初学者,ACCA考试你应该这样开始!
发布时间:2020-03-12
ACCA考试科目比较多,尽管考生需要按照模块顺序报考,但是小伙伴们在面对考试时还是有种无从下手的感觉,尤其是才注册的新学员。鉴于此,51题库考试学习网在下面为大家带来ACCA考试中部分考试科目的考试特点及备考建议的相关信息,以供参考。
ACCA考试的不同科目在内容上是有一定关联的,比如F1《会计师与企业》是P1《公司治理,风险管理与职业道德》和P3《商务分析》的基础。这三个科目的内部知识点是有递进关系的,涵盖了企业组织,公司管理,会计和报告体系,内部财务控制,人力资源管理,会计职业道德几大内容。
虽然考试内容有关联,但是由于ACCA考试规则做了限制,考生是没法同时报考F1与P阶段,中间还隔着F4-F9这六门技能课程。因此小伙伴们在备考这三科时,能做的就是先打好F1的基础,在考到P1以及P3的时候不要把F1的知识还给了老师,毕竟ACCA考试费用较高。同时,考生也可以从这些课程中学到企业是如何运作的,会计师和审计师在企业中的作用,如何运用科学的人力资源管理方式,如何使企业和财务的各个环节的处理符合职业道德和价值观。因此,考生在学习F1时就应该认识到基础的重要性,从头开始打好地基。虽然F1难度较低,但是新考生可以通过该科目,了解ACCA的考查方式。
以上就是关于ACCA考试科目特点及备考建议的相关情况。51题库考试学习网提醒:对于初学者来说,在备考F阶段科目时,要注意及时复习,为最后的P阶段科目做准备。最后,51题库考试学习网预祝准备参加2020年ACCA考试的小伙伴都能顺利通过。
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Volcan, a long-established limited liability company. Volcan operates
a national supermarket chain of 23 stores, five of which are in the capital city, Urvina. All the stores are managed in
the same way with purchases being made through Volcan’s central buying department and product pricing, marketing,
advertising and human resources policies being decided centrally. The draft financial statements for the year ended
31 March 2005 show revenue of $303 million (2004 – $282 million), profit before taxation of $9·5 million (2004
– $7·3 million) and total assets of $178 million (2004 – $173 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) On 1 May 2005, Volcan announced its intention to downsize one of the stores in Urvina from a supermarket to
a ‘City Metro’ in response to a significant decline in the demand for supermarket-style. shopping in the capital.
The store will be closed throughout June, re-opening on 1 July 2005. Goodwill of $5·5 million was recognised
three years ago when this store, together with two others, was bought from a national competitor. It is Volcan’s
policy to write off goodwill over five years. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Volcan for the year ended
31 March 2005.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
3 VOLCAN
(a) Store impairment
(i) Matters
■ Materiality
? The cost of goodwill represents 3·1% of total assets and is therefore material.
? However, after three years the carrying amount of goodwill ($2·2m) represents only 1·2% of total assets –
and is therefore immaterial in the context of the balance sheet.
? The annual amortisation charge ($1·1m) represents 11·6% profit before tax (PBT) and is therefore also
material (to the income statement).
? The impact of writing off the whole of the carrying amount would be material to PBT (23%).
Tutorial note: The temporary closure of the supermarket does not constitute a discontinued operation under IFRS 5
‘Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations’.
■ Under IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ Volcan should no longer be writing goodwill off over five years but
subjecting it to an annual impairment test.
■ The announcement is after the balance sheet date and is therefore a non-adjusting event (IAS 10 ‘Events After the
Balance Sheet Date’) insofar as no provision for restructuring (for example) can be made.
■ However, the event provides evidence of a possible impairment of the cash-generating unit which is this store and,
in particular, the value of goodwill assigned to it.
■ If the carrying amount of goodwill ($2·2m) can be allocated on a reasonable and consistent basis to this and the
other two stores (purchased at the same time) Volcan’s management should have applied an impairment test to
the goodwill of the downsized store (this is likely to show impairment).
■ If more than 22% of goodwill is attributable to the City Metro store – then its write-off would be material to PBT
(22% × $2·2m ÷ $9·5m = 5%).
■ If the carrying amount of goodwill cannot be so allocated; the impairment test should be applied to the
cash-generating unit that is the three stores (this may not necessarily show impairment).
■ Management should have considered whether the other four stores in Urvina (and elsewhere) are similarly
impaired.
■ Going concern is unlikely to be an issue unless all the supermarkets are located in cities facing a downward trend
in demand.
Tutorial note: Marks will be awarded for stating the rules for recognition of an impairment loss for a cash-generating
unit. However, as it is expected that the majority of candidates will not deal with this matter, the rules of IAS 36 are
not reproduced here.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ Board minutes approving the store’s ‘facelift’ and documenting the need to address the fall in demand for it as a
supermarket.
■ Recomputation of the carrying amount of goodwill (2/5 × $5·5m = $2·2m).
■ A schedule identifying all the assets that relate to the store under review and the carrying amounts thereof agreed
to the underlying accounting records (e.g. non-current asset register).
■ Recalculation of value in use and/or fair value less costs to sell of the cash-generating unit (i.e. the store that is to
become the City Metro, or the three stores bought together) as at 31 March 2005.
Tutorial note: If just one of these amounts exceeds carrying amount there will be no impairment loss. Also, as
there is a plan NOT to sell the store it is most likely that value in use should be used.
■ Agreement of cash flow projections (e.g. to approved budgets/forecast revenues and costs for a maximum of five
years, unless a longer period can be justified).
■ Written management representation relating to the assumptions used in the preparation of financial budgets.
■ Agreement that the pre-tax discount rate used reflects current market assessments of the time value of money (and
the risks specific to the store) and is reasonable. For example, by comparison with Volcan’s weighted average cost
of capital.
■ Inspection of the store (if this month it should be closed for refurbishment).
■ Revenue budgets and cash flow projections for:
– the two stores purchased at the same time;
– the other stores in Urvina; and
– the stores elsewhere.
Also actual after-date sales by store compared with budget.
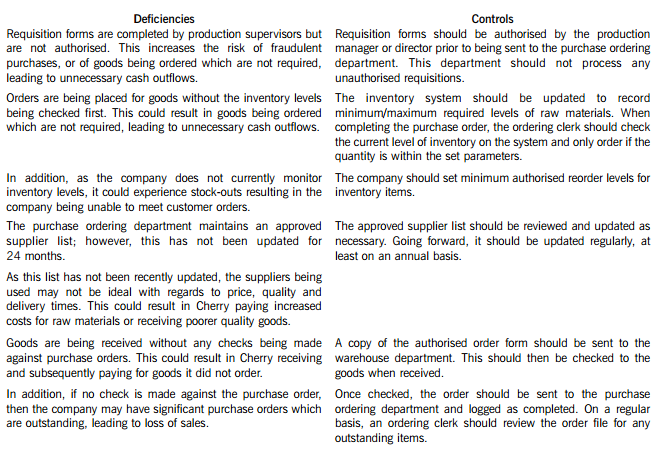
Cherry Blossom Co (Cherry) manufactures custom made furniture and its year end is 30 April. The company purchases its raw materials from a wide range of suppliers. Below is a description of Cherry’s purchasing system.
When production supervisors require raw materials, they complete a requisition form. and this is submitted to the purchase ordering department. Requisition forms do not require authorisation and no reference is made to the current inventory levels of the materials being requested. Staff in the purchase ordering department use the requisitions to raise sequentially numbered purchase orders based on the approved suppliers list, which was last updated 24 months ago. The purchasing director authorises the orders prior to these being sent to the suppliers.
When the goods are received, the warehouse department verifies the quantity to the suppliers despatch note and checks that the quality of the goods received are satisfactory. They complete a sequentially numbered goods received note (GRN) and send a copy of the GRN to the finance department.
Purchase invoices are sent directly to the purchase ledger clerk, who stores them in a manual file until the end of each week. He then inputs them into the purchase ledger using batch controls and gives each invoice a unique number based on the supplier code. The invoices are reviewed and authorised for payment by the finance director, but the actual payment is only made 60 days after the invoice is input into the system.
Required:
In respect of the purchasing system of Cherry Blossom Co:
(i) Identify and explain FIVE deficiencies; and
(ii) Recommend a control to address each of these deficiencies.
Note: The total marks will be split equally between each part.
Cherry Blossom Co’s (Cherry) purchasing system deficiencies and controls

3 Spica, one of the director shareholders of Acrux Ltd, has been in dispute with the other shareholders over plans to
expand the company’s activities overseas. In order to resolve the position it has been agreed that Spica will sell her
shares back to the company. Once the purchase of her shares has taken place, the company intends to establish a
number of branches overseas and acquire a shareholding in a number of companies that are resident and trade in
overseas countries.
The following information has been obtained from client files and meetings with the parties involved.
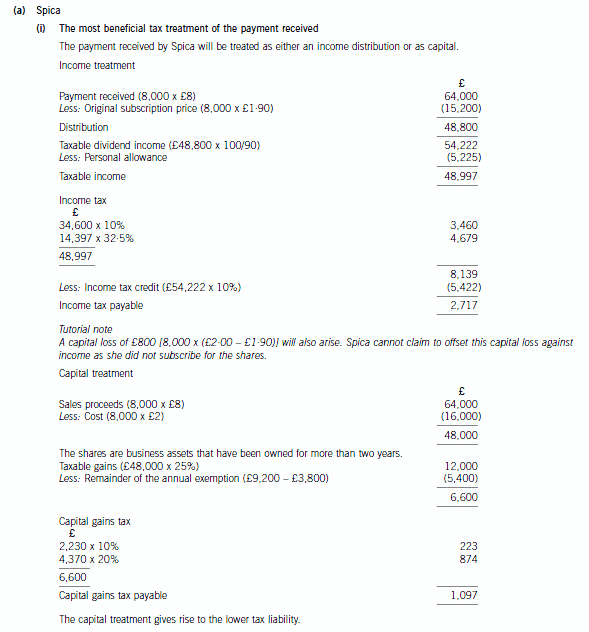
Acrux Ltd:
– An unquoted UK resident company.
– Share capital consists of 50,000 ordinary shares issued at £1·90 per share in July 2000.
– None of the other shareholders has any connection with Spica.
The purchase of own shares:
– The company will purchase all of Spica’s shares for £8 per share.
– The transaction will take place by the end of 2008.
Spica:
– Purchased 8,000 shares in Acrux Ltd for £2 per share on 30 September 2003.
– Has no income in the tax year 2008/09.
– Has chargeable capital gains in the tax year 2008/09 of £3,800.
– Has houses in the UK and the country of Solaris and divides her time between them.
Investment in non-UK resident companies:
– Acrux Ltd will acquire between 15% and 20% of each of the non-UK resident companies.
– The companies will not be controlled foreign companies as the rates of tax in the overseas countries will be
between 23% and 42%.
– There may or may not be a double tax treaty between the UK and the overseas countries in which the companies
are resident. Where there is a treaty, it will be based on the OECD model treaty.
– None of the countries concerned levy withholding tax on dividends paid to UK companies.
– The directors of Acrux Ltd are concerned that the rate of tax suffered on the profits of the overseas companies
will be very high as they will be taxed in both the overseas country and in the UK.
Required:
(a) (i) Prepare detailed calculations to determine the most beneficial tax treatment of the payment Spica will
receive for her shares; (7 marks)
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-03-01
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-05
- 2020-03-01
- 2020-03-11
- 2020-03-01
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09