注意查看!2020年天津市ACCA考试报名时间
发布时间:2020-09-03
ACCA在国内称为“国际注册会计师”,ACCA资格被认为是“国际财会界的通行证”。天津市的考生请注意,2020年ACCA考试报名时间已经公布了,51题库考试学习网为大家带来了报名相关事宜,让我们一起来看看吧!
一、报名时间及费用缴纳:
|
2020年12月ACCA考试报名时间、考试费用- |
|||
|
报名周期 |
报名(截止)日期 |
考试科目 |
考试费用 |
|
提前报名截止 |
2020年8月10日 |
|
|
|
F4-F9 |
123英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Leader |
210英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Reporting |
164英镑 |
||
|
P4-P7(4选2) |
164英镑 |
||
|
常规报名截止 |
2020年11月2日 |
|
|
|
F4-F9 |
130英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Leader |
222英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Reporting |
173英镑 |
||
|
P4-P7(4选2) |
173英镑 |
||
|
后期报名截止 |
2020年11月9日 |
|
|
|
F4-F9 |
332英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Leader |
358英镑 |
||
|
Strategic Business Reporting |
358英镑 |
||
|
P4-P7(4选2) |
358英镑 |
||
二、ACCA报考条件:
(一)凡具有教育部承认的大专以上学历,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
(二)教育部认可的高等院校在校生,顺利完成大一的课程考试,即可报名成为ACCA的正式学员;
(三)未符合(一)、(二)项报名资格的16周岁以上的申请者,也可以先申请参加FIA(Foundations in Accountancy)基础财务资格考试。在完成基础商业会计(FAB)、基础管理会计(FMA)、基础财务会计(FFA)3门课程,并完成ACCA基础职业模块,可获得ACCA商业会计师资格证书(Diploma in Accounting and Business),资格证书后可豁免ACCAF1-F3三门课程的考试,直接进入技能课程的考试。
三、报名规则:
1.申请参加ACCA考试者,必须先注册成为ACCA学员。
2.学员必须按考试大纲设置的先后次序报考,即应用知识模块,应用技能模块,战略专业模块。同一个模块里的课程可以选择任意顺序报考,但建议在同一个模块中也按照课程顺序报考。
3.基础阶段的应用知识模块考试时间为两小时,基础阶段的应用技能模块和战略专业阶段的所有课程考试时间为三小时,及格成绩为50分(百分制)。从2016年起,ACCA实行4个考季,即学员可选择在3、6、9、12月考季在当地考点进行考试。学员每年最多可报考8门不相同的科目。
请注意:中国大陆地区自2018年3月考季开始将取消PM-FM的笔试。
4.基础阶段9门考试不设时限;专业阶段考试年限为7年,从通过第一门战略专业阶段考试之日算起。
5.考试的报名时间不同,考试资费标准就不同(该优惠政策仅限网上报名)。较早报名考试,费用会相对较少。报考时间分为提前报名时段,常规报名时段和后期报名时段。
以上就是今天分享的全部内容了,各位小伙伴根据自己的情况进行查阅,希望本文对各位有所帮助,预祝各位取得满意的成绩,如需了解更多相关内容,请关注51题库考试学习网!
下面小编为大家准备了 ACCA考试 的相关考题,供大家学习参考。
(c) Discuss the ethical and social responsibilities of the Beth Group and whether a change in the ethical and
social attitudes of the management could improve business performance. (7 marks)
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 professional marks for development of the discussion of the ethical and social
responsibilities of the Beth Group.
(c) Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is concerned with business ethics and the company’s accountability to its stakeholders,
and about the way it meets its wider obligations. CSR emphasises the need for companies to adopt a coherent approach to
a range of stakeholders including investors, employees, suppliers, and customers. Beth has paid little regard to the promotion
of socially and ethically responsible policies. For example, the decision to not pay the SME creditors on the grounds that they
could not afford to sue the company is ethically unacceptable. Additionally, Beth pays little regard to local customs and
cultures in its business dealings.
The stagnation being suffered by Beth could perhaps be reversed if it adopted more environmentally friendly policies. The
corporate image is suffering because of its attitude to the environment. Environmentally friendly policies could be cost effective
if they help to increase market share and reduce the amount of litigation costs it has to suffer. The communication of these
policies would be through the environmental report, and it is critical that stakeholders feel that the company is being
transparent in its disclosures.
Evidence of corporate misbehaviour (Enron, World.com) has stimulated interest in the behaviour of companies. There has
been pressure for companies to show more awareness and concern, not only for the environment but for the rights and
interests of the people they do business with. Governments have made it clear that directors must consider the short-term
and long-term consequences of their actions, and take into account their relationships with employees and the impact of the
business on the community and the environment. The behaviour of Beth will have had an adverse effect on their corporate
image.
CSR requires the directors to address strategic issues about the aims, purposes, and operational methods of the organisation,
and some redefinition of the business model that assumes that profit motive and shareholder interests define the core purpose
of the company. The profits of Beth will suffer if employees are not valued and there is poor customer support.
Arrangements should be put in place to ensure that the business is conducted in a responsible manner. The board should
look at broad social and environmental issues affecting the company and set policy and targets, monitoring performance and
improvements.
1 Rowlands & Medeleev (R&M), a major listed European civil engineering company, was successful in its bid to become
principal (lead) contractor to build the Giant Dam Project in an East Asian country. The board of R&M prided itself in
observing the highest standards of corporate governance. R&M’s client, the government of the East Asian country, had
taken into account several factors in appointing the principal contractor including each bidder’s track record in large
civil engineering projects, the value of the bid and a statement, required from each bidder, on how it would deal with
the ‘sensitive issues’ and publicity that might arise as a result of the project.
The Giant Dam Project was seen as vital to the East Asian country’s economic development as it would provide a
large amount of hydroelectric power. This was seen as a ‘clean energy’ driver of future economic growth. The
government was keen to point out that because hydroelectric power did not involve the burning of fossil fuels, the
power would be environmentally clean and would contribute to the East Asian country’s ability to meet its
internationally agreed carbon emission targets. This, in turn, would contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gases
in the environment. Critics, such as the environmental pressure group ‘Stop-the-dam’, however, argued that the
project was far too large and the cost to the local environment would be unacceptable. Stop-the-dam was highly
organised and, according to press reports in Europe, was capable of disrupting progress on the dam by measures such
as creating ‘human barriers’ to the site and hiding people in tunnels who would have to be physically removed before
proceeding. A spokesman for Stop-the-dam said it would definitely be attempting to resist the Giant Dam Project when
construction started.
The project was intended to dam one of the region’s largest rivers, thus creating a massive lake behind it. The lake
would, the critics claimed, not only displace an estimated 100,000 people from their homes, but would also flood
productive farmland and destroy several rare plant and animal habitats. A number of important archaeological sites
would also be lost. The largest community to be relocated was the indigenous First Nation people who had lived on
and farmed the land for an estimated thousand years. A spokesman for the First Nation community said that the ‘true
price’ of hydroelectric power was ‘misery and cruelty’. A press report said that whilst the First Nation would be unlikely
to disrupt the building of the dam, it was highly likely that they would protest and also attempt to mobilise opinion in
other parts of the world against the Giant Dam Project.
The board of R&M was fully aware of the controversy when it submitted its tender to build the dam. The finance
director, Sally Grignard, had insisted on putting an amount into the tender for the management of ‘local risks’. Sally
was also responsible for the financing of the project for R&M. Although the client was expected to release money in
several ‘interim payments’ as the various parts of the project were completed to strict time deadlines, she anticipated
a number of working capital challenges for R&M, especially near the beginning where a number of early stage costs
would need to be incurred. There would, she explained, also be financing issues in managing the cash flows to R&M’s
many subcontractors. Although the major banks financed the client through a lending syndicate, R&M’s usual bank
said it was wary of lending directly to R&M for the Giant Dam Project because of the potential negative publicity that
might result. Another bank said it would provide R&M with its early stage working capital needs on the understanding
that its involvement in financing R&M to undertake the Giant Dam Project was not disclosed. A press statement from
Stop-the-dam said that it would do all it could to discover R&M’s financial lenders and publicly expose them. Sally
told the R&M board that some debt financing would be essential until the first interim payments from the client
became available.
When it was announced that R&M had won the contract to build the Giant Dam Project, some of its institutional
shareholders contacted Richard Markovnikoff, the chairman. They wanted reassurance that the company had fully
taken the environmental issues and other risks into account. One fund manager asked if Mr Markovnikoff could
explain the sustainability implications of the project to assess whether R&M shares were still suitable for his
environmentally sensitive clients. Mr Markovnikoff said, through the company’s investor relations department, that he
intended to give a statement at the next annual general meeting (AGM) that he hoped would address these
environmental concerns. He would also, he said, make a statement on the importance of confidentiality in the
financing of the early stage working capital needs.
(a) Any large project such as the Giant Dam Project has a number of stakeholders.
Required:
(i) Define the terms ‘stakeholder’ and ‘stakeholder claim’, and identify from the case FOUR of R&M’s
external stakeholders as it carries out the Giant Dam Project; (6 marks)
(a) (i) Stakeholders
A stakeholder can be defined as any person or group that can affect or be affected by an entity. In this case, stakeholders
are those that can affect or be affected by the building of the Giant Dam Project. Stakeholding is thus bi-directional.
Stakeholders can be those (voluntarily or involuntarily) affected by the activities of an organisation or the stakeholder
may be seeking to influence the organisation in some way.
All stakeholding is characterised by the making of ‘claims’ upon an organisation. Put simply, stakeholders ‘want
something’ although in some cases, the ‘want’ may not be known by the stakeholder (such as future generations). It is
the task of management to decide on the strengths of each stakeholder’s claim in formulating strategy and in making
decisions. In most situations it is likely that some stakeholder claims will be privileged over others.
R&M’s external stakeholders include:
– The client (the government of the East Asian country)
– Stop-the-dam pressure group
– First Nation (the indigenous people group)
– The banks that will be financing R&M’s initial working capital
– Shareholders
3 You are the manager responsible for the audit of Lamont Co. The company’s principal activity is wholesaling frozen
fish. The draft consolidated financial statements for the year ended 31 March 2007 show revenue of $67·0 million
(2006 – $62·3 million), profit before taxation of $11·9 million (2006 – $14·2 million) and total assets of
$48·0 million (2006 – $36·4 million).
The following issues arising during the final audit have been noted on a schedule of points for your attention:
(a) In early 2007 a chemical leakage from refrigeration units owned by Lamont caused contamination of some of its
property. Lamont has incurred $0·3 million in clean up costs, $0·6 million in modernisation of the units to
prevent future leakage and a $30,000 fine to a regulatory agency. Apart from the fine, which has been expensed,
these costs have been capitalised as improvements. (7 marks)
Required:
For each of the above issues:
(i) comment on the matters that you should consider; and
(ii) state the audit evidence that you should expect to find,
in undertaking your review of the audit working papers and financial statements of Lamont Co for the year ended
31 March 2007.
NOTE: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three issues.
3 LAMONT CO
(a) Chemical leakage
(i) Matters
■ $30,000 fine is very immaterial (just 1/4% profit before tax). This is revenue expenditure and it is correct that it
has been expensed to the income statement.
■ $0·3 million represents 0·6% total assets and 2·5% profit before tax and is not material on its own. $0·6 million
represents 1·2% total assets and 5% profit before tax and is therefore material to the financial statements.
■ The $0·3 million clean-up costs should not have been capitalised as the condition of the property is not improved
as compared with its condition before the leakage occurred. Although not material in isolation this amount should
be adjusted for and expensed, thereby reducing the aggregate of uncorrected misstatements.
■ It may be correct that $0·6 million incurred in modernising the refrigeration units should be capitalised as a major
overhaul (IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment). However, any parts scrapped as a result of the modernisation
should be treated as disposals (i.e. written off to the income statement).
■ The carrying amount of the refrigeration units at 31 March 2007, including the $0·6 million for modernisation,
should not exceed recoverable amount (i.e. the higher of value in use and fair value less costs to sell). If it does,
an allowance for the impairment loss arising must be recognised in accordance with IAS 36 Impairment of Assets.
(ii) Audit evidence
■ A breakdown/analysis of costs incurred on the clean-up and modernisation amounting to $0·3 million and
$0·6 million respectively.
■ Agreement of largest amounts to invoices from suppliers/consultants/sub-contractors, etc and settlement thereof
traced from the cash book to the bank statement.
■ Physical inspection of the refrigeration units to confirm their modernisation and that they are in working order. (Do
they contain frozen fish?)
■ Sample of components selected from the non-current asset register traced to the refrigeration units and inspected
to ensure continuing existence.
■ $30,000 penalty notice from the regulatory agency and corresponding cash book payment/payment per the bank
statement.
■ Written management representation that there are no further penalties that should be provided for or disclosed other
than the $30,000 that has been accounted for.
6 Sergio and Gerard each inherited a half interest in a property, ‘Hilltop’, in October 2005. ‘Hilltop’ had a probate value
of £124,000, but in November 2005 it was badly damaged by fire. In January 2006 the insurance company made
a payment of £81,700 each to Sergio and Gerard. In February 2006 Sergio and Gerard each spent £55,500 of the
insurance proceeds on restoring the property. ‘Hilltop’ was worth £269,000 following the restoration work. In July
2006, Sergio and Gerard sold ‘Hilltop’ for £310,000.
Sergio is 69 years old and a widower with three adult children and seven grandchildren. His annual income consists
of a pension of £9,900 and interest of £300 on savings of £7,600 in a bank deposit account. Sergio owns his home
but no other significant assets. He plans to buy a domestic rental property with the proceeds from the sale of ‘Hilltop’,
such that on his death he will have a significant asset which can be sold and divided between the members of his
family.
Gerard is 34 years old. He is employed by Fizz plc on a salary of £66,500 per year together with a performance
related bonus. Gerard estimates that he will receive a bonus in December 2007 of £4,500, in line with previous
years, and that his taxable benefits in the tax year 2007/08 will amount to £7,140. He also expects to receive
dividends from UK companies of £1,935 and bank interest of £648 in the tax year 2007/08. Gerard intends to set
up a personal pension plan in August 2007. He has not made any pension contributions in the past and proposes to
use part of the proceeds from the sale of ‘Hilltop’ to make the maximum possible tax allowable contribution.
Fizz plc has announced that it intends to replace the performance related bonus scheme with a share incentive plan,
also linked to performance, with effect from 6 April 2008. Gerard estimates that Fizz plc will award him free shares
worth £2,100 each year. He will also purchase partnership shares worth £700 each year and, as a result, will be
awarded matching shares (further free shares) worth £1,400.
Required:
(a) Calculate the chargeable gains arising on the receipt of the insurance proceeds in January 2006 and the sale
of ‘Hilltop’ in July 2006. You should assume that any elections necessary to minimise the gain on the receipt
of the insurance proceeds have been submitted. (4 marks)
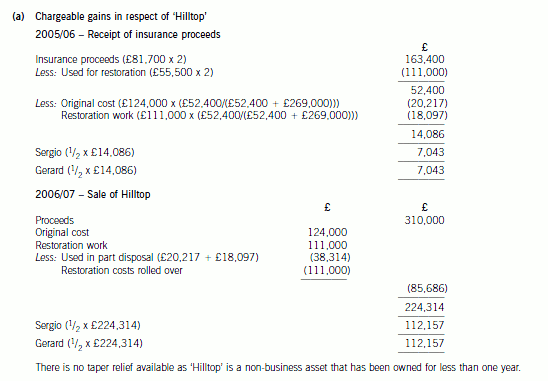
声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献自行上传,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任。如果您发现有涉嫌版权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@51tk.com 进行举报,并提供相关证据,工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
- 2020-01-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-01
- 2020-09-03
- 2021-01-22
- 2020-05-02
- 2020-01-08
- 2021-04-22
- 2020-01-09
- 2021-04-04
- 2021-05-22
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2020-01-10
- 2021-05-06
- 2021-02-03
- 2020-05-07
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-09-03
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-08
- 2020-02-22
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-12-31
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-01-09
- 2020-09-03
- 2021-01-16
- 2020-01-10