在香港,ACCA考试通过了你不这样做你还是不能拿到证书
发布时间:2020-01-08
近些年,随着各式各样的考试风靡全国以来,ACCA证书也是从众多资格证书里脱颖而出,逐渐映入大众的眼帘。了解它的人称之为“金饭碗”,那么有些通过所以ACCA考试全部科目的小伙伴就来咨询51题库考试学习网,成绩通过之后,证书是怎么样领取呢?是等待官方邮寄过来?还是自己去申请领证呢?这些疑问51题库考试学习网会为大家逐一解决,请大家耐心地往下看哟~
首先要恭喜你成为了ACCA准会员了,当你通过14门ACCA考试的那一科开始,你就成为准会员了。但是需要注意的是从准会员并不是会员,想从准会员到ACCA会员,这些事情你必须要做:
1.ACCA每年2月份和8月份会分别公布12月份和6月份的考试成绩。每一个通过ACCA全部考试的学员随后会收到ACCA英国总部邮寄的《ACCA会员或准会员申请手册》(一般收到时间是3月初和9月初)。每人必须根据自身的情况,如是否满足ACCA相关工作经验要求,向ACCA英国申请成为会员或准会员。
2.ACCA总部收到学员申请后,不论是申请会员和准会员,都会给学员颁发ACCA准会员证书,以确认学员成功通过所有考试。
3.对于申请会员的学员,要求如实填写会员申请手册,并总结平时记录的STR(Student Training Record)中的主要工作经历和取得的工作能力,填入申请手册(在递交会员申请表时,可以暂时不提交STR,但是,一旦ACCA英国总部通知需要提交STR,以便了解更详细的信息完成评估,学员需要再补交STR)。ACCA英国总部会对学员所填的工作记录进行评估和并与其监督人联系进行核查,确认无误后,则批准其成为ACCA会员,一般这个过程需要两个月的时间。
4.如果学员在规定的时间内没有收到以上申请手册,可以直接登陆ACCA全球官网下载。
5.对于暂时未满足工作经验的准会员,可以在条件满足的任何时间向ACCA递交ACCA会员申请表。
完成了以上所有步骤之后,你就算是成功申请ACCA会员了,只需要等待官方发送证书即可。
都说,阳光总在风雨后,当你拿到通过自己努力获得的证书时,那份喜悦肯定是独一无二的,那一刻你也明白了自己的努力是值得的;所以,为了那一天的到来,各位ACCAer们加油复习,早日完成目标~
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(b) Discuss the key issues which will need to be addressed in determining the basic components of an
internationally agreed conceptual framework. (10 marks)
Appropriateness and quality of discussion. (2 marks)
(b) There are several issues which have to be addressed if an international conceptual framework is to be successfully developed.
These are:
(i) Objectives
Agreement will be required as to whether financial statements are to be produced for shareholders or a wide range of
users and whether decision usefulness is the key criteria or stewardship. Additionally there is the question of whether
the objective is to provide information in making credit and investment decisions.
(ii) Qualitative Characteristics
The qualities to be sought in making decisions about financial reporting need to be determined. The decision usefulness
of financial reports is determined by these characteristics. There are issues concerning the trade-offs between relevance
and reliability. An example of this concerns the use of fair values and historical costs. It has been argued that historical
costs are more reliable although not as relevant as fair values. Additionally there is a conflict between neutrality and the
traditions of prudence or conservatism. These characteristics are constrained by materiality and benefits that justify
costs.
(iii) Definitions of the elements of financial statements
The principles behind the definition of the elements need agreement. There are issues concerning whether ‘control’
should be included in the definition of an asset or become part of the recognition criteria. Also the definition of ‘control’
is an issue particularly with financial instruments. For example, does the holder of a call option ‘control’ the underlying
asset? Some of the IASB’s standards contravene its own conceptual framework. IFRS3 requires the capitalisation of
goodwill as an asset despite the fact that it can be argued that goodwill does not meet the definition of an asset in the
Framework. IAS12 requires the recognition of deferred tax liabilities that do not meet the liability definition. Similarly
equity and liabilities need to be capable of being clearly distinguished. Certain financial instruments could either be
liabilities or equity. For example obligations settled in shares.
(iv) Recognition and De-recognition
The principles of recognition and de-recognition of assets and liabilities need reviewing. Most frameworks have
recognition criteria, but there are issues over the timing of recognition. For example, should an asset be recognised when
a value can be placed on it or when a cost has been incurred? If an asset or liability does not meet recognition criteria
when acquired or incurred, what subsequent event causes the asset or liability to be recognised? Most frameworks do
not discuss de-recognition. (The IASB’s Framework does not discuss the issue.) It can be argued that an item should be
de-recognised when it does not meet the recognition criteria, but financial instruments standards (IAS39) require other
factors to occur before financial assets can be de-recognised. Different attributes should be considered such as legal
ownership, control, risks or rewards.
(v) Measurement
More detailed discussion of the use of measurement concepts, such as historical cost, fair value, current cost, etc are
required and also more guidance on measurement techniques. Measurement concepts should address initial
measurement and subsequent measurement in the form. of revaluations, impairment and depreciation which in turn
gives rise to issues about classification of gains or losses in income or in equity.
(vi) Reporting entity
Issues have arisen over what sorts of entities should issue financial statements, and which entities should be included
in consolidated financial statements. A question arises as to whether the legal entity or the economic unit should be the
reporting unit. Complex business arrangements raise issues over what entities should be consolidated and the basis
upon which entities are consolidated. For example, should the basis of consolidation be ‘control’ and what does ‘control’
mean?
(vii) Presentation and disclosure
Financial reporting should provide information that enables users to assess the amounts, timing and uncertainty of the
entity’s future cash flows, its assets, liabilities and equity. It should provide management explanations and the limitations
of the information in the reports. Discussions as to the boundaries of presentation and disclosure are required.
(ii) the factors that should be considered in the design of a reward scheme for BGL; (7 marks)
(ii) The factors that should be considered in the design of a reward scheme for BGL.
– Whether performance targets should be set with regard to results or effort. It is more difficult to set targets for
administrative and support staff since in many instances the results of their efforts are not easily quantifiable. For
example, sales administrators will improve levels of customer satisfaction but quantifying this is extremely difficult.
– Whether rewards should be monetary or non-monetary. Money means different things to different people. In many
instances people will prefer increased job security which results from improved organisational performance and
adopt a longer term-perspective. Thus the attractiveness of employee share option schemes will appeal to such
individuals. Well designed schemes will correlate the prosperity of the organisation with that of the individuals it
employs.
– Whether the reward promise should be implicit or explicit. Explicit reward promises are easy to understand but in
many respects management will have their hands tied. Implicit reward promises such as the ‘promise’ of promotion
for good performance is also problematic since not all organisations are large enough to offer a structured career
progression. Thus in situations where not everyone can be promoted there needs to be a range of alternative reward
systems in place to acknowledge good performance and encourage commitment from the workforce.
– The size and time span of the reward. This can be difficult to determine especially in businesses such as BGL
which are subject to seasonal variations. i.e. summerhouses will invariably be purchased prior to the summer
season! Hence activity levels may vary and there remains the potential problem of assessing performance when
an organisation operates with surplus capacity.
– Whether the reward should be individual or group based. This is potentially problematic for BGL since the assembly
operatives comprise some individuals who are responsible for their own output and others who work in groups.
Similarly with regard to the sales force then the setting of individual performance targets is problematic since sales
territories will vary in terms of geographical spread and customer concentration.
– Whether the reward scheme should involve equity participation? Such schemes invariably appeal to directors and
senior managers but should arguably be open to all individuals if ‘perceptions of inequity’ are to be avoided.
– Tax considerations need to be taken into account when designing a reward scheme.
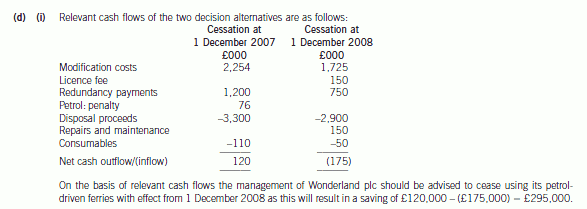
(d) The management of Wonderland plc have become concerned about the increased level of operating costs
associated with its petrol-driven ferries and have made a strategic decision to dispose of these. They are now
considering entering into a contract with the Newman Steamship Company (NSC), a shipping organisation based
in Robynland. The contract would entail NSC providing transport to and from Cinola Island for all visitors to the
zoo and circus.
As a result of negotiations with NSC, the directors of Wonderland plc are considering two options whereby NSC
will become responsible for the transportation of visitors to and from Cinola Island with effect from 1 December
2007 or 1 December 2008.
Additional information is available as follows:
(1) NSC would require Wonderland plc to pay for the necessary modifications to their steamships in order that
they would satisfy marine regulations with regard to passenger transportation. The only firm which could
undertake this work is currently working to full capacity and would require a payment of £2,450,000 in
order to undertake the work necessary so that the ferries could be in operation by 1 December 2007. The
same firm would require a payment of £1,725,000 in order to make the necessary modifications so that
the ferries could be in operation by 1 December 2008. The government of Robynland would be willing to
pay a grant of 8% towards the cost of getting the ferries into operation by 1 December 2007, but would not
be willing to pay a grant in respect of any later date.
(2) On 1 December 2002 Wonderland plc paid £500,000 to the Port Licencing Authority of Robynland. This
payment was for a licence which entitles Wonderland plc to use all harbour facilities in Robynland during
the five-year period ending 30 November 2007. The licence could be renewed on 1 December 2007 at a
cost of £150,000 per annum.
(3) Redundancy payments would need to be paid in respect of loss of employment. These would amount to
£1,200,000 if the contract with NSC commenced on 1 December 2007. This amount would reduce to
£750,000 if the contract commenced on 1 December 2008.
(4) Wonderland plc has a contract for the provision of petrol for its ferries which is due to expire on 30 November
2008. Early termination of the contract would incur a penalty charge of £76,000. An emergency reserve
stock of petrol held by Wonderland plc, which cannot be used after 30 November 2007 due to marine
regulations regarding the age of fuel, could be sold for £55,000 on 1 December 2007 but not on any date
thereafter.
(5) The ferries could be sold for £3,300,000 on 1 December 2007. If retained after 1 December 2007 the
ferries would require servicing during the year ending 30 November 2008 which would incur costs
amounting to £150,000. The resale value of the ferries on 1 December 2008 would be £2,900,000.
(6) Stock of consumable items which originally cost £150,000 could be sold on 1 December 2007 for
£110,000 and on 1 December 2008 for £50,000.
Required:
(i) On purely financial grounds, advise whether the management of Wonderland plc should enter into a
contract with NSC with effect from 1 December 2007 or 1 December 2008. You may ignore the time
value of money. (9 marks)
5 The directors of Blaina Packaging Co (BPC), a well-established manufacturer of cardboard boxes, are currently
considering whether to enter the cardboard tube market. Cardboard tubes are purchased by customers whose
products are wound around tubes of various sizes ranging from large tubes on which carpets are wound, to small
tubes around which films and paper products are wound. The cardboard tubes are usually purchased in very large
quantities by customers. On average, the cardboard tubes comprise between 1% and 2% of the total cost of the
customers’ finished product.
The directors have gathered the following information:
(1) The cardboard tubes are manufactured on machines which vary in size and speed. The lowest cost machine is
priced at $30,000 and requires only one operative for its operation. A one-day training course is required in order
that an unskilled person can then operate such a machine in an efficient and effective manner.
(2) The cardboard tubes are made from specially formulated paper which, at times during recent years, has been in
short supply.
(3) At present, four major manufacturers of cardboard tubes have an aggregate market share of 80%. The current
market leader has a 26% market share. The market shares of the other three major manufacturers, one of which
is JOL Co, are equal in size. The product ranges offered by the four major manufacturers are similar in terms of
size and quality. The market has grown by 2% per annum during recent years.
(4) A recent report on the activities of a foreign-based multinational company revealed that consideration was being
given to expanding operations in their packaging division overseas. The division possesses large-scale automated
machinery for the manufacture of cardboard tubes of any size.
(5) Another company, Plastic Tubes Co (PTC) produces a narrow, but increasing, range of plastic tubes which are
capable of housing small products such as film and paper-based products. At present, these tubes are on average
30% more expensive than the equivalent sized cardboard tubes sold in the marketplace.
Required:
(a) Using Porter’s five forces model, assess the attractiveness of the option to enter the market for cardboard
tubes as a performance improvement strategy for BPC. (10 marks)
(a) In order to assess the attractiveness of the option to enter the market for spirally-wound paper tubes, the directors of BPC
could make use of Michael Porter’s ‘five forces model’.
In applying this model to the given scenario one might conclude that the relatively low cost of the machine together with the
fact that an unskilled person would only require one day’s training in order to be able to operate a machine, constitute
relatively low costs of entry to the market. Therefore one might reasonably conclude that the threat of new entrants might be
high. This is especially the case where the market is highly fragmented.
The fact that products are usually purchased in very large quantities by customers together with the fact that there is little real
difference between the products of alternative suppliers suggests that customer (buyer) power might well be very high. The
fact that the paper tubes on average only comprise between 1% and 2% of the total cost of the purchaser’s finished product
also suggests that buyer power may well be very high.
The threat from suppliers could be high due to the fact that the specially formulated paper from which the tubes are made is
sometimes in short supply. Hence suppliers might increase their prices with consequential diminution in gross margin of the
firms in the marketplace.
The threat from competitive rivals will be strong as the four major players in the market are of similar size and that the market
is a slow growing market. The market leader currently has 26% of the market and the three nearest competitors hold
approximately 18% of the market.
The fact that Plastic Tubes Co (PTC) produces a narrow range of plastic tubes constitutes a threat from a substitute product.
This threat will increase if the product range of PTC is extended and the price of plastic tubes is reduced.
The fact that a foreign-based multinational company is considering entering this market represents a significant threat from a
potential new entrant as it would appear that the multinational company might well be able to derive economies of scale from
large scale automated machinery and has manufacturing flexibility.
Low capital barriers to entry might appeal to BPC but they would also appeal to other potential entrants. The low growth
market, the ease of entry, the existence of established competitors, a credible threat of backward vertical integration by
suppliers, the imminent entry by a multi-national, a struggling established competitor and the difficulty of differentiating an
industrial commodity should call into question the potential of BPC to achieve any sort of competitive advantage. If BPC can
achieve the position of lowest cost producer within the industry then entry into the market might be a good move. In order
to assess whether this is possible BPC must consider any potential synergies that would exist between its cardboard business
and that of the tubes operation.
From the information available, the option to enter the market for cardboard tubes appears to be unattractive. The directors
of BPC should seek alternative performance improvement strategies.
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-20
- 2021-05-23
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-02
- 2021-05-23
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2021-08-12
- 2020-09-04
- 2019-07-20
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-20
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-09-04
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-01-08
- 2019-07-20