementandexpansionprogramme),ratherthantopooroperatingperformance,andinfutureperiodsthismaybereversed.ItshouldalsobenotedthathadtheROCEbeencalculatedontheaveragecapitalemployedduringtheyear(ratherthantheyearendcapitalemployed),whichisarguablymorecorrect,thenthedeteriorationintheROCEwouldnothavebeenaspronounced.
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Lamont Co. The company’s principal activity is wholesaling frozen
fish. The draft consolidated financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 show revenue of $67·0 million
(2006 – $62·3 million), profit before taxation of $11·9 million (2006 – $14·2 million) and total assets of
$48·0 million (2006 – $36·4 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In early 2007 a chemical leakage from refrigeration units owned by Lamont caused contamination of some of its
property. Lamont has incurred $0·3 million in clean up costs, $0·6 million in modernisation of the units to
prevent future leakage and a $30,000 fine to a regulatory agency. Apart from the fine, which has been expensed,
these costs have been capitalised as improvements. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Lamont Co for the year ended
31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
3 LAMONT CO
(a) Chemical leakage
(i) Matters
■ $30,000 fine is very immaterial (just 1/4% profit before tax). This is revenue expenditure and it is correct that it
has been expensed to the income statement.
■ $0·3 million represents 0·6% total assets and 2·5% profit before tax and is not material on its own. $0·6 million
represents 1·2% total assets and 5% profit before tax and is therefore material to the financial statements.
■ The $0·3 million clean-up costs should not have been capitalised as the condition of the property is not improved
as compared with its condition before the leakage occurred. Although not material in isolation this amount should
be adjusted for and expensed, thereby reducing the aggregate of uncorrected misstatements.
■ It may be correct that $0·6 million incurred in modernising the refrigeration units should be capitalised as a major
overhaul (IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment). However, any parts scrapped as a result of the modernisation
should be treated as disposals (i.e. written off to the income statement).
■ The carrying amount of the refrigeration units at 31 March 2007, including the $0·6 million for modernisation,
should not exceed recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell). If it does,
an allowance for the impairment loss arising must be recognised in accordance with IAS 36 Impairment of Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A breakdown/analysis of costs incurred on the clean-up and modernisation amounting to $0·3 million and
$0·6 million respectively.
■ Agreement of largest amounts to invoices from suppliers/consultants/sub-contractors, etc and settlement thereof
traced from the cash book to the bank statement.
■ Physical inspection of the refrigeration units to confirm their modernisation and that they are in working order. (Do
they contain frozen fish?)
■ Sample of components selected from the non-current asset register traced to the refrigeration units and inspected
to ensure continuing existence.
■ $30,000 penalty notice from the regulatory agency and corresponding cash book payment/payment per the bank
statement.
■ Written management representation that there are no further penalties that should be provided for or disclosed other
than the $30,000 that has been accounted for.
5 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Blod Co, a listed company, for the year ended 31 March 2008. Your
firm was appointed as auditors of Blod Co in September 2007. The audit work has been completed, and you are
reviewing the working papers in order to draft a report to those charged with governance. The statement of financial
position (balance sheet) shows total assets of $78 million (2007 – $66 million). The main business activity of Blod
Co is the manufacture of farm machinery.
During the audit of property, plant and equipment it was discovered that controls over capital expenditure transactions
had deteriorated during the year. Authorisation had not been gained for the purchase of office equipment with a cost
of $225,000. No material errors in the financial statements were revealed by audit procedures performed on property,
plant and equipment.
An internally generated brand name has been included in the statement of financial position (balance sheet) at a fair
value of $10 million. Audit working papers show that the matter was discussed with the financial controller, who
stated that the $10 million represents the present value of future cash flows estimated to be generated by the brand
name. The member of the audit team who completed the work programme on intangible assets has noted that this
treatment appears to be in breach of IAS 38 Intangible Assets, and that the management refuses to derecognise the
asset.
Problems were experienced in the audit of inventories. Due to an oversight by the internal auditors of Blod Co, the
external audit team did not receive a copy of inventory counting procedures prior to attending the count. This caused
a delay at the beginning of the inventory count, when the audit team had to quickly familiarise themselves with the
procedures. In addition, on the final audit, when the audit senior requested documentation to support the final
inventory valuation, it took two weeks for the information to be received because the accountant who had prepared
the schedules had mislaid them.
Required:
(a) (i) Identify the main purpose of including ‘findings from the audit’ (management letter points) in a report
to those charged with governance. (2 marks)
5 Blod Co
(a) (i) A report to those charged with governance is produced to communicate matters relating to the external audit to those
who are ultimately responsible for the financial statements. ISA 260 Communication of Audit Matters With Those
Charged With Governance requires the auditor to communicate many matters, including independence and other ethical
issues, the audit approach and scope, the details of management representations, and the findings of the audit. The
findings of the audit are commonly referred to as management letter points. By communicating these matters, the auditor
is confident that there is written documentation outlining all significant matters raised during the audit process, and that
such matters have been formally notified to the highest level of management of the client. For the management, the
report should ensure that they fully understand the scope and results of the audit service which has been provided, and
is likely to provide constructive comments to help them to fulfil their duties in relation to the financial statements and
accounting systems and controls more effectively. The report should also include, where relevant, any actions that
management has indicated they will take in relation to recommendations made by the auditors.
In relation to the law of contract, distinguish between and explain the effect of:
(a) a term and a mere representation; (3 marks)
(b) express and implied terms, paying particular regard to the circumstances under which terms may be implied in contracts. (7 marks)
This question requires candidates to consider the law relating to terms in contracts. It specifically requires the candidates to distinguish between terms and mere representations and then to establish the difference between express and implied terms in contracts.
(a) As the parties to a contract will be bound to perform. any promise they have contracted to undertake, it is important to distinguish between such statements that will be considered part of the contract, i.e. terms, and those other pre-contractual statements which are not considered to be part of the contract, i.e. mere representations. The reason for distinguishing between them is that there are different legal remedies available if either statement turns out to be incorrect.
A representation is a statement that induces a contract but does not become a term of the contract. In practice it is sometimes difficult to distinguish between the two, but in attempting to do so the courts will focus on when the statement was made in relation to the eventual contract, the importance of the statement in relation to the contract and whether or not the party making the statement had specialist knowledge on which the other party relied (Oscar Chess v Williams (1957) and Dick
Bentley v Arnold Smith Motors (1965)).
(b) Express terms are statements actually made by one of the parties with the intention that they become part of the contract and
thus binding and enforceable through court action if necessary. It is this intention that distinguishes the contractual term from
the mere representation, which, although it may induce the contractual agreement, does not become a term of the contract.
Failure to comply with the former gives rise to an action for breach of contract, whilst failure to comply with the latter only gives rise to an action for misrepresentation.
Such express statements may be made by word of mouth or in writing as long as they are sufficiently clear for them to be enforceable. Thus in Scammel v Ouston (1941) Ouston had ordered a van from the claimant on the understanding that the balance of the purchase price was to be paid ‘on hire purchase terms over two years’. When Scammel failed to deliver the van Ouston sued for breach of contract without success, the court holding that the supposed terms of the contract were too
uncertain to be enforceable. There was no doubt that Ouston wanted the van on hire purchase but his difficulty was that
Scammel operated a range of hire purchase terms and the precise conditions of his proposed hire purchase agreement were
never sufficiently determined.
Implied terms, however, are not actually stated or expressly included in the contract, but are introduced into the contract by implication. In other words the exact meaning and thus the terms of the contract are inferred from its context. Implied terms can be divided into three types.
Terms implied by statute
In this instance a particular piece of legislation states that certain terms have to be taken as constituting part of an agreement, even where the contractual agreement between the parties is itself silent as to that particular provision. For example, under s.5 of the Partnership Act 1890, every member of an ordinary partnership has the implied power to bind the partnership in a contract within its usual sphere of business. That particular implied power can be removed or reduced by the partnership agreement and any such removal or reduction of authority would be effective as long as the other party was aware of it. Some implied terms, however, are completely prescriptive and cannot be removed.
Terms implied by custom or usage
An agreement may be subject to terms that are customarily found in such contracts within a particular market, trade or locality. Once again this is the case even where it is not actually specified by the parties. For example, in Hutton v Warren (1836), it was held that customary usage permitted a farm tenant to claim an allowance for seed and labour on quitting his tenancy. It should be noted, however, that custom cannot override the express terms of an agreement (Les Affreteurs Reunnis SA v Walford (1919)).
Terms implied by the courts Generally, it is a matter for the parties concerned to decide the terms of a contract, but on occasion the court will presume that the parties intended to include a term which is not expressly stated. They will do so where it is necessary to give business efficacy to the contract.
Whether a term may be implied can be decided on the basis of the officious bystander test. Imagine two parties, A and B, negotiating a contract, when a third party, C, interrupts to suggest a particular provision. A and B reply that that particular term is understood. In just such a way, the court will decide that a term should be implied into a contract.
In The Moorcock (1889), the appellants, owners of a wharf, contracted with the respondents to permit them to discharge their ship at the wharf. It was apparent to both parties that when the tide was out the ship would rest on the riverbed. When the tide was out, the ship sustained damage by settling on a ridge. It was held that there was an implied warranty in the contract that the place of anchorage should be safe for the ship. As a consequence, the ship owner was entitled to damages for breach of that term.
Alternatively the courts will imply certain terms into unspecific contracts where the parties have not reduced the general agreement into specific details. Thus in contracts of employment the courts have asserted the existence of implied terms to impose duties on both employers and employees, although such implied terms can be overridden by express contractual provision to the contrary.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-03-21
- 2020-02-29
- 2020-05-15
- 2020-01-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-29
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-04-15
- 2020-02-20
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-19
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-28
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-21
- 2020-02-21
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-03-04
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-03-17
- 2020-03-13
- 2020-01-09