考取ACCA证书有什么好处,如何自学通过?
发布时间:2021-08-29
ACCA是国际财会领域含金量比较高的证书,近年来深受国内考生们的青睐,究竟考取ACCA证书有什么好处?如何自学通过呢?下面就跟随51题库考试学习网来看看详细内容吧!
一、ACCA的价值
ACCA的真正价值并不只是证书,而是学习的过程。ACCA教给了我们西方管理的精华,提升了我们的国际化视野。ACCA培养的不只是一名专业会计师,而是未来的CFO。ACCA更专注于培养复合型高级财务管理人才,着重培养学员的分析、判断、决策能力,更契合当前中国财会人才的需求。ACCA被许多国家立法许可,ACCA会员从事审计、投资顾问等工作。
二、ACCA的就业方向
学员通过ACCA资格考试之后,便拥有一项国际认可的专业会计师资格。ACCA专业资格在英国、中国及世界上其他一些主要国家,尤其在欧盟被认为具有法定会计师资格,会员可以成为执业会计师,受法律许可从事审计、税务、破产执行及投资顾问等专业会计师的工作。
ACCA学员的就业方向主要为:
(1)国际、国内金融机构、大型银行、投资银行。
如:中国工商银行、中国银行、中国国际金融公司、交通银行、汇丰银行、花旗银行、渣打银行、法国兴业银行、荷兰银行、高盛等。
(2)跨国企业,国内大型企业。
如:宝洁、联合利华、壳牌石油、微软、强生、GE、中石化、阿里巴巴集团、中国移动等大型企业。
ACCA如何自学通过?
1、持之以恒,坚持到底。
对于ACCA考试,越到最后关头越是要坚持到底。你需要坚持完成每天的学习任务以及背诵任务等,争取做到今日事今日毕。
2、心理状态,注意调节。
考试中,要克服满不在乎的自负心理,要抛弃“胜败在此一举”的负重心理,要克服畏首畏尾的胆怯心理。面对难、中、易的考题,要调节好心理,积极应对。
3、提高复习效率
无论从长期还是短期来看,工作时间越长,工作效率和效益就越低。如果连续两个月,每周都工作超过60个小时,你的生产力下降甚至会导致整个工期效率的下降。而同样的工作,一周40个小时就够了。这样的道理放在学习上也是行得通的,控制好时间,在该学习的时候专注投入,学累了就该休息。对我们来说,不过度劳累和充足的睡眠结合是要想变得更加有效率的保障。
好的,以上就是今天51题库考试学习网为大家分享的全部内容,大家是否清楚了呢?希望本篇文章能够帮助到大家,如有其他疑问请继续关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Donald actually decided to operate as a sole trader. The first year’s results of his business were not as he had
hoped, and he made a trading loss of £8,000 in the year to 31 March 2007. However, trading is now improving,
and Donald has sufficient orders to ensure that the business will make profits of at least £30,000 in the year to
31 March 2008.
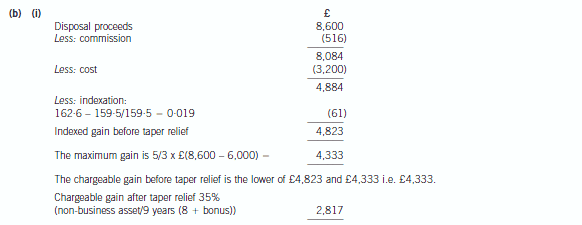
In order to raise funds to support his business over the last 15 months, Donald has sold a painting which was
given to him on the death of his grandmother in January 1998. The probate value of the painting was £3,200,
and Donald sold it for £8,084 (after deduction of 6% commission costs) in November 2006.
He also sold other assets in the year of assessment 2006/07, realising further chargeable gains of £8,775 (after
indexation of £249 and taper relief of £975).
Required:
(i) Calculate the chargeable gain on the disposal of the painting in November 2006. (4 marks)
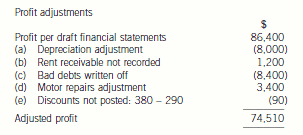
2 The draft financial statements of Choctaw, a limited liability company, for the year ended 31 December 2004 showed
a profit of $86,400. The trial balance did not balance, and a suspense account with a credit balance of $3,310 was
included in the balance sheet.
In subsequent checking the following errors were found:
(a) Depreciation of motor vehicles at 25 per cent was calculated for the year ended 31 December 2004 on the
reducing balance basis, and should have been calculated on the straight-line basis at 25 per cent.
Relevant figures:
Cost of motor vehicles $120,000, net book value at 1 January 2004, $88,000
(b) Rent received from subletting part of the office accommodation $1,200 had been put into the petty cash box.
No receivable balance had been recognised when the rent fell due and no entries had been made in the petty
cash book or elsewhere for it. The petty cash float in the trial balance is the amount according to the records,
which is $1,200 less than the actual balance in the box.
(c) Bad debts totalling $8,400 are to be written off.
(d) The opening accrual on the motor repairs account of $3,400, representing repair bills due but not paid at
31 December 2003, had not been brought down at 1 January 2004.
(e) The cash discount totals for December 2004 had not been posted to the discount accounts in the nominal ledger.
The figures were:
$
Discount allowed 380
Discount received 290
After the necessary entries, the suspense account balanced.
Required:
Prepare journal entries, with narratives, to correct the errors found, and prepare a statement showing the
necessary adjustments to the profit.
(10 marks)

(ii) authority; (3 marks)
(ii) AUTHORITY is the scope and amount of discretion given to a person to make decisions by virtue of the position held within the organisation. The authority and power structure of an organisation defines the part each member of the organisation is expected to perform. and the relationship between the organisation’s members so that its efforts are effective. The source of authority may be top down (as in formal organisations) or bottom up (as in social organizations and politics). In the scenario, authority is from the top and should be delegated downwards.
4 Hogg Products Company (HPC), based in a developing country, was recently wholly acquired by American Overseas
Investments (AOI), a North American holding company. The new owners took the opportunity to completely review
HPC’s management, culture and systems. One of the first things that AOI questioned was HPC’s longstanding
corporate code of ethics.
The board of AOI said that it had a general code of ethics that HPC, as an AOI subsidiary, should adopt. Simon Hogg,
the chief executive of HPC, disagreed however, and explained why HPC should retain its existing code. He said that
HPC had adopted its code of ethics in its home country which was often criticised for its unethical business behaviour.
Some other companies in the country were criticised for their ‘sweat shop’ conditions. HPC’s adoption of its code of
ethics, however, meant that it could always obtain orders from European customers on the guarantee that products
were made ethically and in compliance with its own highly regarded code of ethics. Mr Hogg explained that HPC had
an outstanding ethical reputation both locally and internationally and that reputation could be threatened if it was
forced to replace its existing code of ethics with AOI’s more general code.
When Ed Tanner, a senior director from AOI’s head office, visited Mr Hogg after the acquisition, he was shown HPC’s
operation in action. Mr Hogg pointed out that unlike some other employers in the industry, HPC didn’t employ child
labour. Mr Hogg explained that although it was allowed by law in the country, it was forbidden by HPC’s code of
ethics. Mr Hogg also explained that in his view, employing child labour was always ethically wrong. Mr Tanner asked
whether the money that children earned by working in the relatively safe conditions at HPC was an important source
of income for their families. Mr Hogg said that the money was important to them but even so, it was still wrong to
employ children, as it was exploitative and interfered with their education. He also said that it would alienate the
European customers who bought from HPC partly on the basis of the terms of its code of ethics.
Required:
(a) Describe the purposes and typical contents of a corporate code of ethics. (9 marks)
(a) Purposes of codes of ethics
To convey the ethical values of the company to interested audiences including employees, customers, communities and
shareholders.
To control unethical practice within the organisation by placing limits on behaviour and prescribing behaviour in given
situations.
To be a stimulant to improved ethical behaviour in the organisation by insisting on full compliance with the code.
[Tutorial note: other purposes, if relevant, will be rewarded]
Contents of a corporate code of ethics
The typical contents of a corporate code of ethics are as follows:
Values of the company. This might include notes on the strategic purpose of the organisation and any underlying beliefs,
values, assumptions or principles. Values may be expressed in terms of social and environmental perspectives, and
expressions of intent regarding compliance with best practice, etc.
Shareholders and suppliers of finance. In particular, how the company views the importance of sources of finances, how it
intends to communicate with them and any indications of how they will be treated in terms of transparency, truthfulness and
honesty.
Employees. Policies towards employees, which might include equal opportunities policies, training and development,
recruitment, retention and removal of staff. In the case of HPC, the policy on child labour will be covered by this part of the
code of ethics.
Customers. How the company intends to treat its customers, typically in terms of policy of customer satisfaction, product mix,
product quality, product information and complaints procedure.
Supply chain/suppliers. This is becoming an increasingly important part of ethical behaviour as stakeholders scrutinise where
and how companies source their products (e.g. farming practice, GM foods, fair trade issues, etc). Ethical policy on supply
chain might include undertakings to buy from certain approved suppliers only, to buy only above a certain level of quality, to
engage constructively with suppliers (e.g. for product development purposes) or not to buy from suppliers who do not meet
with their own ethical standards.
Community and wider society. This section concerns the manner in which the company aims to relate to a range of
stakeholders with whom it does not have a direct economic relationship (e.g. neighbours, opinion formers, pressure groups,
etc). It might include undertakings on consultation, ‘listening’, seeking consent, partnership arrangements (e.g. in community
relationships with local schools) and similar.
[Tutorial note: up to six points to be identified and described but similar valid general contents are acceptable]
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-08
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-05
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-02-01
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-03-07
- 2020-05-16
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-11
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-15
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-05-09
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-14
- 2020-04-09
- 2021-04-24
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-11-13
- 2020-01-03
- 2021-08-29
- 2020-02-27
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-04-20
- 2020-01-10